Agriculture
-
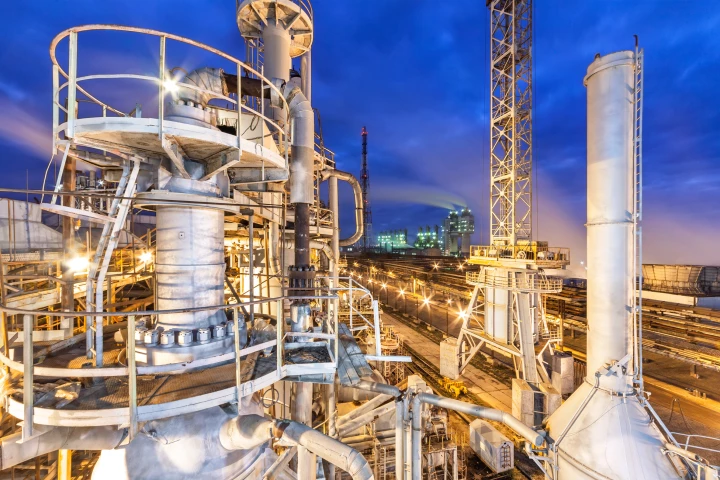
To find the right mix of metals for their green ammonia catalyst, scientists turned to AI. The result was a breakthrough that makes their technique of producing ammonia from air and water more efficient and much more accessible.
-
As agriculture tries to clean up its act, the roar of the diesel engine is likely to become a thing of the past. But e-farmers don't want to their battery-powered beasts idling for hours charging. The ONOX tractor's modular hotswap approach could help.
-
Beekeepers in many regions are having a hard time of it, as their honeybees struggle to find enough pollen. Scientists are now addressing that problem with a new nutritional supplement which is described as being like "a PowerBar for bees."
-
Measuring tape is a neat material, in that it's rigid enough to hold its shape when extended, but flexible enough to give way under pressure. Scientists have taken advantage of that dual nature in a robo-gripper designed for handling fragile items.
-
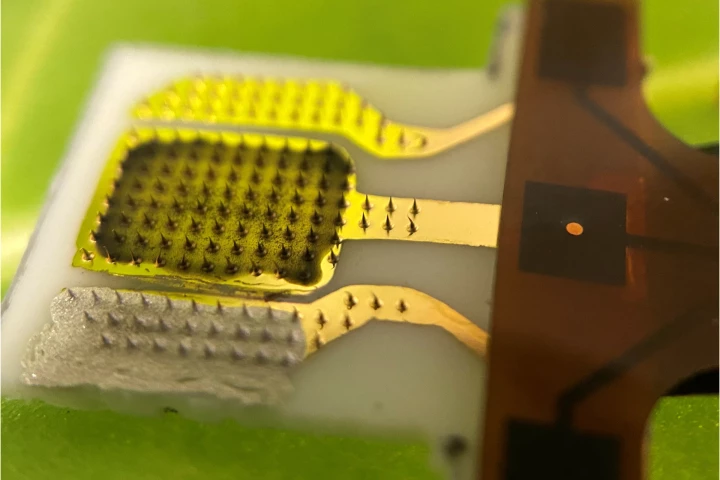
The sooner a farmer knows that their crops are suffering, the faster they can take action to prevent major crop failure. A new plant-leaf-poking sensor could soon help them do so, by sending an alert as soon as the plant gets stressed.
-
Crop fertilizers are a major source of pollution, as the chemicals make their way out of the soil and into the environment. Scientists are now working on a solution to that problem, by developing a fertilizer that takes the form of tiny glass beads.
-
When most people think of duckweed, they likely picture a green film growing across the surface of a stinky, stagnant slough. The protein-rich plant may soon be on your plate, however, as it's been approved for human consumption in Europe.
-
In the latest bid to greenify ammonia production, researchers have built a portable device to cheaply produce ammonia wherever it's needed by simply using air at room temperature and standard atmospheric pressure.
-
When it comes to monitoring the health of crops, aerial images captured by aircraft are only going to tell you so much. That's where an experimental new spectral sensor comes in, as it's mounted directly on the underside of individual plants' leaves.
-
The spraying of orchards and vineyards certainly isn't an eco-friendly process, with tractors spewing exhaust as they douse crops in herbicides and pesticides. That's one of the main reasons the electric, autonomous Prospr robot was created.
-
It's always best if farmers can detect drought stress before crop plants become wilted, weakened and lower-yielding. An experimental new portable device could help in that regard, as it uses ultrasound to spot such stress in its earliest stages.
-
Many indoor plant enthusiasts know that mirrors can be used to direct more sunlight onto plants that need it. Scientists have now developed a method of applying that same principle to tree seedlings that are struggling to grow in shady forests.
Load More