Bacteria
-
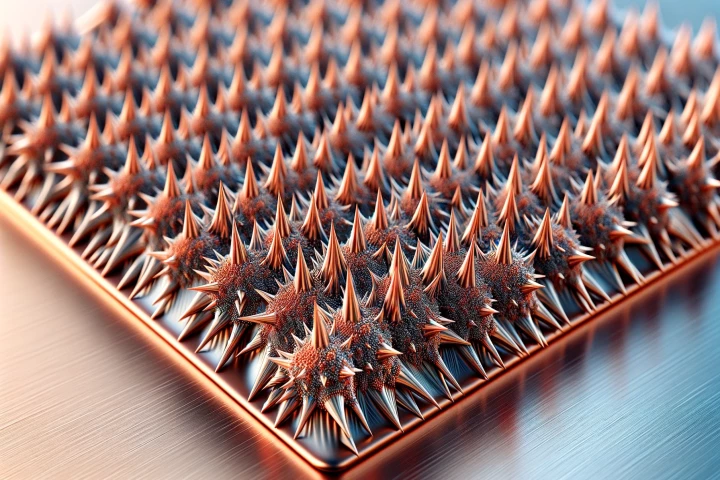
To help combat the rise of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, researchers have been experimenting for years with drug-free methods to blast disease-causing bugs. A new type of stainless steel does exactly that, in a convenient and affordable way.
-
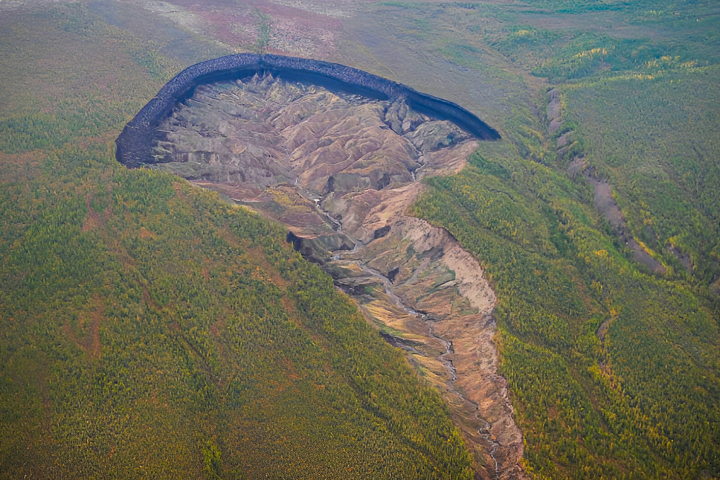
Whether a John Carpenter fan or not, you shouldn't need much convincing to see that the thawing of subterranean permafrost at the poles is not really a good thing. Siberia's biggest sinkhole is now devouring the landscape around it at an alarming rate.
-
A new biodegradable plastic embedded with spores of plastic-eating bacteria manages to break down 90% of the material after five months in landfill. Weirdly, this actually made the plastic tougher and stronger during use.
-
Fish farming may be getting much more eco-friendly, courtesy of soybean processing wastewater. Microbes in the liquid have been used to produce proteins that could replace the fishmeal which is currently fed to farmed fish.
-
Abundant, diverse bacterial communities have been found deep beneath the almost uninhabitable surface of the Atacama Desert in Chile. The researchers who discovered them say they're likely 19,000 years old and could be linked to microbial life on Mars.
-
Pothos plants are already known for being particularly good at purifying indoor air, so imagine if it were possible to make them 30 times better at doing so. Neoplants claims its Neo PX system does just that, using special soil-dwelling bacteria.
-
The four spikes on a new nanocrystal developed in Spain spin up under light and move through liquid, blasting any bacteria unfortunate to be in their path. The development could spell trouble for bacteria that resists traditional drug treatments.
-
Scientists have discovered that a once-in-a-billion-years evolutionary event is underway, as two lifeforms have merged into one organism that boasts abilities its peers would envy. Last time this happened, Earth got plants.
-
Fractals are a fascinating type of pattern for mathematics nerds, with their repeating, artificial-looking structures. Now, scientists have discovered the first known fractal protein – and it seems to be an evolutionary accident.
-
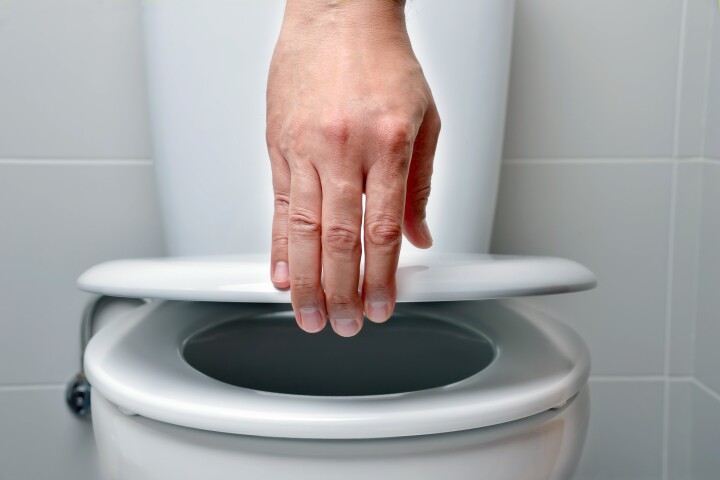
When it comes to toilet etiquette, do you put the lid down before you flush, or leave it up? A new study has shown just what happens when you leave it up – and the results might have you questioning just what you do behind closed doors.
-
An oral vaccine that prevents urinary tract infections (UTIs) recurring has shown to provide protection for nearly a decade in a majority of patients, according to a new study. This easy treatment offers a safe, effective method of UTI prevention.
-
Bacteria-produced leather is already an eco-friendly alternative to its cow-derived counterpart, but it could soon be even eco-friendlier. Scientists have gotten the microbes to color the stuff themselves, eliminating the need for toxic dyes.
Load More