3D Printing
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, has advanced rapidly to enable the production of everything from tiny screws to engine components to entire houses ... and it's only just getting started. Keep up with the latest developments here.
Top News
-
Bambu Lab's latest flagship 3D printer does a whole lot more than 3D printing for makers, and promises to be good at every one of its tasks. It can handle laser cutting and engraving, drawing, and printing with two materials at once.
-
The 3D printing of certain items could soon get a lot faster, simpler and more eco-friendly. That's because scientists have developed a new 3D printing ink which is easily extruded as a liquid, then solidifies on contact with a saltwater solution.
-
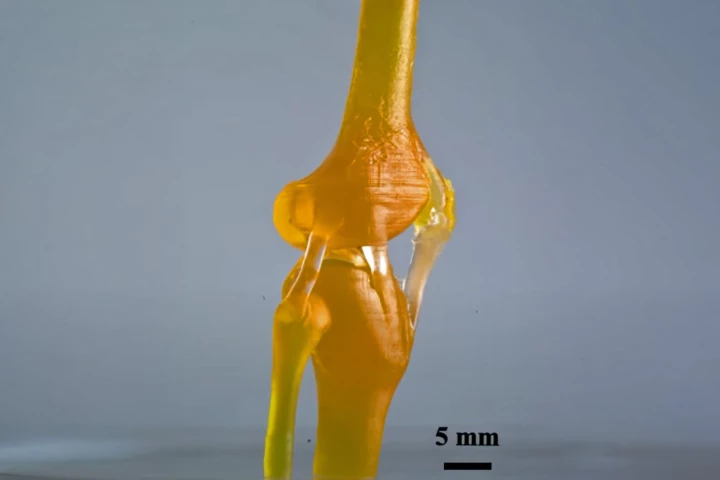
If an object that's composed of two types of material is going to fail, the break will usually occur at the interface where the two meet. A new type of light-activated 3D printing resin addresses that problem, by gradually morphing from hard to soft states within a single object.
Load More
Latest News
-
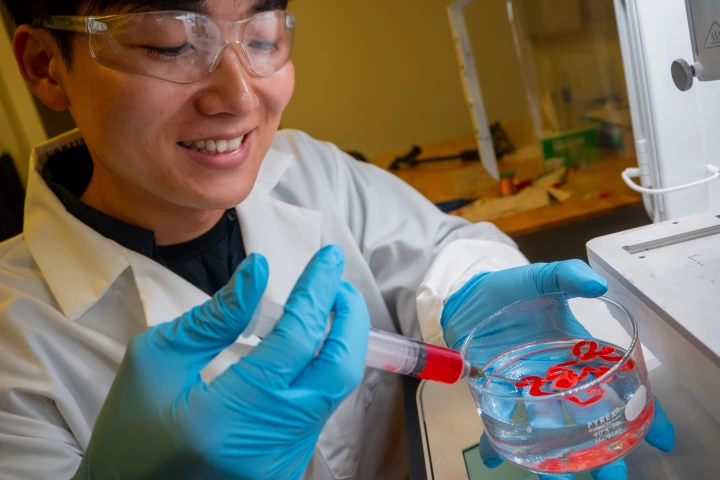
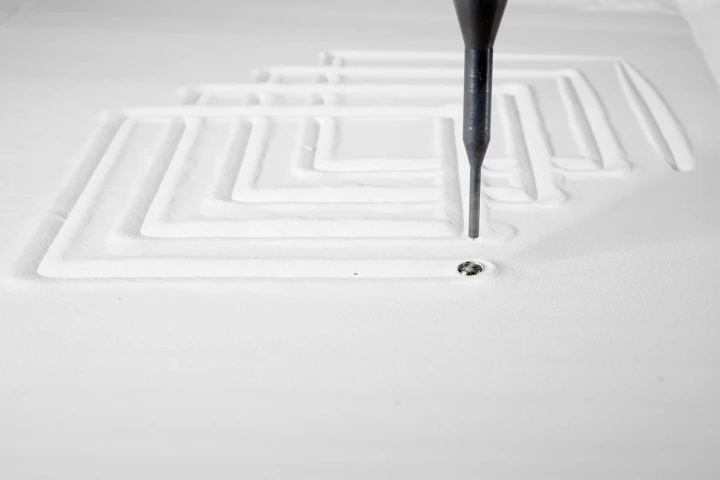
June 04, 2025 | Ben CoxworthWhile 3D printing is a burgeoning technology, it's limited by the fact that items can only be printed from a single material. A new system still uses just one print resin, but that substance can form into two different solid materials as needed.
-
October 11, 2024 | Ben CoxworthOrdinarily, the 3D printing of multi-colored objects is a relatively complex and inefficient process. That could soon change, however, thanks to a clever new technique in which a temperature-sensitive print media gets "ironed" after being extruded.
-
April 08, 2024 | Ben CoxworthA recently developed system could revolutionize the world of 3D printing, by streamlining the adoption of new print media. Such materials could include ones made from all-renewable ingredients, or that are more recyclable than current options.
