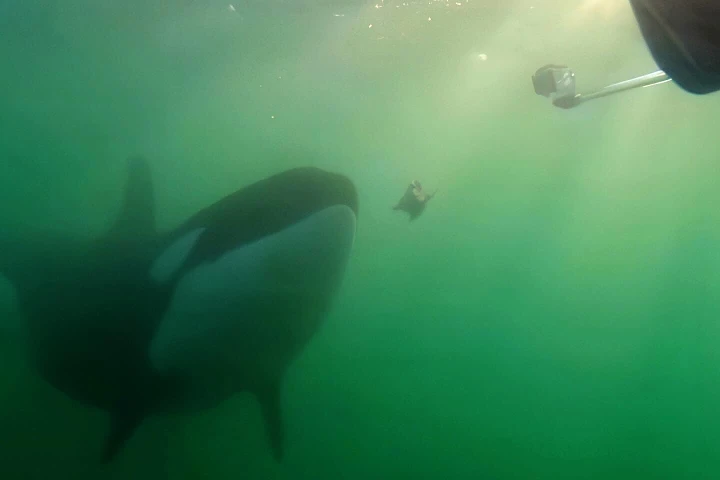Biology
From the smallest microbe to the largest dinosaurs and from the tiniest spore to the biggest giant sequoia, biological research continues to shed new light on the weird and wonderful world of living organisms.
Top News
-
We're one step closer to that elusive goal preventing hair loss and enabling new growth, as scientists identify the crucial role that one all-important protein has in protecting the hard-working cells on the production line.
-
You could compensate for broken speakers by cranking up the volume on others that still work. It turns out that the brain does the same thing when damaged hair cells in the ear lead to hearing loss – and this could be causing your tinnitus.
-
From fleas to mosquitoes, there's no shortage of organisms we consider pests. But thanks to new genetic detective work, scientists have named and shamed the resilient, highly adaptive – and frustratingly hard to kill – bug that got to us first.
Load More
Latest News
-
July 02, 2025 | Paul McClureA new study has cast doubt on the idea that women are biologically wired to wake more to a crying baby than men. It suggests that the significant disparity in nighttime care is due to social, rather than biological, factors.
-
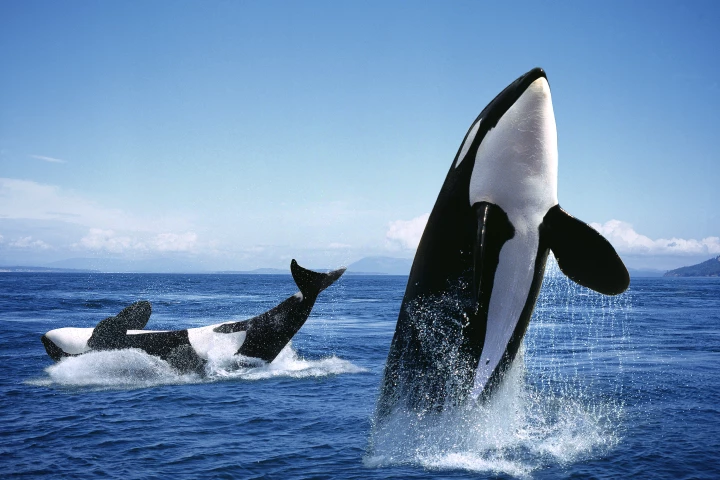
July 02, 2025 | Abhimanyu GhoshalResearchers have identified a fascinating behavior in killer whales: they sometimes offer to share their prey with humans. And while the orcas haven't gone on the record to confirm it, it's likely their way of building relationships with us.
-
June 30, 2025 | Jay KakadeFor years, we’ve admired plants for their ability to cleanse the air but our green ally might be contributing to air pollution in an unexpected way. While they may be just trying to fend off pests, this mechanism is also harming the environment.
-
June 29, 2025 | Michael FrancoThe evolutionary ladder is meant to be climbed one rung at a time with an organism shedding some traits and gaining others on the way up. However, in a very surprising twist, some tomatoes on the Galapagos islands are inching back down the ladder.
-
June 26, 2025 | Michael FrancoA new organelle has been found by scientists at the University of Virginia. The super-small specialized structure has a role recycling material inside our cells, and its discovery could lead to improved treatments for a wide range of diseases.
-
June 24, 2025 | Bronwyn ThompsonIf you, like us, were under the impression that two-legged dinosaurs were pacy beasts that could zip across the ground at around 40 mph, researchers have some bad news. A new study suggests they were much, much slower than previously thought.
