molecular biology
-
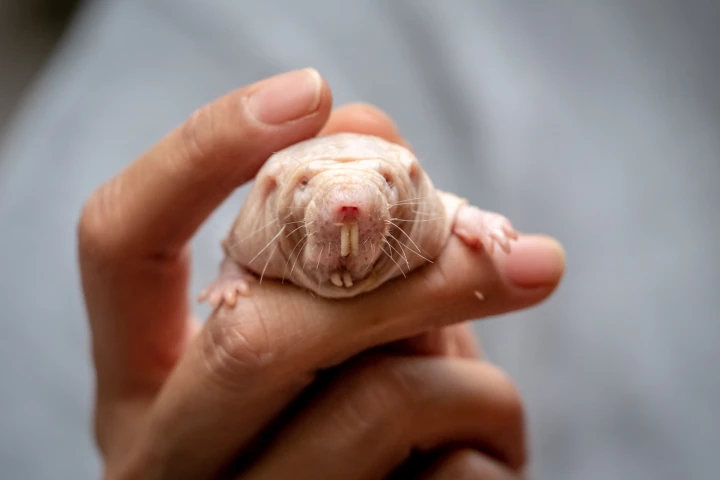
What naked mole-rats lack in the looks department they make up for it in longevity, living healthily for nearly four decades. Now, scientists have found just how they repair their DNA – and it has the potential to be harnessed by humans to do the same.
-
Scientists have taken the most detailed look yet at the biology of a record-breaking woman who lived 117 years and 168 days free of cancer, cardiovascular disease and dementia. And many things they discovered could help us achieve our own longevity.
-
Got asthma? Then you might also go on to get Parkinson's. Celiac? You'll want to watch out for lung cancer. That's the kind of information you can get on a new website that uncovers the links between common conditions based on genetic analysis.
-
Even without noses, octopuses are able to determine which food sources are good to eat and which have gone past their prime simply by touching them. The secret, says a new study, lies with surface microbiomes and some very sensitive suckers.
-
The first-ever "biological computer" powered by human cells, which form an ever-learning neural network, has been launched. It's an entirely new kind of AI – Synthethic Biological Intelligence – and not even its creators can predict its full potential.
-
Built to be carnivorous, giant pandas spend up to 16 hours a day on their backsides eating bamboo. But contrary to all the panda jokes, it's not because they're lazy or too dumb to know better. It's far more fascinating – and it may help humans, too.
-
Common ivy is better known as a garden invader or a rather attractive indoor plant that's prone to triggering allergies. Now, for the first time, it's been found to be very effective in blocking pain signals – by instead invading a key pain receptor.
-
A peptide hormone produced in the brain that triggers physiological changes in reproduction has been 'hacked' to create an effective, safe and non-invasive way to treat chronic gut pain. Scientists are calling it an entirely new class of painkiller.
-
Insect venom may seem like an unlikely ally in the discovery of new human pain treatments, but the latest findings into the "unique" way a small ant causes us such agony is a big leap forward – and one that's expected to progress rapidly.
-
We’ve all spent time and effort on pointless tasks so we look busy when the boss walks past. But now scientists have discovered a new type of fat cell in the body that does the same thing, burning energy and producing heat with pointless busywork.
-
Instead of focusing on fighting the plaques linked to Alzheimer's, researchers took a look at boosting electrical oscillations in the brain. The molecule they invented got the job done in mice, offering hope for a new treatment path for humans.
-
The world's first human trial of a drug that can regenerate teeth will begin in a few months, less than a year on from news of its success in animals. This paves the way for the medicine to be commercially available as early as 2030.
Load More