Insect
-
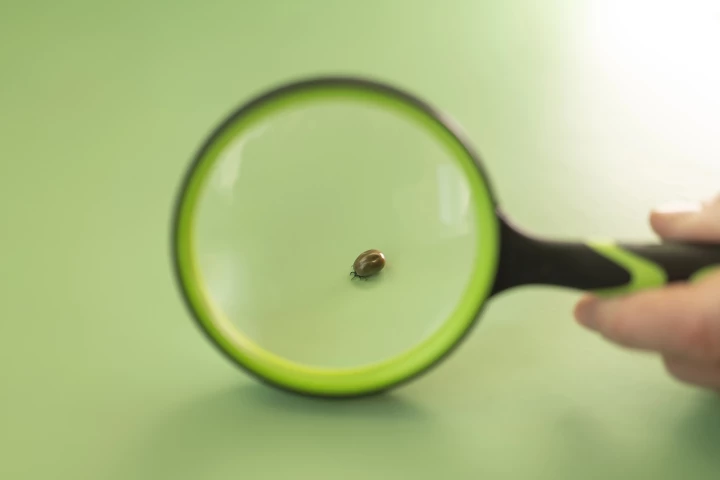
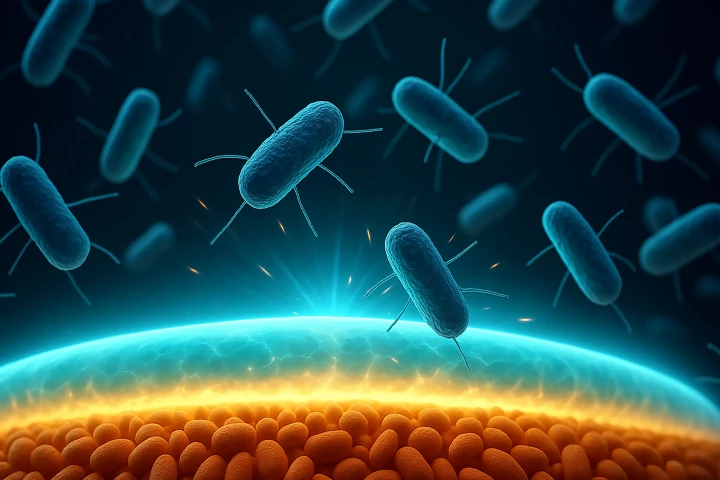
Researchers have developed a new method for preventing bacteria from adhering to surfaces, such as medical devices. It relies on the unique properties of resilin, a natural insect protein that enables fleas to jump hundreds of times their body length.
-
From fleas to mosquitoes, there's no shortage of organisms we consider pests. But thanks to new genetic detective work, scientists have named and shamed the resilient, highly adaptive – and frustratingly hard to kill – bug that got to us first.
-
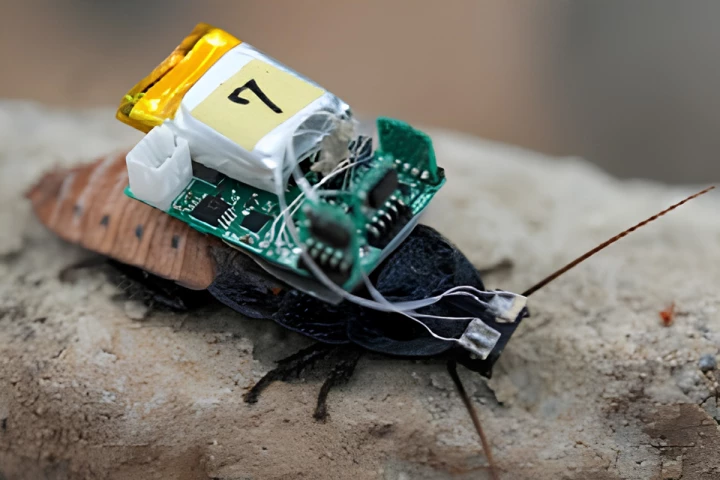
I bet that headline wasn't on your bingo card this week. Researchers at the University of Osaka have equipped cyborg insects with teeny tiny helmets to steer them around various environments, without the need for invasive surgery or internal wiring.