-
June 23, 2025 | Bronwyn ThompsonKiller whales have joined the rare club of animal species that craft tools out of nature and use them to their advantage. For the first time, they've been observed making a brush of sorts out of kelp and then using it on each other.
-
June 22, 2025 | Bronwyn ThompsonMore than a third of large animals that feast on dead animals are struggling to survive, and a new report from scientists warns that their downfall could present a serious risk to human life, with an uptick in zoonotic disease spread as a result.
-
June 22, 2025 | Jay KakadeJust like fingerprints, your breathing patterns may be unique. Scientists found they can identify people using only breathing patterns. And it's not just identification, researchers can predict BMI, and anxiety or depression from the way you breathe.
-
June 21, 2025 | Chelsea HaneyA new study from scientists at Michigan State University sheds light on a recently discovered microbe and its potential for scavenging pollutants in deep soil. Further work could lead to novel solutions in providing clean drinking water worldwide.
-
June 18, 2025 | Michael FrancoEven without noses, octopuses are able to determine which food sources are good to eat and which have gone past their prime simply by touching them. The secret, says a new study, lies with surface microbiomes and some very sensitive suckers.
-
June 17, 2025 | Abhimanyu GhoshalTalk about thinking small: researchers at Harvard University have devised a new way to implant flexible bioelectronic devices in the embryos of frogs, mice, and lizards, enabling them to monitor brain activity as these creatures develop.
-
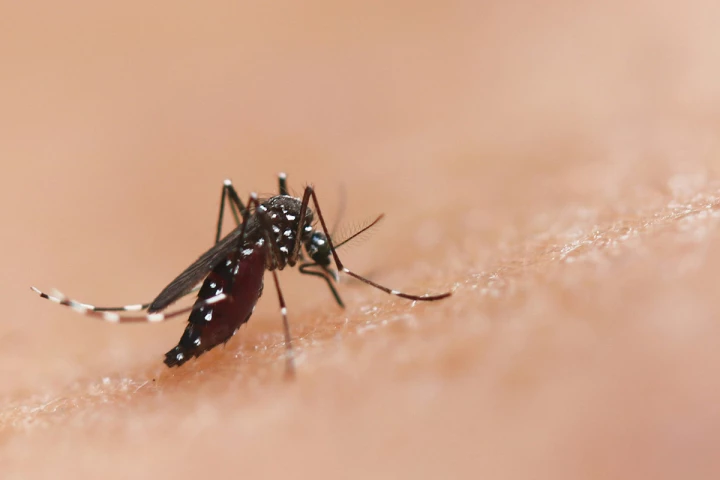
June 16, 2025 | Jay KakadeMosquitoes have long been among humanity’s most formidable adversaries, causing more deaths than any other animal. With traditional control methods facing mounting resistance, researchers are seeking innovative ways to combat mosquito-borne disease.
-
June 11, 2025 | Bronwyn ThompsonFor the first time, scientists have pieced together the diverse diet of a sauropod species, using advanced technology to assess the fossilized stomach contents that make up the dinosaur's last meal, which took place around 95 million years ago.
-
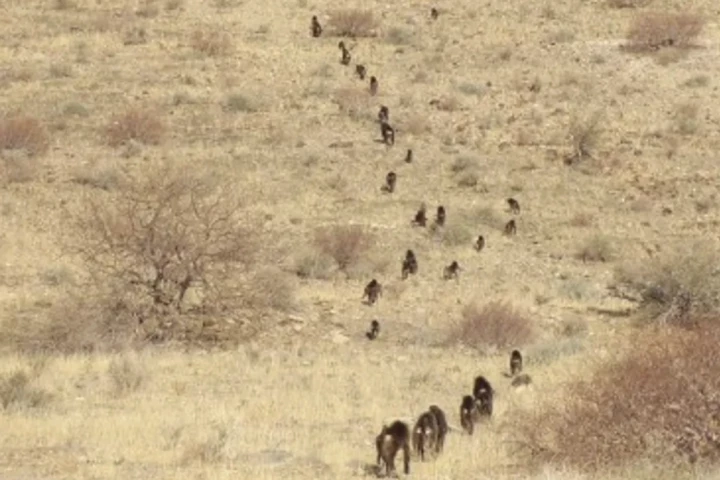
June 07, 2025 | Bronwyn ThompsonIt's not a simple case of "follow the leader" when it comes to baboons on foot. Researchers have made a surprising discovery on why they appear to move in an orderly line, and it's something that can help us better understand human behavior, too.
Load More