Genetics
-
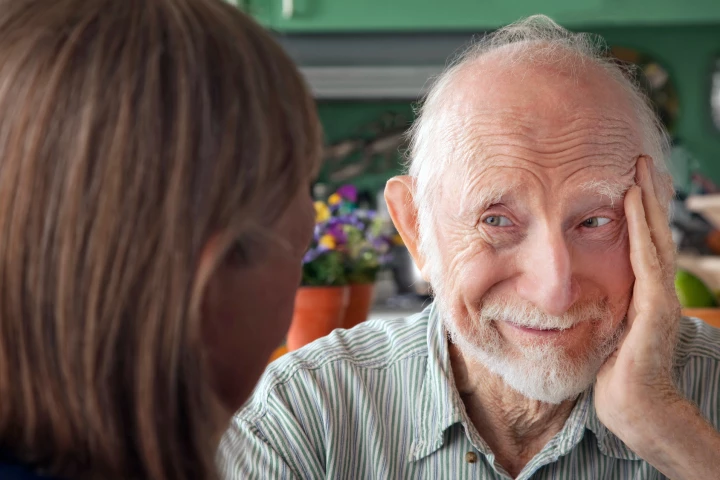
Using the largest sample of super-agers to date, scientists have found convincing evidence that supports what many of us have suspected: Longevity isn’t just about healthy lifestyle choices, but also a good draw in the genetic lottery.
-
A tool long used to probe neural circuits in the lab is now being floated as a new way to treat human patients. The technique uses light to turn specific neurons on or off, and it could be used to treat everything from chronic pain to epilepsy.
-
Americans are being urged to be extra vigilant, as a new influenza A variant is spreading more rapidly and evading our abilities to fight it off. With more than 110,000 hospitalizations so far, scientists expect this wave to worsen as the season peaks.
-
It's that time of year – and my personal favorite corner of science to look back on – when we recap the many fascinating discoveries in the plant and animal kingdom in 2025. Orcas have again made news, but no luxury yachts were hurt in the process.
-
High on sheer cliffs in China, ancient coffins are wedged into rock faces hundreds of feet above the ground. These dramatic burials, now re-examined using ancient DNA, point to a broader practice where disparate cultures all had their own "sky graves."
-
Most pet dogs carry a little wolf inside them; tiny snippets of wolf DNA that slipped into dog genomes after domestication. Now a new study has found almost two-thirds of dog breeds have a small amount of wolf genes, including some breeds you wouldn't expect.
-
Groundbreaking research has uncovered three gene variants that increase the risk of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder by up to 15 times. It's a remarkable finding, considering that thousands of mutations only come with a nominal elevated risk.
-
A new study has pinpointed how the APOE4 gene variant sabotages the brain’s energy balance, blocking neurons from burning fat for fuel when glucose runs low, a discovery that could reveal new ways to prevent or slow Alzheimer’s disease.
-
A one-time gene therapy using a patient’s own stem cells has effectively cured a deadly immune disorder in 95% of treated children, offering a lasting, donor-free solution to ADA-SCID, known as the “bubble boy” disease.
-
A high-fat, low-carb ketogenic diet may protect the brain from early Alzheimer’s disease changes in people genetically at risk, new research suggests, by rebalancing gut bacteria and restoring brain energy metabolism.
-
Scientists have rejected claims that acetaminophen is a key driver of autism spectrum disorder, cautioning that research is inconclusive and excludes genetics and a suite of other influences. What's more, it focuses on a "cure," not understanding.
-
A study involving more than 1,000 cancer patients has found that a low dose of aspirin halves the risk of colorectal tumors returning after surgery. This readily available and affordable treatment could change the health outcomes of many survivors.
Load More