Pain
-
A tool long used to probe neural circuits in the lab is now being floated as a new way to treat human patients. The technique uses light to turn specific neurons on or off, and it could be used to treat everything from chronic pain to epilepsy.
-
In a major brain science breakthrough, researchers discovered a nerve signaling mechanism that takes place outside the cell, flipping on a 'pain switch.' This could shed light on a path to safer pain medication without the usual side effects.
-
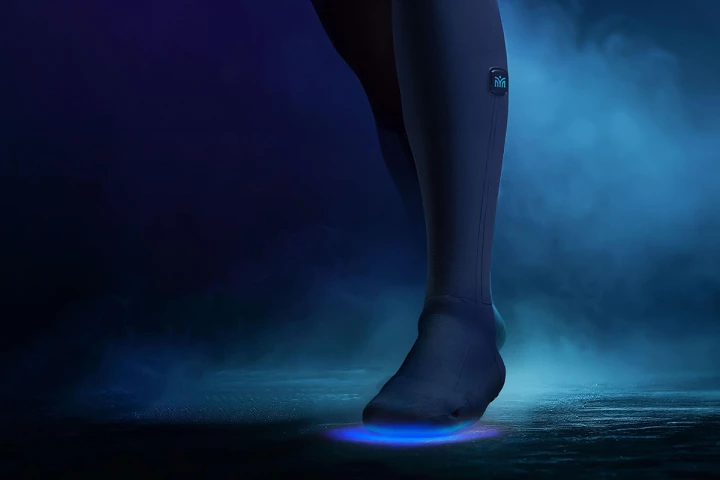
Researchers in Switzerland have stuffed a bunch of chips and sensors into socks to help people who suffer from some of the worst symptoms of diabetes – chronic pain and a loss of sensation in the feet that make it hard to walk.
-
Pain is hard to measure. One person’s “ouch” is another’s agony. Now, scientists say they’ve found a better way to assess pain: putting a price on it. By translating pain into dollars, they’ve created a more accurate, comparable way to measure suffering.
-
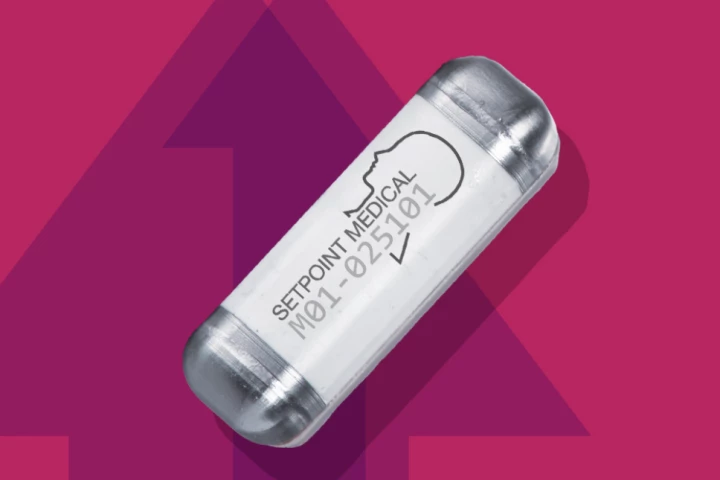
The first-ever neuroimmune modulation implant has been approved for people with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis. It's a potentially life-changing technology that zaps chronic pain with daily one-minute electrical pulses to the vagus nerve.
-
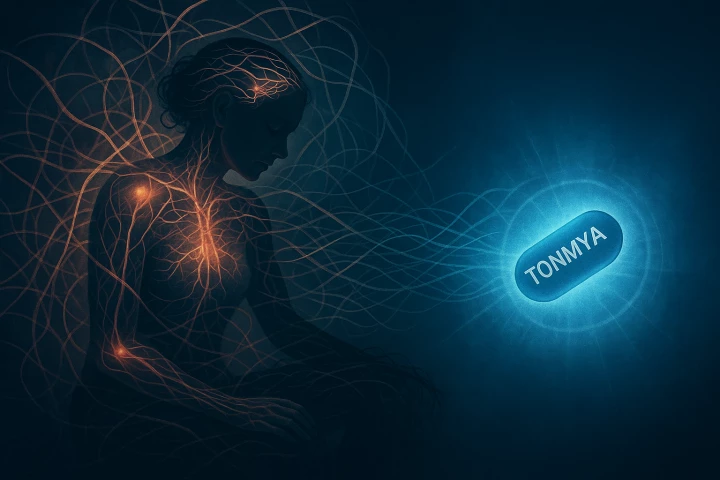
People with fibromyalgia will soon have access to a new drug that treats the chronic pain condition's most elusive trigger: Poor sleep. Tonmya, a non-opioid under-the-tongue tablet, is the first FDA-approved drug for fibromyalgia in more than 15 years.
-
Scientists have developed a non-opioid oral painkiller known as ADRIANA, the world's first α2B-adrenoceptor antagonist – which hasn't been targeted for analgesics before. It's provided powerful pain relief without sedation or risk of addiction.
-
We've long known how the nerve endings in our skin detect cold and swiftly relay the information to our brains, but we haven't understood exactly how it works. Scientists have now solved the puzzle, unlocking the mystery of this temperature pathway.
-
Scientists have discovered a brain circuit that gives pain its emotional sting, explaining why some hurts linger as suffering. The breakthrough challenges our beliefs about how we process pain and may transform chronic pain treatments.
-
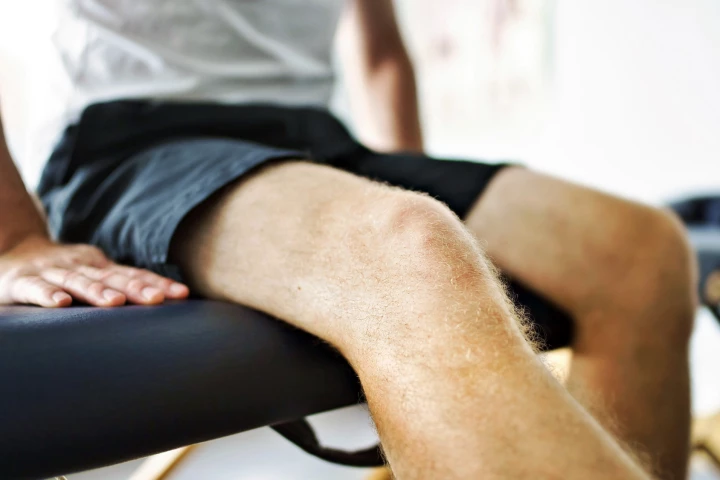
Researchers have analyzed clinical trial data and ranked 12 different non-drug physical therapy treatments for knee osteoarthritis, based on their effectiveness in reducing pain and stiffness, and improving physical function.
-
Diagnosing celiac disease often means exposure to the thing that makes you sick, which can be debilitating. It may soon be simpler and pain-free, with a first-of-a-kind test that can detect and gauge the severity of the disease in a test tube instead.
-
In the ongoing search to find an intervention that does away with opioids, a new game-based system has shown huge promise in tackling chronic neuropathic pain. Using a game and a headset, it "trains" patients to rewire brain signals to relieve pain.
Load More