MIT
-
After an analysis of data from over 131,000 people, researchers found that drinking coffee and tea daily seems to guard against the development of Alzheimer's disease and other forms of cognitive decline - caffeine may be the key protective compound.
-
Don’t remember if you took your pills? Try MIT’s SAFARI (Smart Adherence via FARaday cage And Resorbable Ingestible). The capsule has its own bioresorbable radio that activates itself when swallowed, so you’ll never worry about missing a dosage.
-
A new method converts user-selected 3D structures into string-pulled pop-up structures of connected tiles. Ideal for rapid creation and deployment in disaster zones, these pop-ups can also “pop-down” for re-use and easy transport.
-
A new MIT method eliminates the need for hour-long infusions of antibodies for immunocompromised patients. With highly concentrated particles of antibodies created without a centrifuge, mass-manufacturing of better single-shot antibodies is here.
-
The tons of discarded mussel shells generated by the seafood industry may be organic, but they're still very slow to biodegrade in landfills. They may soon find new life, however, sandblasting jeans in the textile industry.
-
Although they're constantly improving, robots aren't necessarily known for their gentle touch. A new robotic system from MIT and Stanford takes a unique stab at changing that, with a robot that uses vine-like tendrils to do its lifting.
-
A startup founded by MIT alumni wants robots to do some heavy lifting, literally. Pickle Robot Company's systems feature AI smarts and single-armed machines to quickly unload shipping containers filled with cases weighing up to 50 lb each.
-
Researchers at MIT have developed blood glucose sensing tech that uses near-infrared light to scan tissue in your skin and accurately measure blood sugar – no needles necessary.
-
MIT researchers have found a way to use the mechanical vibrations of sound waves to shake water molecules free from a storage medium. The breakthrough significantly speeds up the process of harvesting drinking water from thin air.
-
Researchers at MIT have just developed a new lipid nanoparticle that super-enhances the effectiveness of the mRNA vaccine in mice to a hundred times its stand-alone effectiveness, reducing required dosages while also reducing toxicity in the liver.
-
Researchers at MIT have created a revolutionary platform to treat a vast array of neurological diseases and mental illnesses. It could not only prove more effective than traditional methods, but also negate the need for invasive brain surgery.
-
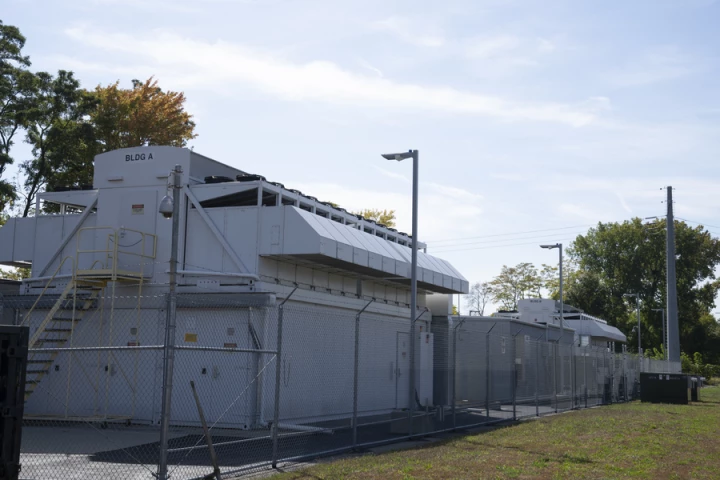
At MIT, a new kind of AI model has come online. A supercomputer capable of two AI-exaflops, fuses more than six hundred GPUs into a single pulse of intelligence. It promises to accelerate breakthroughs in medicine, climate modeling, and beyond.
Load More