Trinity College Dublin
-
Using humble waste eggshells to pull rare earth elements from water, researchers have developed a simple, low-cost and sustainable procedure to provide the essential materials needed for a transition to green energy technologies.
-
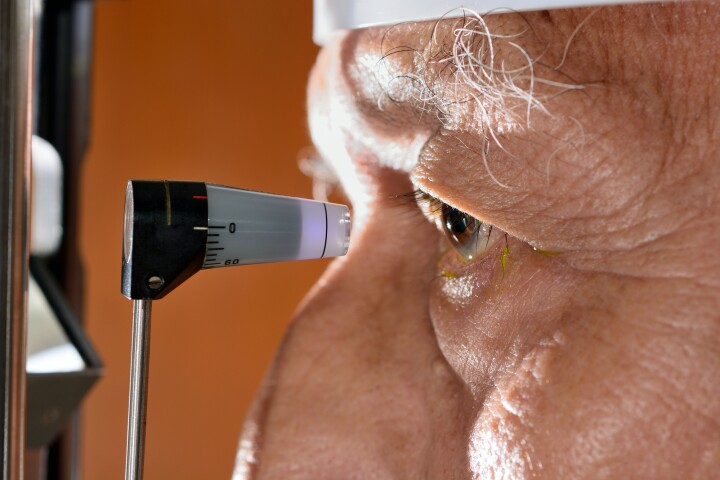
The high eye pressure seen in glaucoma slowly leads to blindness. For some, treatment with eye drops doesn’t work. Researchers have used gene therapy to develop a promising new way of treating the high eye pressure associated with glaucoma.
-
Scientists have found that modifying so-called "checkpoint proteins" in the immune system can regulate inflammation in fat tissue, with the result being significant reductions in obesity and diabetes in pre-clinical models.
-
Asthma is a very common condition and, while it’s treatable, there’s always a need for new options. Researchers at Trinity College Dublin have now found that an inflammatory “off switch” molecule could help treat severe asthma.
-
Research into a rare type of dementia has uncovered a genetic mutation that results in dysfunctional white blood cells and a breakdown of the blood-brain barrier, a mechanism that may play a role in common types of dementia such as Alzheimer's.
-
A new gene therapy treatment may be able to save the vision of patients with a blindness-causing genetic disease. DOA currently has no preventative or cure, but in tests in mice and human cells the team was able to slow progression of the disease.
-
Tinnitus is an aggravating disorder, causing sufferers to constantly hear a ringing in their ears. A new system could help, though, by simultaneously zapping their tongue and delivering sounds to their ears.
-
Scientists working with shield volcanoes in the Galapagos Archipelago have found evidence to suggest that volcanoes which ordinarily produce slow moving rivers of fire have the potential to create far more explosive and dangerous eruptions.
-
After a heart attack has occurred, some of the beating cardiac tissue ends up being replaced with non-beating scar tissue – this permanently compromises the function of the heart. A new patch, however, is designed to help.
-
Our bodies need vitamin D, but many peoples' indoor lifestyles keep them from getting enough via sunlight exposure. So, how can someone find out just how high their D levels are? Well, blood sampling works, although levels can now also be determined simply by analyzing one of the person's hairs.
-
Like so many other diseases, tuberculosis is becoming increasingly resistant to treatment by antibiotics. There may be hope, however, as scientists have developed a new vitamin-based treatment which could both halt the disease, and prevent antibiotic-resistance from developing further.
-
If you've watched even one TV show about sharks, then chances are you've seen awesome footage of great whites jumping completely out of the water. As it turns out, though, they're not the only ones who like getting high. Their even larger cousin, the basking shark, has also been spotted doing so.
Load More