-
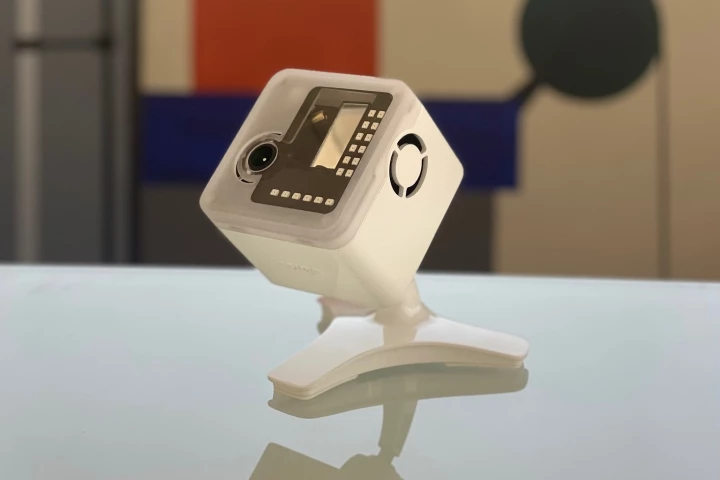
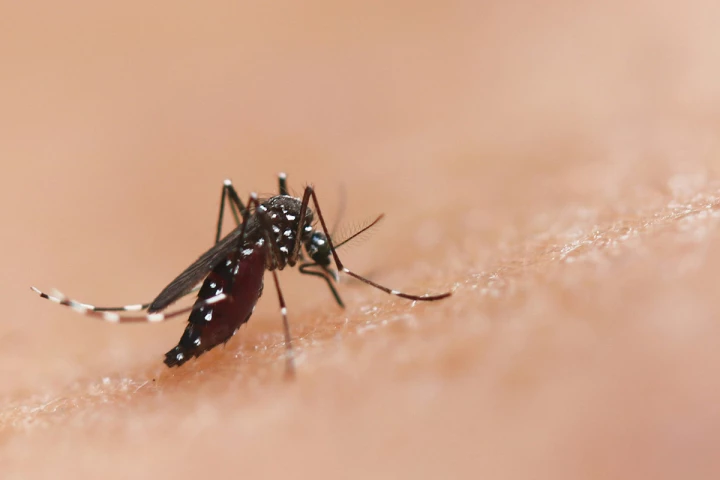
Nobody likes hearing a mosquito somewhere in their bedroom, without being able to see where it is. Well, the Bzigo Iris tracks and highlights mozzies, so you can swat them. It's now 50% cheaper, and doesn't require a Wi-Fi connection.
-
Zombies are real – not in the walking dead sense, but parasites that can force creatures to do things against their will. The launch of The Last of Us season 2 feels like a great time to explore some of the real-world zombie stories that inspired it.
-
If you ever travel back in time to the reign of dinosaurs, don’t touch any flowers – it might just be a parasitic wasp in disguise. Analysis of wasps preserved in amber show how the insect ensnared hosts for its larvae with a Venus flytrap-like butt.
-
Methylmercury is an extremely toxic compound, and unfortunately it's often present in the fish that we eat. Scientists are now developing a method of removing it from the environment, utilizing engineered fish and flies that take up the compound and neutralize it.
-
Mosquitoes looking to mate in Australia are about to have the worst sex of their lives – thanks to genetic modifications turning their semen toxic. That could kill females swiftly, and greatly reduce their ability to spread deadly diseases.
-
Genetic studies have revealed that when male mosquitoes lose their hearing, they also lose their sex lives. The surprising discovery could lead to new ways to reduce mosquito populations and the diseases they spread.
-
For 50 years now, camera company Nikon has been highlighting microscopic marvels with the annual Nikon Small World photomicrography competition. Headlining this year’s winners is a groundbreaking view of mouse brain tumor cells.
-
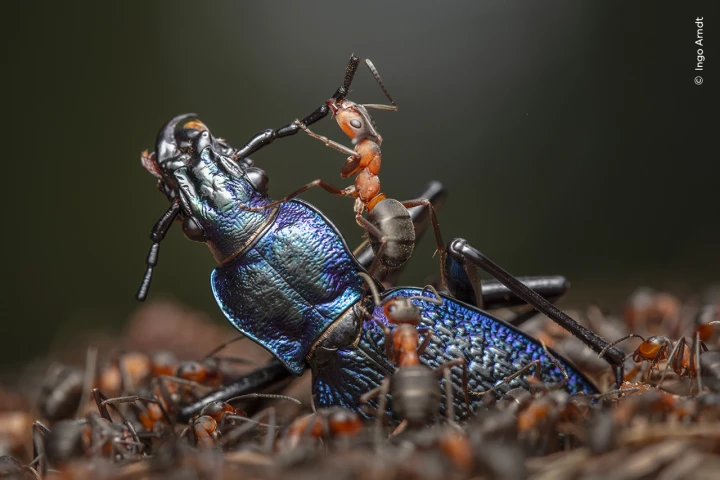
For the 60th year in a row, the Natural History Museum of London has held its Wildlife Photographer of the Year awards. And for the 60th year in a row, the images are guaranteed to stir your love of the natural world and the animals that live in it.
-
Despite what you might say when drunk, you’re not the best backflipper in the world. That honor belongs to a tiny little bug called a globular springtail, whose superfast backflips have now been caught on slow-motion camera for the first time.
Load More