Enzyme
-
Researchers have identified an enzyme that's key to updating existing memories with new information, a process that declines naturally with age. Blocking the enzyme reduced memory impairment, opening the door to developing treatments for age-related memory problems.
-
Using enzymes produced by a bacteria that almost everyone has in their gut, researchers have removed the antigens from red blood cells that determine blood type, putting us within reach of producing universal donor blood.
-
Scientists have discovered a new mechanism for how type 2 diabetes takes hold, and demonstrated in mice that blocking a particular enzyme could open a new avenue of treatment for the disease.
-
CRISPR systems are powerful tools for genetic engineering, but they have their limitations. Now, scientists have discovered almost 200 new CRISPR systems in bacteria, and found that some can edit human cells even more precisely than existing ones.
-
CRISPR-Cas9 is the household name of genetic engineering tools, but there might be other, better ways. MIT scientists have now demonstrated an alternative called Fanzor, which is naturally found in animals so could be a better fit for human use.
-
Scientists have reconstructed the genomes of microbes from the Stone Age, and used them to produce new molecules. The complex puzzle was pieced together from DNA fragments of bacteria on the teeth of ancient humans and Neanderthals.
-
Researchers fed mice a probiotic designed to release an alcohol-metabolizing enzyme. Then they got them drunk. The results showed success in keeping the mice from getting too buzzed, and in helping them clear the alcohol from their systems faster.
-
Scientists have identified the role an enzyme, crucial to the body’s metabolism, plays in the development of kidney disease, opening the door to new methods of prevention and treatment of this increasingly prevalent condition.
-
Researchers have resurrected ancient CRISPR proteins from millions and even billions of years ago. Not only can they still edit human cells, but they’re more versatile than modern versions, paving the way for new synthetic CRISPR gene-editing tools.
-
A new technique has been added to the CRISPR gene-editing toolbox. Known as PASTE, the system uses virus enzymes to “drag-and-drop” large sections of DNA into a genome, which could help treat a range of genetic diseases.
-
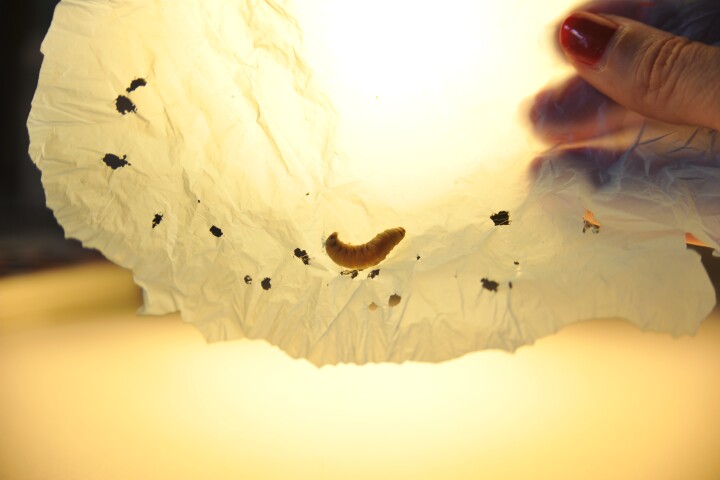
Scientists continue to unearth enzymes that can eat away plastic materials with high efficiency, and a team in Spain has just discovered more in the saliva of wax worms, which have the ability to degrade plastic bags in hours at room temperature.
-
Scientists have identified two molecules that could help treat leukemia, in a way that’s far less damaging to healthy cells than existing chemotherapy. The compounds work using a different mechanism that’s more selective for cancerous cells.
Load More