Empa
-
When it comes to closing incisions or other wounds in the digestive tract, sutures alone aren't enough to keep fluids or food waste from leaking out into the abdomen. A new hydrogel patch is designed to help, by thoroughly sealing such injuries up.
-
Although optical fibers are highly effective at data transmission, they're also relatively brittle. An experimental new type of optical fiber addresses that limitation, by incorporating a core made of liquid glycerol.
-
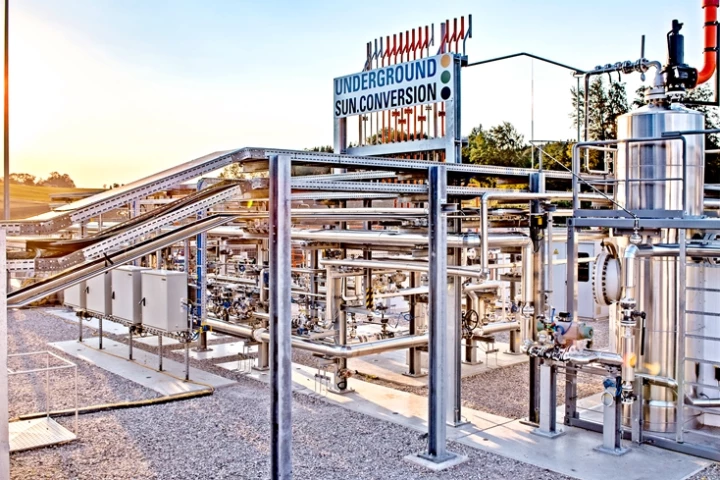
In many countries, long, dark winters limit the amount of solar energy that can be generated for much of the year. That's where the Underground Sun Conversion system comes in, as it's intended to use sunlight to help produce natural gas underground.
-
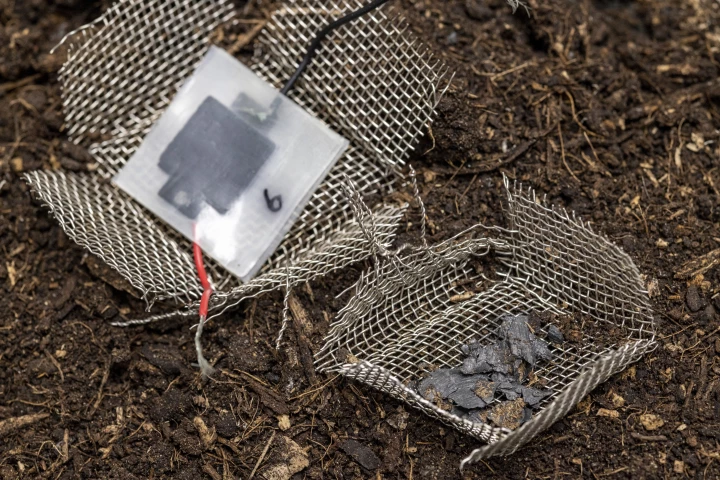
As technology continues to evolve, we're going to see an increasing number of battery-powered connected devices – some of which will be single-use, like shipping packaging. A new biodegradable mini-capacitor has been created with such uses in mind.
-
Researchers have demonstrated how patterns of string carefully laid out by robotic arms can be used to bind asphalt together in place of environmentally damaging bitumen, resulting in greener roads that are also easier to recycle after use.
-
In order for a thief to bypass a security system's interface, they generally have to see that interface in the first place. That's why Swiss scientists have designed an access code keypad which is completely transparent.
-
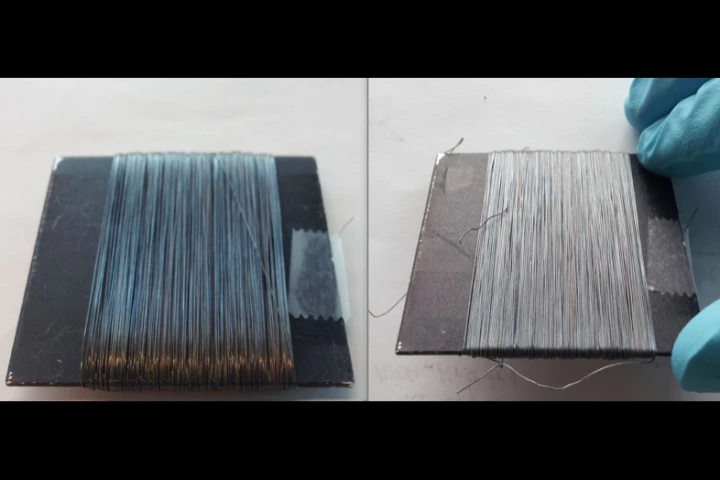
There are untold energy sources all around us, if we can just figure out how to tap into them. Swiss researchers have now demonstrated an environmentally friendly way to make spongy wood flooring that can generate electricity with every step.
-
When a rope is heated – either by friction or by fire – it may lose its structural integrity, subsequently breaking when put under load. A new surface coating, however, could cause ropes to change color if they've been overheated, providing a warning to users.
-
When you think of processes that could benefit from a high-tech makeover, the drying of fruit may not be the first that comes to mind. It turns out, however, that the use of "ionic wind" for fruit-dehydration saves energy and preserves nutrients.
-
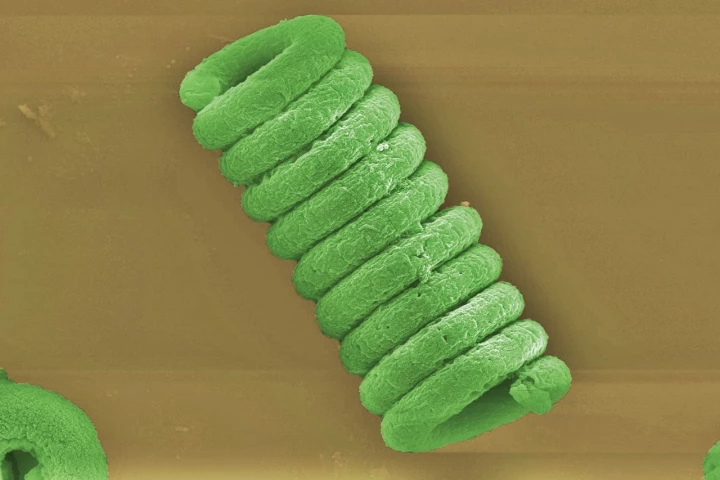
Many people take Spirulina as a dietary supplement, but researchers at the Swiss Federal Laboratories for Material Science have found a way to put the tiny spirals to work removing contaminants from water, and then make biofuels from their remains.
-
Although it's vitally important to keep wounds free of harmful bacteria, antibacterial ointments have to be regularly reapplied, requiring bandages to be removed. A new wound dressing, however, is claimed to continuously kill bacteria all on its own.
-
A new adaptation of a pre-stressing technique has been used to produce concrete that is lighter but with comparable strength, an advance that if widely applied, could save significant amounts of CO2.
Load More