North Carolina State University
-
Cable cars are handy for transporting cargo up mountain slopes, but what if you want to do the same sort of thing on a smaller scale? Well, you could try using a tiny new light-powered robot, which is cable of carrying items up thin mid-air tracks.
-
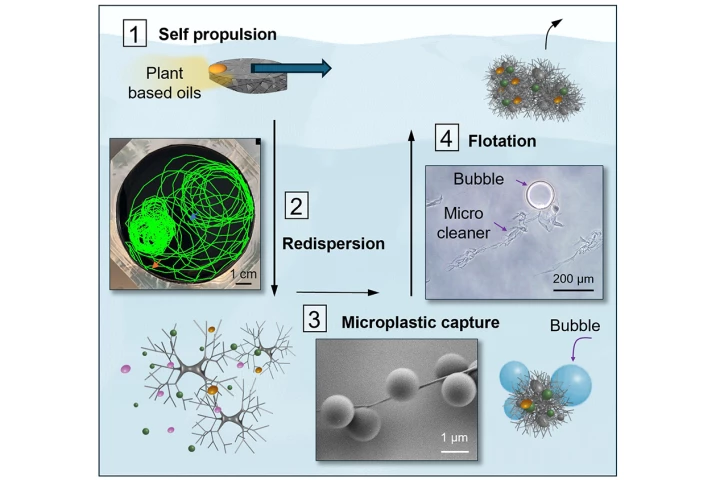
Wouldn't it be great if there were a way of chasing down waterborne microplastic particles and catching them for removal, as opposed to just passively filtering them out of water bodies? Well, new "microcleaners" can reportedly do that very thing.
-
Scientists at North Carolina State University have created a magnetic “metasheet” that can move objects and liquids around without needing robot arms or grippers.
-
It was just two years ago that a tiny robotic manta ray became the world's fastest-swimming soft-bodied robot. Well, one of its descendants has now smashed that record – and it uses less energy than its predecessor, to boot.
-
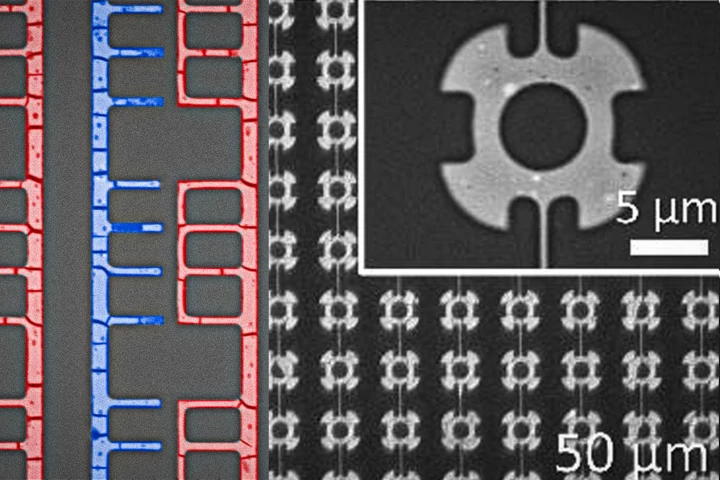
A remarkable proof-of-concept project has successfully manufactured nanoscale diodes and transistors using a fast, cheap new production technique in which liquid metal is directed to self-assemble into precise 3D structures.
-
Despite what you might say when drunk, you’re not the best backflipper in the world. That honor belongs to a tiny little bug called a globular springtail, whose superfast backflips have now been caught on slow-motion camera for the first time.
-
A full DNA computer is a step closer, thanks to a new technology that could store petabytes of data in DNA for thousands or even millions of years. The system can also process data, as demonstrated by solving sudoku puzzles.
-
For some time now, scientists have known that electrical stimulation speeds the healing of chronic wounds. A thin, flexible, inexpensive new bandage delivers that healing current right to the wound site, and it's activated simply by adding water.
-
Gels and glasses are on opposite ends of the material spectrum, but engineers at North Carolina State University (NCSU) have developed a new class called “glassy gels” that are both strong and flexible, as well as sticky and self-healing.
-
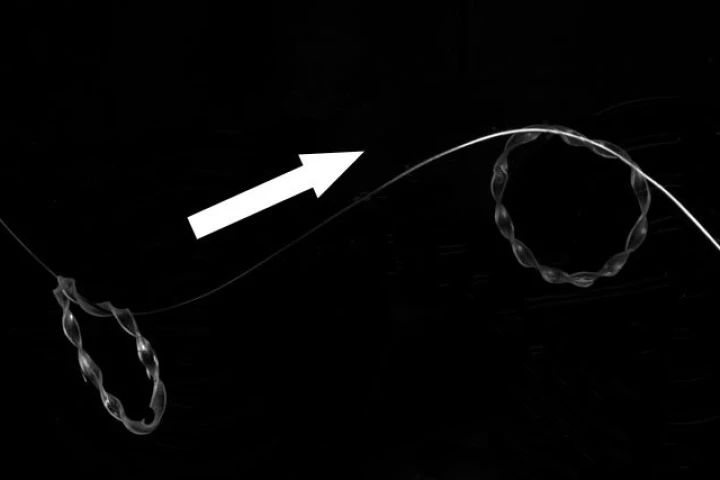
If a soft-bodied robot uses rigid actuators to move its body, then it isn't really soft now, is it? An experimental new caterpillar-inspired bot gets around that conundrum by using soft, collapsible origami segments to squirm and steer its way into our hearts.
-
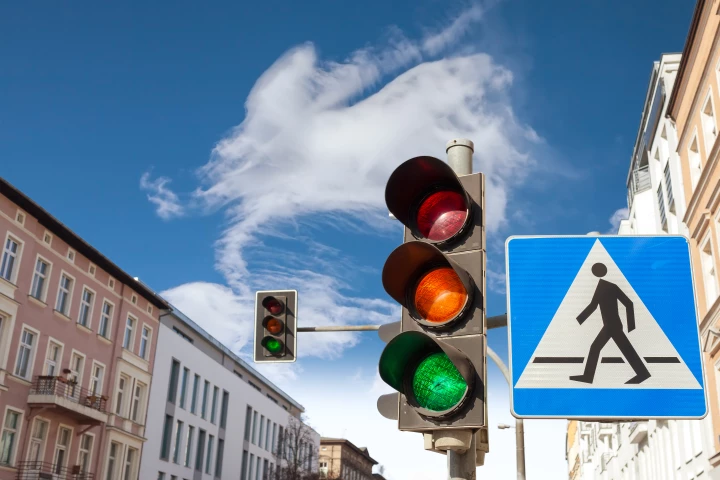
If you're comfortable with the present green, amber, and red traffic lights, be prepared to get uncomfortable. New research suggests that adding a white light will speed up traffic and improve safety for both cars and pedestrians.
-
Composite metal foams (CMFs) offer big advantages over traditional solid metal. And while the welding of CMFs usually poses some challenges, it has now been been discovered that the use of an alternative type of welding works like a charm.
Load More