University of Arizona
-
People with severe chronic pain were far more likely to have elevated levels of eosinophils, a type of white blood cell, a new study found, hinting at an immune link to pain – but the rise in these cells didn’t make treatments any less effective.
-
Wearing face masks and maintaining social distances were a significant part of the world's reaction to the COVID-19 pandemic. Now, new research says the practices are not only effective at saving human lives, but chimp lives as well.
-
Looking for life on Saturn's largest moon Titan may be trickier than first thought. New computer simulations suggest that if life exists, there may not be a lot of it about. In fact, the mass probably wouldn't amount to much of anything at all.
-
Asteroid Bennu seems to have come from a long-lost world on the fringes of the solar system, where saltwater pooled and dried over thousands of years and life’s basic ingredients were widespread.
-
The subatomic world is hard to image not just because it’s incredibly tiny, but super fast too. Now University of Arizona physicists have developed the world’s fastest electron microscope to capture events lasting just one quintillionth of a second.
-
Not all fiber is created equal, and one particular type – which is most highly concentrated in common breakfast oats – may trigger the same beneficial metabolic functions that GLP-1 agonists like Ozempic do, without the price tag or side-effects.
-
Many asteroids can be traced back to their parent body – the planet or moon they broke off from. But for the first time, scientists now claim to have traced the origins of an asteroid back to the specific crater it was birthed from.
-
What did your area look like 1,000 years ago? Well, people in the year 3023 might have the luxury of finding out, thanks to an art/science project called the Millennium Camera, which will take an extremely long-exposure photo of the Arizona desert.
-
The mystery of what created a pair of craters on the far side of the Moon has been put to rest after a new study from the University of Arizona confirmed that the most likely cause was a spent rocket booster from China's Chang'e 5-T1 lunar mission.
-
Phosphorus – a key ingredient for life as we know it – was thought to be relatively rare in space. But now, astronomers have detected a surprising amount of the stuff on the fringes of the galaxy, suggesting life may be more common in the cosmos.
-
A new study has found that remembering an event drives the production of memory-related brain waves more than engaging in the event does. The finding could improve the treatment of memory loss in people with brain damage or cognitive impairments.
-
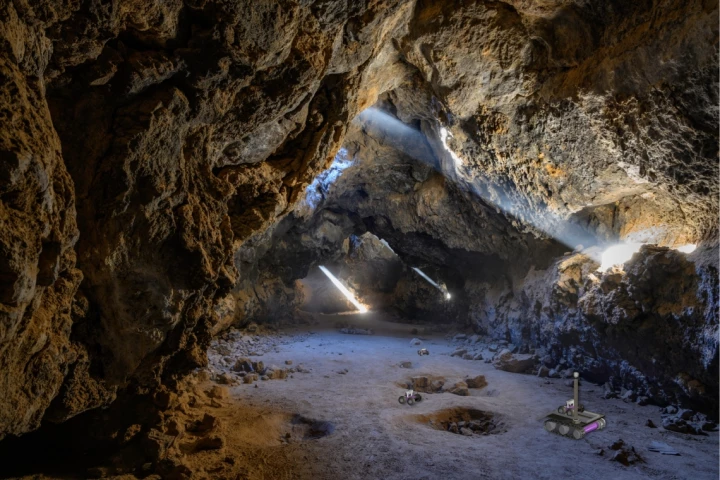
Exploring an unmapped cave system is a daunting enough prospect on its own, but think how risky it would be to do so on another planet such as Mars. That's why a new system is in the works, which would use "breadcrumb"-dropping rovers to do the job.
Load More