Genetics
-
The evolutionary ladder is meant to be climbed one rung at a time with an organism shedding some traits and gaining others on the way up. However, in a very surprising twist, some tomatoes on the Galapagos islands are inching back down the ladder.
-
A new organelle has been found by scientists at the University of Virginia. The super-small specialized structure has a role recycling material inside our cells, and its discovery could lead to improved treatments for a wide range of diseases.
-
Exposure to common metals has again been linked to ADHD and specific symptoms. It builds on existing research that has found a strong association between environmental contaminants like lead and a higher rate of people diagnosed with the condition.
-
If you have an aversion to the bitterness of foods like cabbage or broccoli, you might be a "super-taster," carrying a specific genetic code that dials up taste sensitivity. It may also put you at higher risk of kidney disease and bipolar disorder.
-
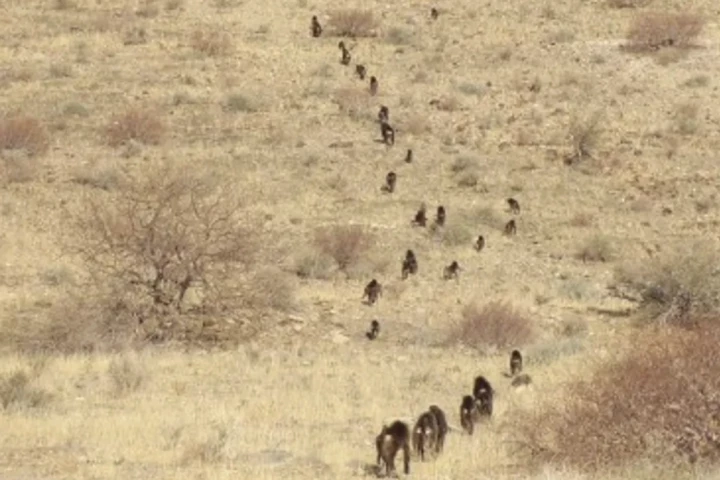
It's not a simple case of "follow the leader" when it comes to baboons on foot. Researchers have made a surprising discovery on why they appear to move in an orderly line, and it's something that can help us better understand human behavior, too.
-
A surprising finding from researchers in Japan has shown how an environmental factor can influence the development of sex organs in unborn mice. The discovery challenges the longstanding belief that sex is determined purely by genetic factors.
-
Men who carry two copies of a common genetic variant are twice as likely to develop dementia than women with the same mutations. This discovery may now lead to early detection and novel interventions to block how these variants impact the brain.
-
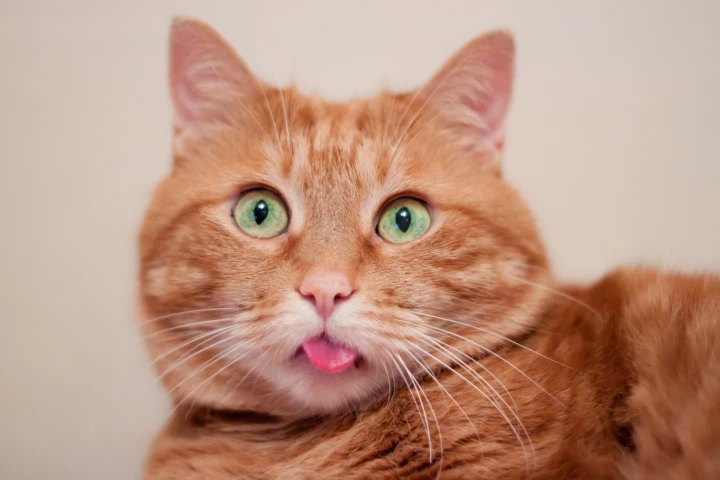
The existence of orange cats dates back to the 12th century, but the DNA driving this color has been a mystery – until now. Scientists have solved the puzzle, finding a surprise variant that triggers ginger fur, one not seen in any other orange animal.
-
Why do elephants, one of the biggest animals on the planet, paradoxically experience unusually low rates of cancer? The question has led scientists to discover these remarkable mammals carry unique genetic variants that reduce their risk of tumors.
-
Researchers have genetically modified spiders for the first time using the CRISPR gene-editing process. Adding a single gene to unfertilized eggs resulted in the creation of a spider that could produce red, fluorescent silk.
-
Like a plot mashup of Jurassic Park meets Game of Thrones, John Hammond meets Jon Snow, scientists at Colossal Biosciences claims to have pulled off the world's first de-extinction event. It's brought back the dire wolf.
-
You don't often find crowds flocking to take in the pungent scent of rotting flesh, yet that's just what happens when a corpse flower blooms at a public garden. But this iconic endangered plant is now facing a new threat – our aversion to paperwork.
Load More