Ions
-
If, like me, you can't go a day without making sure your watch is synced to the second, you'll be delighted to learn that a new atomic clock has broken the record with an accuracy of 5.5 x 10⁻¹⁹ – gaining or losing one second in 57.6 billion years.
-
NASA scientists have discovered a third global energy field around Earth. Known as the ambipolar electric field, this force drives charged particles into space above the poles and joins the known gravity and electromagnetic fields.
-
Scientists have discovered the potential existence of a bizarre new molecule related to water. Dubbed “aquodiium,” this ion could form under extreme conditions and may explain some of the weirdness of our solar system’s ice giant planets.
-
Heating and cooling systems are among the biggest guzzlers of energy. Berkeley Lab has now developed a new technology that heats and cools by switching a material between solid and liquid states, inducing a large temperature change from a small voltage.
-
MIT engineers have developed a new type of artificial synapse that’s extremely energy efficient and ultra-fast, processing data a million times faster than synapses in the human brain. The analog device shuttles protons around instead of electrons.
-
The Moon may look like a big dry ball, but there’s more water up there than you might expect. In a new study, scientists have shown that at least some of it could have been showered onto the lunar surface from the Earth’s atmosphere.
-
Transmitting data from medical implants in the body can be tricky, but a new technique can essentially write data to ions in human tissue, where it can then be read from a receiver outside the body at high transmission speeds.
-
Artificial devices usually don’t communicate well with nature. Now, researchers have created artificial organic neurons and synapses that can integrate with natural biological systems, and demonstrated this by making a Venus flytrap close on demand.
-
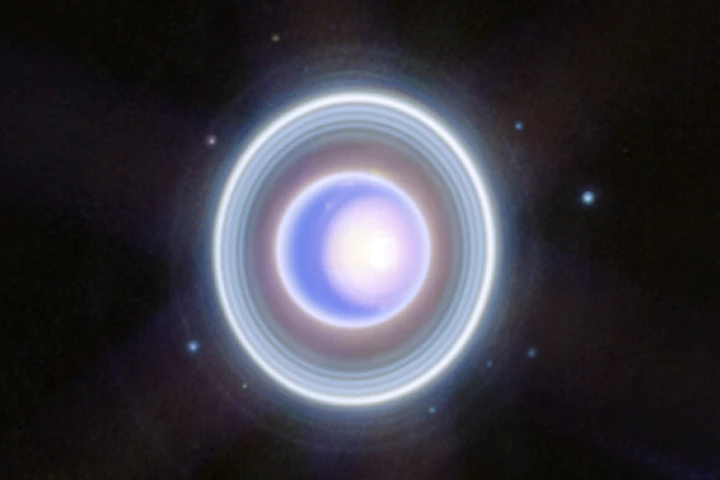
Water can take on far more forms than many people give it credit for, and now scientists have recreated a particularly bizarre one in the lab – a “hot black ice” that may exist deep inside planets like Uranus and Neptune.
-
Antimatter is hard to study, not least because it annihilates any container you try to put it in. Now CERN physicists have developed a new antimatter trap that can cool samples in seconds, which could help unlock a fundamental mystery of the universe.
-
Dark matter should be all around us, but the stuff is frustratingly elusive. Now physicists at NIST have developed a new sensor that could help us detect certain hypothetical dark matter particles, using a two-dimensional quantum crystal.
-
When you think of processes that could benefit from a high-tech makeover, the drying of fruit may not be the first that comes to mind. It turns out, however, that the use of "ionic wind" for fruit-dehydration saves energy and preserves nutrients.
Load More