MIT
-
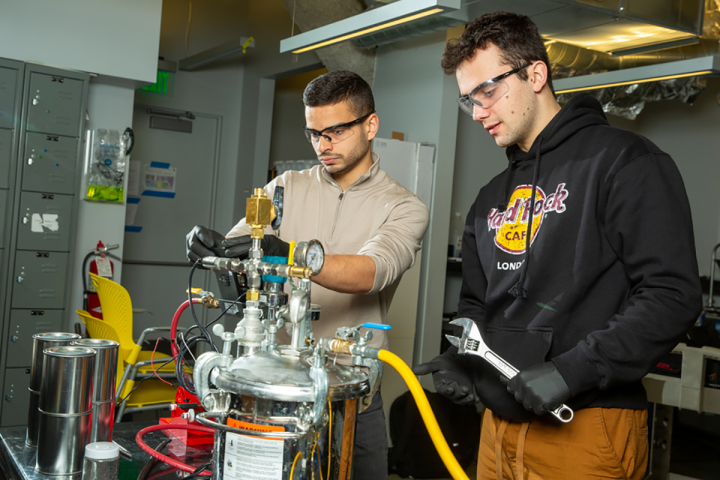
MIT scientists have discovered an intriguing new way to produce hydrogen fuel, using just soda cans, seawater and coffee grounds. The team says the chemical reaction could power engines or fuel cells in marine vehicles that suck in seawater.
-
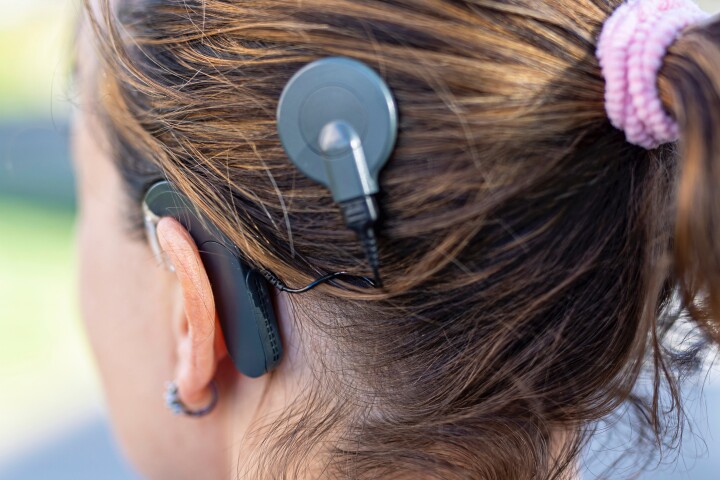
While cochlear implants do allow some deaf people to hear, they also incorporate potentially problematic external components located on the side of the head. That could soon change, however, thanks to an experimental new implantable microphone.
-
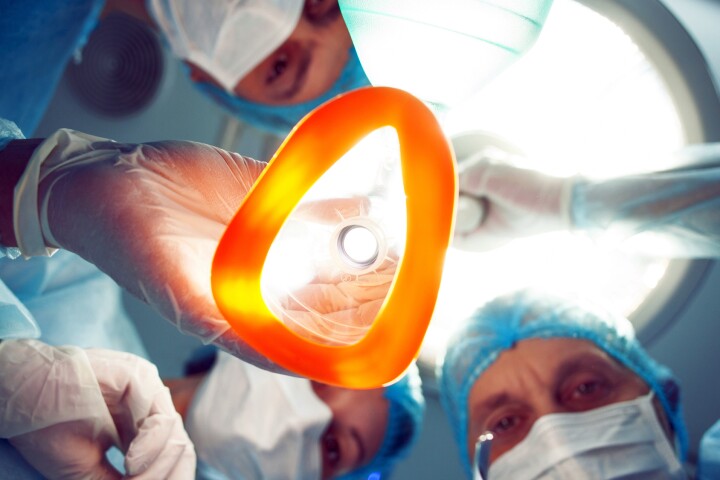
Researchers have figured out how a commonly used general anesthetic drug induces unconsciousness by causing brain activity to become increasingly unstable. The findings could lead to better anesthetic control in the operating room.
