University of Sheffield
-
In good news for nearly half the world's men, scientists have found that a naturally occurring sugar in humans and animals can be harnessed as a an effective topical gel for baldness. It sets it up as an inexpensive and safer alternative to minoxidil.
-
The application of crushed rock to farmers' fields may not only reduce greenhouse gases, it could also boost crop yields by up to 16%. These are the findings of a new study conducted by scientists from the University of Sheffield.
-
In a world first, Budapest Zoo gorilla Liesel has received stem-cell therapy for her arthritis. It's hoped that this groundbreaking procedure, which aims to rejuvenate her damaged joint cartilage, will not just help her but be adapted for human use too.
-
Astronomers have discovered the cosmic equivalent of a parent crashing a teenagers’ party to make sure they have enough water. An aging star has been detected passing through a young star-forming region, delivering elements crucial for life to form.
-
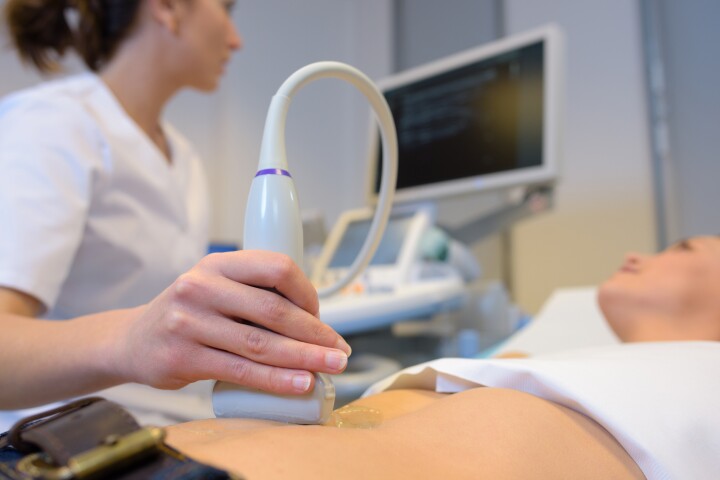
Researchers have developed a breakthrough ultrasound method that uses shear waves to, for the first time, measure tension in human tissue. The discovery has to the potential to revolutionize disease diagnosis.
-
As many couples trying to conceive know, much can go wrong during that fateful meeting of sperm and egg. Now scientists have identified a new protein eggs use to draw in sperm, which could one day lead to new fertility treatments and contraceptives.
-
We're seeing a growing emphasis on direct air capture technology in our efforts to combat climate change, and an interesting new take on this technology could see it put to use on railways around the world.
-
A new type of imaging tech has detected lung damage not visible on MRI or CT scans in patients suffering from the long-term effects of COVID-19. The technology will help clinicians understand the breathing impairments seen in long COVID.
-
Scientists have discovered the fossil of what may be the earliest multicellular animal ever found. Dating back a billion years, the microscopic fossil contains two distinct cell types, potentially making it an ancestor to advanced animals.
-
A new study out of the University of Sheffield makes a case for a geoengineering technique known as enhanced rock weathering, which essentially involves supercharging soil’s ability to remove CO2 from the atmosphere by sprinkling it with rock dust.
-
Two new studies are offering novel insights into celiac disease. One study is suggesting immune responses to gluten lead to neurological damage, while another offers hope for a cure demonstrating a nanoparticle treatment can induce immune tolerance.
-
Scientists have determined that lycopene, which is a pigment that naturally occurs in tomatoes, greatly improves sperm quality.
Load More