EPFL
-
If you're releasing a robot into the aquatic environment with no intention of retrieving it, that bot had better be biodegradable. Swiss scientists have gone a step better, with a li'l robot that can be consumed by fish when its job is done.
-
Factory wood-cutting robots may be capable of fast and intricate carpentry tasks, but they're expensive – plus they put actual carpenters out of work. A new augmented reality system splits the difference, by guiding the hands of human carpenters.
-
A new study has tested innovative proof-of-concept technology that syncs electrical stimulation with rehabilitation robotics to enable individuals paralyzed after spinal injury to move more naturally. The tech should improve recovery outcomes.
-
If a robot is going to excel at traversing multiple types of terrain, it shouldn't have an unadaptable "Jack of all trades, master of none" body shape. That's where the GOAT comes in, as it automatically changes shape depending on the landscape.
-
If a robot is being used to gather data in sensitive aquatic environments, it shouldn't have a whirring propeller that could harm wildlife or get caught in weeds. A new bot addresses that issue by utilizing a swimming mechanism inspired by flatworms.
-
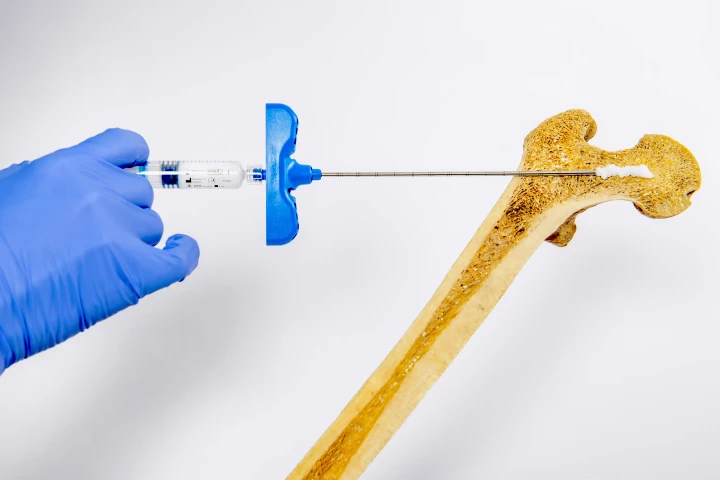
Osteoporosis is typically treated with orally administered drugs, which may take up to a year to have a noticeable effect. A new injectable hydrogel, however, is claimed to drastically boost bone density in as little as two weeks.
-
Two patients with spinal injuries have seen improvements in their ability to walk again, thanks to deep brain stimulation. Intriguingly, the therapy targets a region of the brain that normally isn’t associated with motor skills.
-
While autonomous flying robots have some intriguing potential applications, their usefulness is limited if they can't move across uneven terrain once they land. A new bio-inspired bot can do so, however, by mimicking the gait of the raven.
-
Meteorology may not seem like an eco-unfriendly field, but it does need to clean up its act in at least one way. A new high-tech glider could help it do so, by allowing single-use weather-balloon-carried devices to be reclaimed and reused.
-
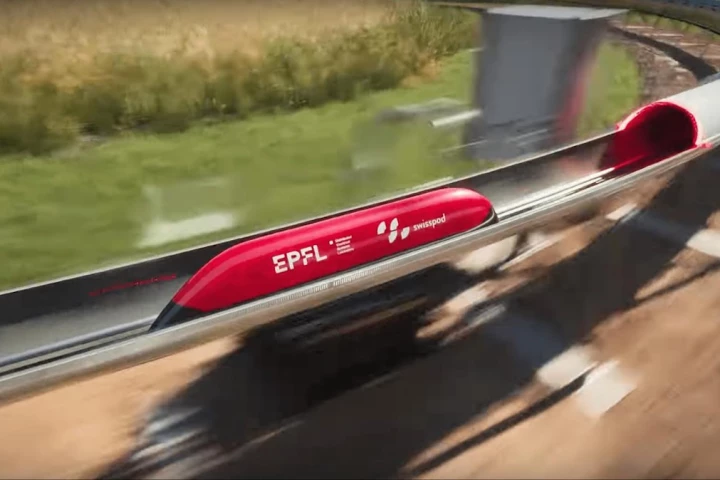
In what feels like news straight out of 2016, a Hyperloop testing facility in Europe has completed the longest-ever vacuum capsule journey. The milestone could bring this oft-forgotten promise of high-speed transport one step closer to reality.
-
Combining VR and non-invasive deep-brain electrical stimulation, has improved memory – the kind that remembers where you left the car keys - in healthy people. The approach has great potential as a surgery- and drug-free treatment for cognitive decline
-
The prospect of virtually unlimited clean geothermal power is substantially brighter. EPFL’s Laboratory of Experimental Rock Mechanics has shown that the semi-plastic, gooey rock at supercritical depths can still be fractured to let water through.
Load More