Genome
-
A new CRISPR-based one-off therapy that lowers "bad" cholesterol is set to enter its Phase I trial. If successful, it could be the first approved genetic-editing method, replacing ongoing medication and slashing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
-
An ambitious plan to generate sequence genomes for 1.85 million species on our planet is underway. It's a major undertaking that'll dramatically enhance our understanding of biology, and inform conservation efforts. Thankfully, AI is lending a hand.
-
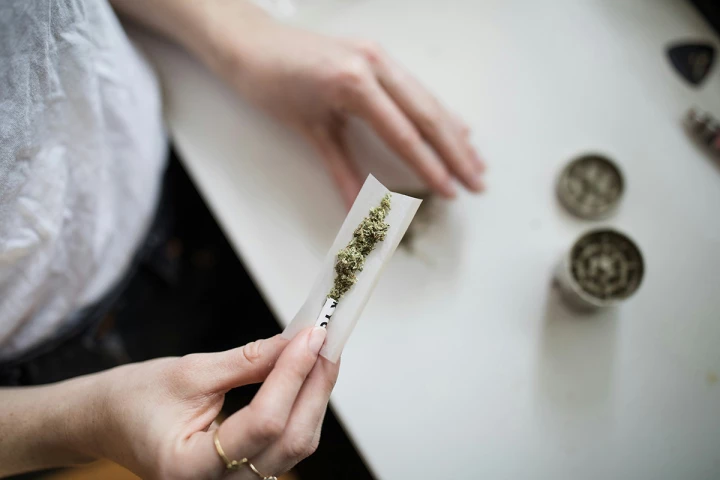
Researchers have identified specific regions of the human genome connected to cannabis use, which means the propensity to get addicted to weed may be encoded in our DNA.
-
Researchers believe they have developed the first blood test to diagnose chronic fatigue syndrome, or myalgic encephalomyelitis, and it has the potential to be a game-changer for millions around the globe suffering with the debilitation condition.
-
A groundbreaking discovery reveals how HIV integrates its genetic material into human DNA, exposing a key viral vulnerability that could lead to new therapies and bring the world closer to a functional HIV cure.
-
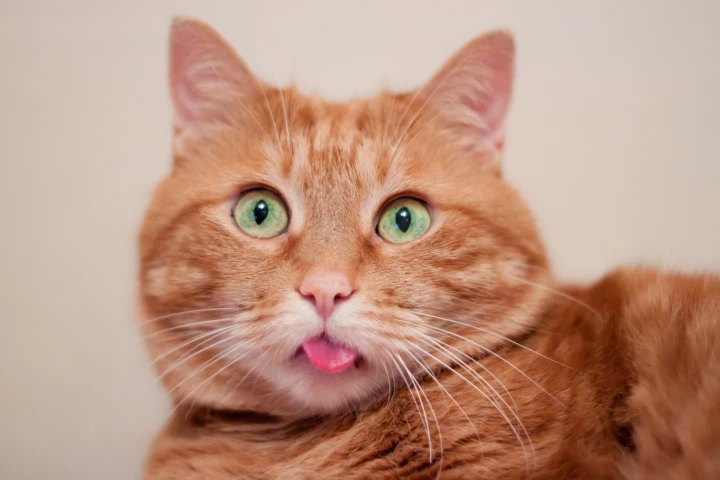
The existence of orange cats dates back to the 12th century, but the DNA driving this color has been a mystery – until now. Scientists have solved the puzzle, finding a surprise variant that triggers ginger fur, one not seen in any other orange animal.
-
Researchers at UCSF have developed a single genomic test that can quickly detect virtually any kind of pathogen in a patient. This allows for much quicker diagnoses, enables targeted treatment to begin sooner, and could lower healthcare costs.
-
Scientists have stored the entire human genome on a five-dimensional crystal capable of storing up to 360 terabytes of information and is built to survive for billions of years. The tech could be used to create an enduring record of human, animal, and plant genomes.
-
Scientists have assembled the most complete woolly mammoth genome in 3D, thanks to an incredible “freeze-dried” specimen. With its DNA preserved in a glass-like state, chromosomes were found for the first time, and even gene expression patterns.
-
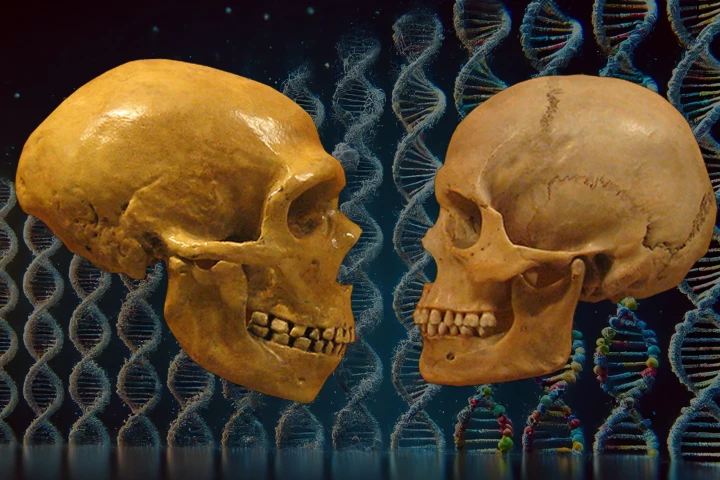
Since Neanderthals' whole genome was sequenced, there’s been growing interest in how their genetics influences our health. New research has found that genetic variations derived from our ancient relatives are associated with an increased susceptibility to autism.
-
Scientists have discovered the organism with the largest known genome. At 160 billion base pairs, it's 50 times bigger than the human genome, and the organism it’s describing is a tiny fern you wouldn’t even notice if you tripped over it on a hike.
-
We now know just how the earliest land plants, ancient algae, conquered terrestrial Earth hundreds of millions of years ago and laid the (literal) groundwork for all subsequent life. It highlights the fascinating genetic strategies of plant evolution.
Load More