Kyushu University
-
Harsh, eco-unfriendly synthetic herbicides are definitely one of those things that you shouldn't be using if you don't have to. Japanese researchers are thus now developing a green alternative, derived from the leaves of a humble walnut tree.
-
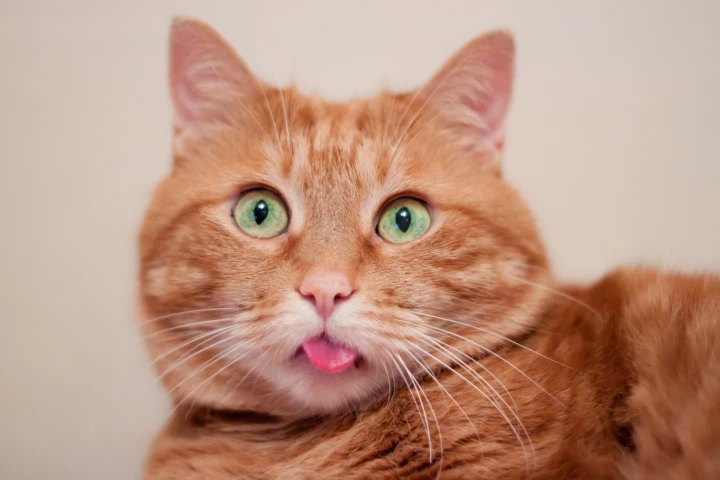
The existence of orange cats dates back to the 12th century, but the DNA driving this color has been a mystery – until now. Scientists have solved the puzzle, finding a surprise variant that triggers ginger fur, one not seen in any other orange animal.
-
Even if you don't know what 3D microfluidic networks are, that doesn't change the fact that they have some very valuable possible uses. Scientists have now devised a much easier method of making the things, by taking casts of plant roots.
-
Scientists in Japan have developed a new organic device that can harvest energy from heat. Unlike other thermoelectric generators, this one works at room temperature without a heat gradient.
-
Researchers have converted brain immune cells into neurons, replacing damaged ones and restoring function to stroke-affected mice. If the same results can be achieved in human cells, it opens the door to a potential treatment for stroke.
-
Most memory devices us electric signals, but an emerging technology uses light, so data can be read back just by checking if an LED is on or off. Now, researchers have developed a new device based entirely on perovskite that can do both at once.
-
Engineers have found a way to make liquid metals switch between reflective surfaces or those that scatter light. The transition only requires a small zap of electricity and could be used to make mirrors that can be switched on or off.
-
A new Japanese study simulated interstellar clouds of dust and gas, and managed to produce some of the building blocks of DNA.
-
Could scent-tracking sniffer dogs be out of a job? Well, perhaps eventually. Scientists from Japan's Kyushu University have developed a prototype robot that can detect and follow odors left on the ground, such as those deposited in footprints.
-
Some theories suggest there could be many more dimensions that we’re unaware of, mostly because they’re imperceptibly tiny. Now researchers have taken the search for extra dimensions down to the nanoscale, using a neutron beam to study gravitational forces more precisely than ever before.
-
A new development is allowing scientists to finely tune the electrical properties of organic materials, paving the way for efficient OLEDs, organic solar panels and transparent or flexible displays.