Max Planck Institute
-
High on sheer cliffs in China, ancient coffins are wedged into rock faces hundreds of feet above the ground. These dramatic burials, now re-examined using ancient DNA, point to a broader practice where disparate cultures all had their own "sky graves."
-
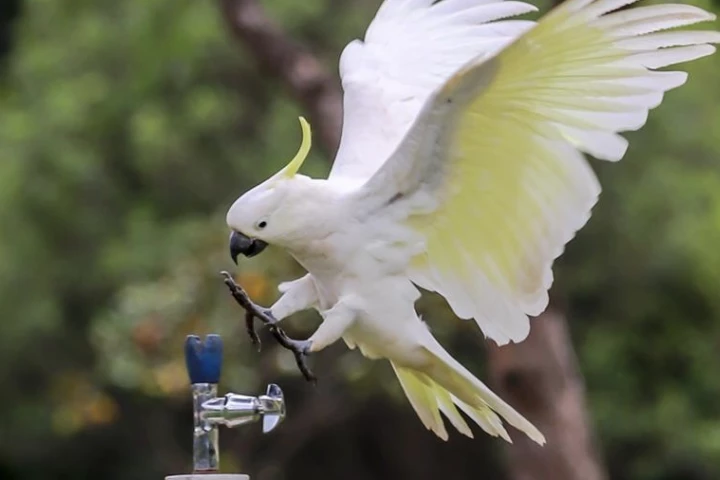
In an impressive feat of urban adaptation, sulphur-crested cockatoos have worked out how to use their feet and their large bodies to twist the taps of drinking fountains. And much like another of their moves, they're learning to do this en masse.
-
It's never a good thing, when a bacterial biofilm forms on the surface of a medical implant. There could soon be a new way of eradicating such films, however, using tiny remote-control liquid-bodied robots.
-
You lean back from the dinner table, feeling like you physically couldn’t fit another bite in – but then someone offers pie and you just can’t say no. Scientists have now identified the neurons behind the “dessert stomach” phenomenon.
-
Astrophysicists have detected the most energetic electrons ever recorded raining down on Earth. With trillions of times the energy of visible light, these cosmic rays seem to be coming from a powerful source relatively close to our solar system.
-
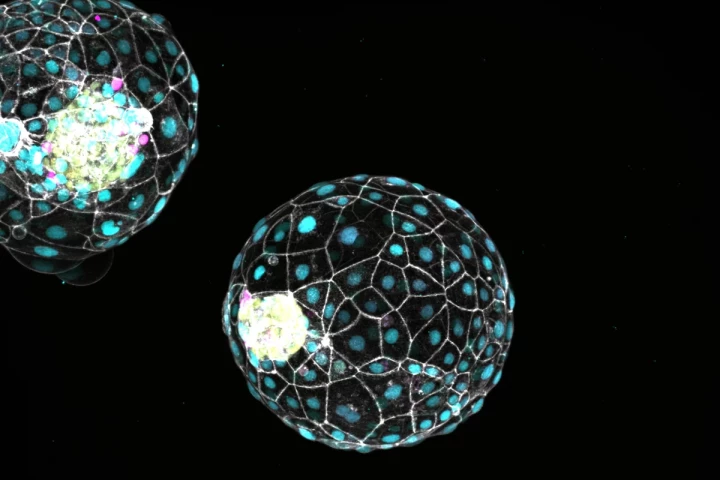
Scientists have discovered a kind of “pause button” in early human development. This biological mechanism has long been known in other mammals, but its discovery in humans could aid IVF procedures.
-
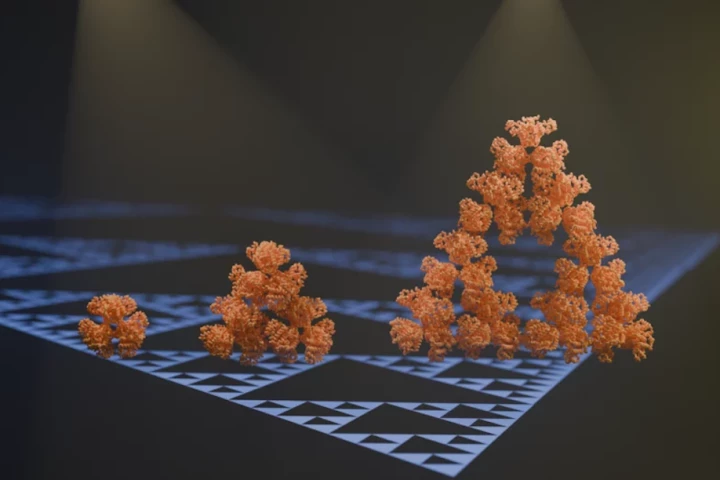
Fractals are a fascinating type of pattern for mathematics nerds, with their repeating, artificial-looking structures. Now, scientists have discovered the first known fractal protein – and it seems to be an evolutionary accident.
-
Researchers have devised an economical way of reducing the environmental impact of both the steel and aluminum industries by using hydrogen to melt down the toxic red mud left over from aluminum production to produce green steel in around 10 minutes.
-
Astronomers have mapped out half the universe in X-ray light, using a space telescope called eROSITA. The new map, which contains almost a million X-ray sources, is the basis of dozens of new scientific papers, with many more to come.
-
Astronomers have discovered a neutron star orbiting a mysterious object that, by all accounts, shouldn’t be able to exist. Seemingly invisible in light, and too small to be a black hole, the object defies explanation.
-
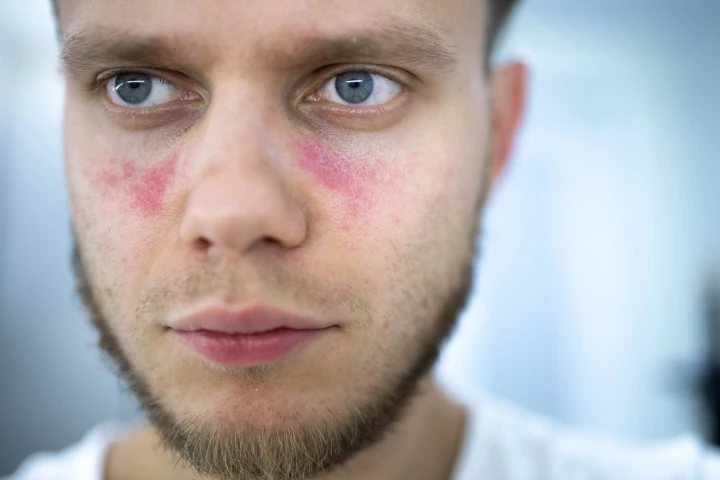
In two separate studies, researchers have identified the mutation that can lead to the autoimmune disease lupus. The discovery opens the door to new therapeutic approaches and testing for the mutation, which would ensure early disease diagnosis.
-
Scientists have developed a synthetic pathway that can capture CO2 from the air more efficiently than in nature, and shown how to implement it into living bacteria. The technique could help make biofuels and other products in a sustainable way.
Load More