Plastic
-
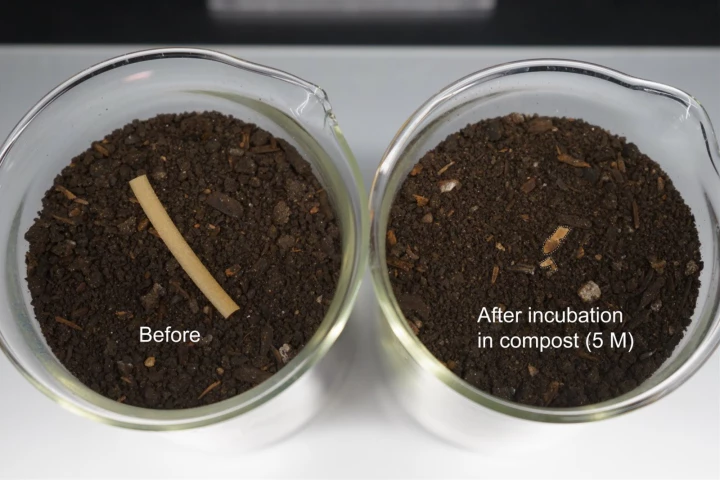
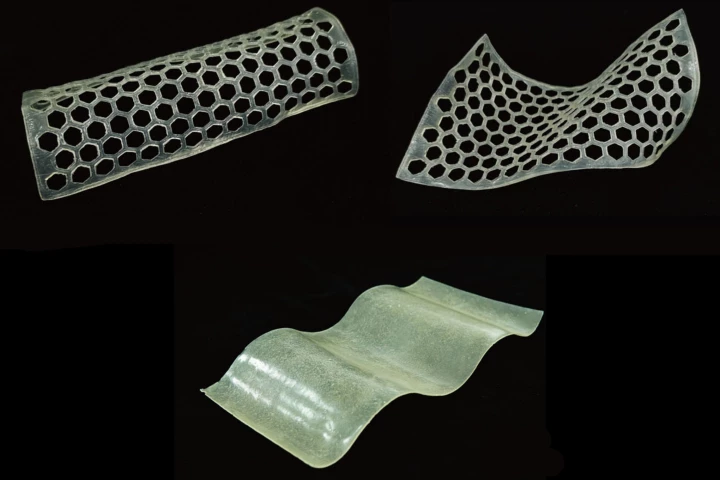
Researchers in China have devised a new method for producing bamboo-based plastic which results in a strong material that can compete with traditional plastics, be flexibly shaped as needed, and can also degrade in soil in less than two months.
-
Scientists in China have devised a way to capture carbon dioxide stored in seawater, and convert it into biodegradable plastic precursors. This approach could reduce the acidification effect of CO2 emissions in marine ecosystems, with an added bonus.
-
We know microplastic particles are in the soil our food grows from but is it infiltrating our food chain, or just stirring up trouble at the roots? For the first time scientists have demonstrated how plastic could move from soil to food while it grows.
-
A new study analyzed beverages like water, soda, wine, and beer to find out how many microplastic particles were in each. The results were a surprise, with a container commonly thought to be safe actually found to carry the highest volume of particles.
-
Researchers in Switzerland have developed a new film-like material that incorporates living cells from fungi, so it's biodegradable and can help break down waste too. Oh, and you can eat it, if you're curious like that.
-
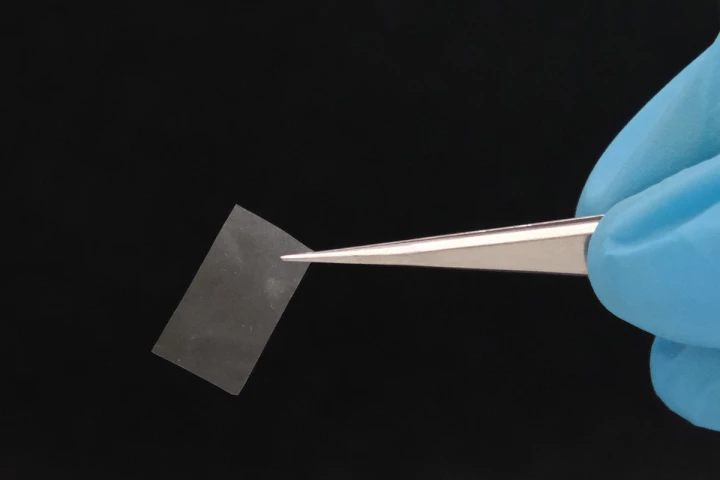
Scientists at RIKEN in Japan have developed a new type of plastic that’s just as stable in everyday use as regular plastic, but dissolves quickly in saltwater, leaving behind only safe compounds.
-
By now, you've no doubt heard that modern living is filling our bodies with microplastics. But an alarming study now shows just how much of the non-degradable particles are in our brains, and how much higher they are in dementia patients.
-
If you've ever had a packing peanut stick to your clothes as you unbox your Amazon delivery, then you know that Styrofoam is pretty good at generating static electricity. A new invention turns that quality into a workable energy-saving solution.
-
A new biodegradable plastic embedded with spores of plastic-eating bacteria manages to break down 90% of the material after five months in landfill. Weirdly, this actually made the plastic tougher and stronger during use.
-
Even when it’s ground into microparticles, 97% of an algae-based plastic biodegrades in compost and water in under seven months, a new study has reported. The researchers hope their plastic will eventually replace existing petroleum-based ones.
-
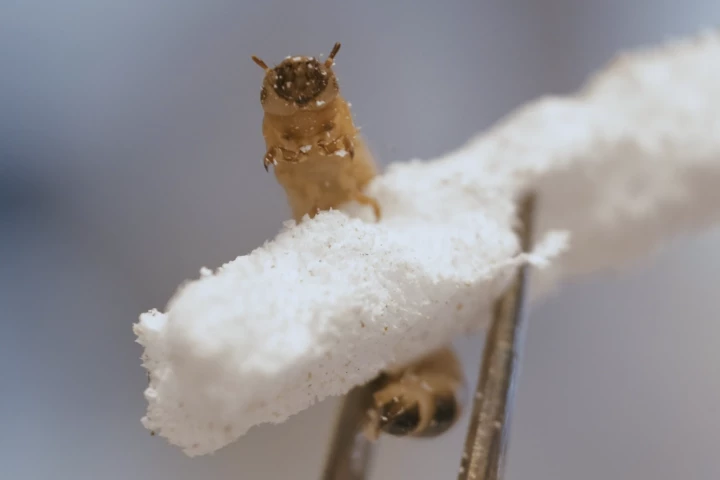
Scientists have created a lab-grown microbiome like the one found in a tiny plastics-munching worm, and it has the potential to efficiently and sustainably biodegrade the world's most common and troublesome plastics – all without the need for the worms.
-
Exposure to phthalates, a commonly used chemical in plastics, has been estimated to be the primary cause of one in 10 preterm births, according to a new study led by researchers from the New York University Grossman School of Medicine.
Load More