-
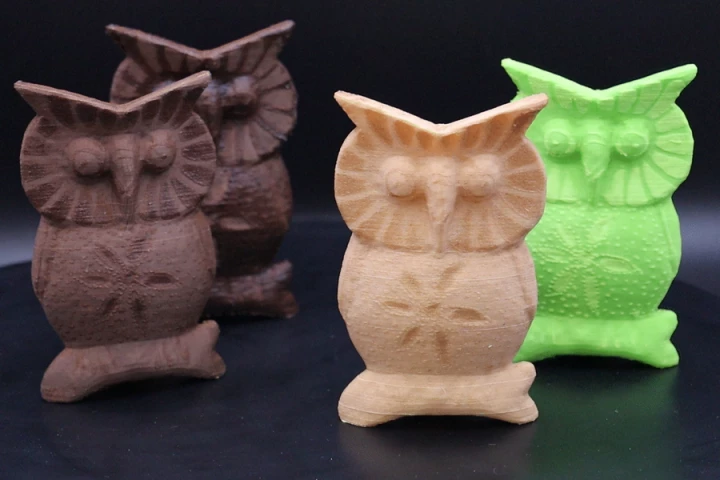
March 20, 2024 | Ben CoxworthScientists have developed a new "ink" that allows objects to be 3D-printed out of wood. The material could reduce the amount of wood that gets wasted in the manufacturing of various products, plus it could utilize existing wood waste.
-
February 20, 2024 | Ben CoxworthScientists have created a 3D-printing media that can take on different colors in different parts of a single print job. The secret lies in utilizing ultraviolet light to selectively alter the surface structure of the material as it's being dispensed.
-
January 26, 2024 | Paul RiddenResearchers have come up with a 3D printing method using liquid metal that's claimed to produce structures at least 10 times faster than existing metal additive manufacturing processes, though it does so at the expense of fine detail.
-
December 08, 2023 | Ben CoxworthIn order to keep surgeries minimally invasive, it would be great if implants could be injected into the body in liquid form, then solidified once in place. Well, a new ultrasound-based 3D printing process may one day make that very thing possible.
-
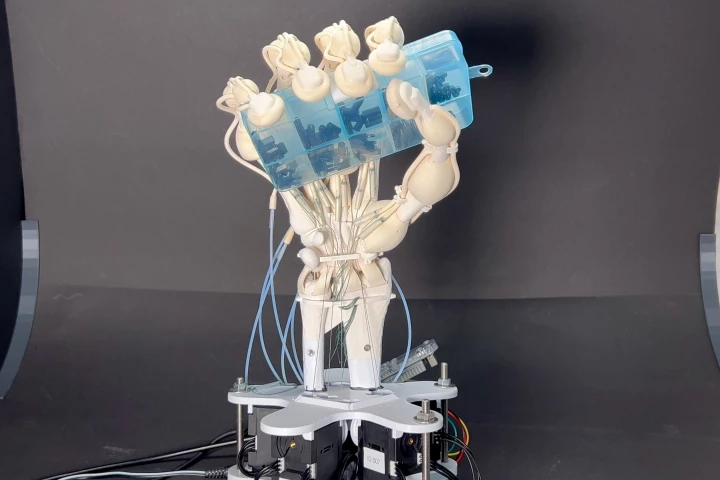
November 16, 2023 | Ben Coxworth3D printing single objects out of different materials can be difficult, if those materials cure at different rates. The new Inkbit system addresses that problem, and has been used to print a complex functional robotic hand… in just one print job.
-
October 27, 2023 | Loz BlainIf you can 3D-scan it, you can 3D-print it – and Matter and Form has announced a super-versatile new way to do so. The Three system creates photorealistic, high-detail, full-color 3D scans of objects from coins to cars, and potentially beyond.
-
September 26, 2023 | Ben CoxworthAlthough an increasing number of devices are being developed for use on or in our bodies, such devices tend not to be very … "body-like." A new 3D printing resin could change that, by allowing for variable stiffness throughout single objects.
-
August 02, 2023 | Paul RiddenLast year, Anker breezed into the desktop 3D printing space with the AnkerMake M5, launching on Kickstarter to test the market and fund production. Now the company has announced a more affordable follow up called the M5C.
-
July 06, 2023 | Ben CoxworthAlthough there are several methods of 3D-printing metal objects, all of them involve heat – which isn't conducive to producing heat-sensitive electronics, among other things. A new gel, however, can be used to print such items at room temperature.
-
June 22, 2023 | Ben CoxworthDifferent types of metal have different qualities, so combining them can result in items that outperform those made of any one metal. A new technique now allows such mixing to be performed by 3D printers, faster and easier than ever before.
-
June 21, 2023 | Michael IrvingScientists have created the world’s smallest wine glass, narrower than a human hair. Made out of actual glass, the model is a test run of a new 3D-printing process that could help make nanoscale glass components for electronic and optical devices.
-
April 03, 2023 | Ben Coxworth3D concrete printing (3DCP) technology is already known to offer a more efficient approach to constructing buildings. A new type of 3DCP is said to be better, resulting in walls that are a claimed 72% lighter than their conventional counterparts.
Load More