Neural Network
-
For the first time, Cortical Labs' mini-brain system has shown how its breakthrough biological computer system can, in response to drug intervention, alter activity and improve performance. It's a huge milestone for synthetic biological intelligence.
-
Unlike current translation devices that focus on one speaker, researchers have just developed a pair of headphones that can determine how many people are speaking, follow them through space, and translate each person's words as a separate stream.
-
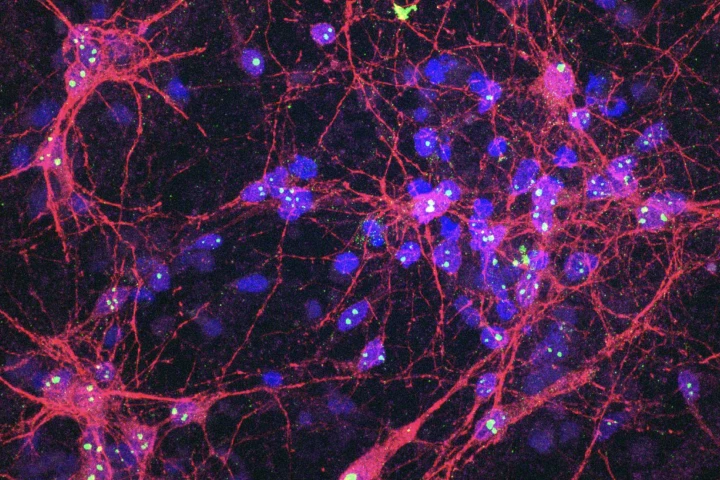
The first-ever "biological computer" powered by human cells, which form an ever-learning neural network, has been launched. It's an entirely new kind of AI – Synthethic Biological Intelligence – and not even its creators can predict its full potential.
-
Every day new articles about "revolutionary breakthrough!" in AI hit my screen. The latest headline was "Torque Clustering" and "autonomous AI is on the horizon." But is it really? I did a deep dive with simple analogies to figure it out.
-
Binge-drinking in early adult years fundamentally changes how brain neurons communicate, in what scientists equate to a faulty gas pedal in a car that needs more pressure applied to "go." This type of dysfunction is also seen in Alzheimer's disease.
-
Ever been caught in the crossfire of a wet dog firing droplets of water away from their fur with a mad shake? Well, they can't help it. Scientists have identified the innate sense-motor function mechanism that drives dogs to twist and spout.
-
Fascinating new findings uncover how clusters of 'brain stars' retain our learnings – and it changes what we previously understood about how memories are held and retrieved in our minds. The medical implications of this are vast.
-
Whether we've watched athletes do it or experienced it ourselves, 'choking' in a high-stakes moment comes down to more than composure. For the first time, scientists have uncovered a set of neurons that fail to do their job when the payoff is greatest.
-
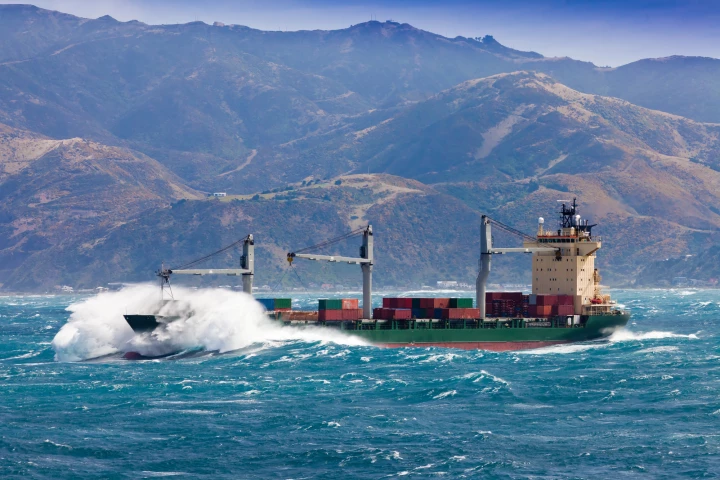
Unpredictable monster waves at sea can severely damage ships and offshore platforms, putting the lives of those who work on them at risk. A new system out of the University of Maryland uses a neural network to provide valuable early-warning alerts.
-
Sleep studies provide a lot of important information but aren’t very patient-friendly. So, researchers redesigned the process, eliminating the multitudes of wires normally used while producing results that are on par with the current gold-standard method.
-
Instead of equipping its sharp-looking GR-1 general purpose humanoid with a full next-gen sensor suite including such things as radar and LiDAR, Fourier Intelligence's engineers have gone vision-only.
-
Based on fractal patterns in neurons, researchers believe our brains exist at or near a state called criticality where they're extremely close to shifting from one state of matter to another. They also admit they don't know what either state is.
Load More