Electronic
-
Fraunhofer scientists have used ultra-thin diamond membranes to drastically cool electronic components and boost electric vehicle charging speeds, taking advantages of diamond's outstanding thermal conductivity.
-
Around this time last year, as part of its 50-year celebrations, California's Drum Workshop announced the upcoming release of an acoustic/electronic drum set featuring wireless triggering tech. Now the DWe convertible kits have officially launched.
-
Scientists have found that a “superatomic” material is the fastest and most efficient semiconductor ever. Taking advantage of a tortoise-and-hare mechanism, the new material can transport energy much faster than silicon.
-
Everybody’s favorite wonder material, graphene, continues to surprise. MIT physicists have discovered yet another brand new electronic state hiding in this overachieving little material – something they give the bizarre name of “ferro-valleytricity.”
-
AI machine learning uses so much computing power and energy that it's typically done in the cloud. But a new microtransistor, 100X more efficient than the current tech, promises to bring new levels of intelligence to mobile and wearable devices.
-
The estimated shipping date for successful Kickstarters can often prove to be a bit ambitious, but backers of the Oscilloscope Watch project are finally being rewarded for their patience – almost 10 years after the campaign ended.
-
A brand new form of silicon might help extend its use into the future. Engineers at North Carolina State University have discovered a material called Q-silicon, with new properties that could have important uses in quantum computers and spintronics.
-
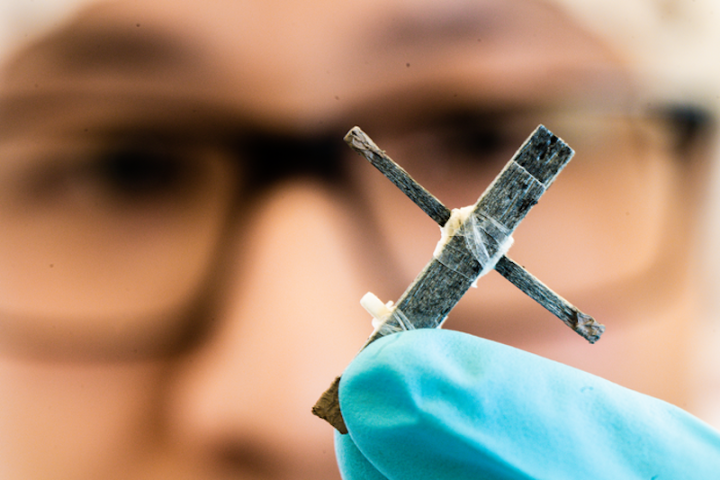
Wood isn’t usually very good at conducting electricity, but now scientists have created the first functional wooden transistor. It’s not the best, and it requires some processing, but it does work and could help make for biodegradable electronics.
-
In order to protect the F-16 fighter from modern electronic threats, Northrop Grumman put its AN/ALQ-257 Integrated Viper Electronic Warfare Suite up against "attacks" from the US Air Force Laboratory Intelligence Validated Emulator testing system.
-
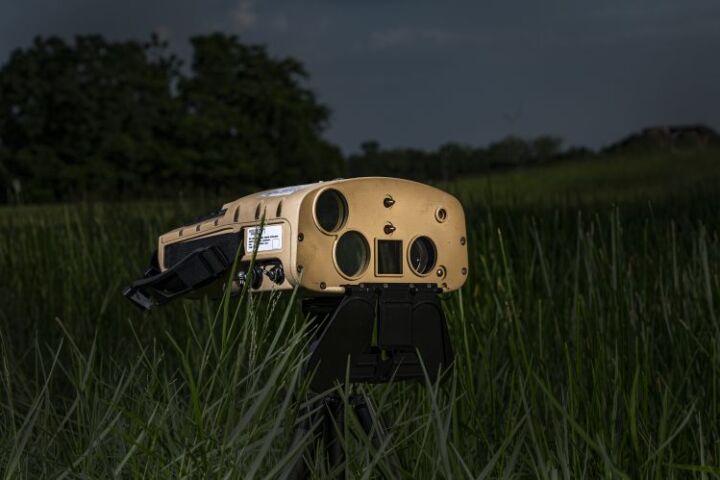
The US Marine Corps has decided to purchase Northrop Grumman's all-in-one Next Generation Handheld Targeting System (NGHTS) that packs a suite of day/night targeting sensors in a 10-lb (4.5-kg) package and can operate in GPS-denied areas.
-
It sounds like a sci-fi movie scene, but scientists have successfully created electrodes in living tissue using a viscous gel of enzymes. It could signal a fresh approach to bioelectronics and, in the future, new therapies for neurological disorders.
-
Water is usually something you’d want to keep away from electronic circuits, but engineers in Germany have now developed a new concept for water-based switches that are much faster than current semiconductor materials.
Load More