-
It’s ironic that while many regions struggle with water shortages, there’s heaps of the stuff floating around in the air everywhere. A new MIT water harvester design can pull enough fresh water out of the air to meet the daily needs of several people.
-
A new surgical technique for below-the-knee amputations retains a person’s ability to receive sensory feedback from remaining muscles. Having a prosthetic leg driven by an amputee’s own nervous system enables them to walk much more naturally, new research has shown.
-
DNA is a much denser data storage medium than anything humans can design, but the problem is that it’s fragile. So now scientists have taken another page out of nature’s book and created artificial amber to protect data stored in DNA longer term.
-
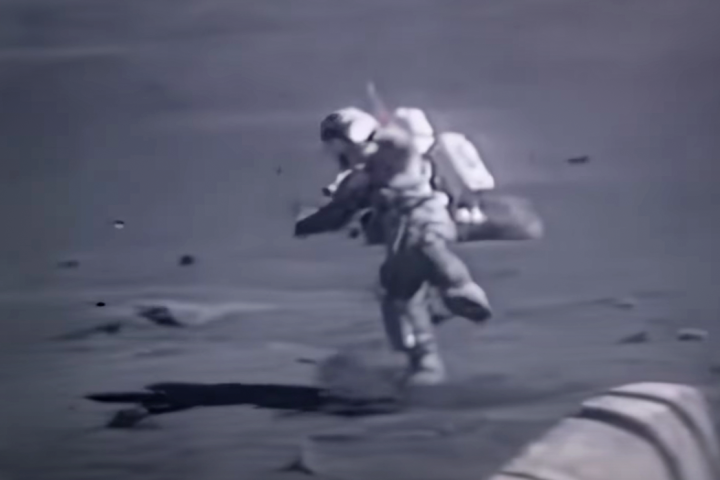
It's a genuine joy watching Apollo-era astronauts bounce around on the lunar surface, and it's hysterically funny watching them fall over and struggle to get back up in their spacesuits. MIT wishes to rob us of this hilarity for future missions.
-
Formless 'slime' robots that shape-change to complete complex tasks – it sounds like science fantasy. However, MIT researchers have developed a machine-learning technique that brings shape-changing soft robots a step closer to reality.
-
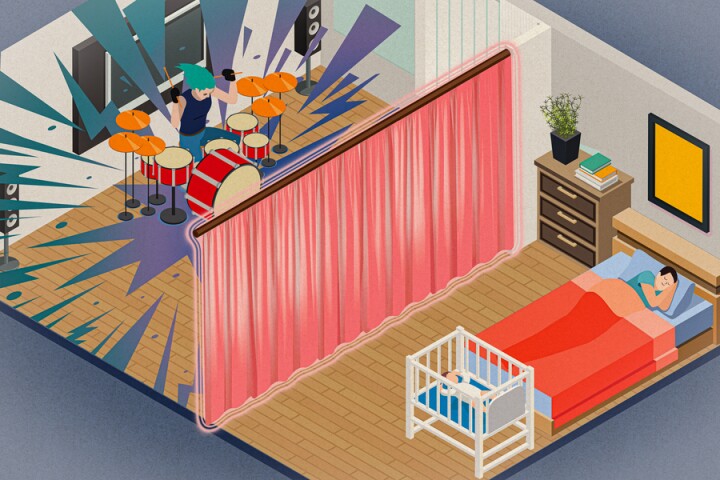
There may be new hope for people with noisy neighbors. Scientists at MIT have developed a method of using thin sheets of fabric to either cancel or block sound – in the latter case, the racket even gets reflected back to its maker.
-
We all know that water evaporates when the temperature climbs, but researchers have just shown that there's another factor at play. The breakthrough could solve long-standing atmospheric mysteries and lead to future technological advances.
-
Specially tagged "sentinel plants" could soon provide an early warning of crop problems such as insect damage or bacterial infection. These plants would utilize two "glowing" sensors that react to stress-related compounds in the leaves.
-
The tracking of squid and other soft-bodied sea creatures may soon be a lot more doable, thanks to a new bioadhesive interface. It's claimed to be much gentler than current attachment methods, while still remaining up to the task.
Load More