University of Arizona
-
Ordinarily, pacemakers correct irregular heartbeats by delivering an electric shock to the entire heart – which can be painful. An experimental new one takes a different approach, and it does so by encompassing the heart with light-emitting "petals."
-
Humans might not be the first lifeforms to face self-induced climate change. A new model suggests Mars was once habitable enough to support microbes, and they may have wiped themselves out by causing irreparable damage to the Red Planet’s atmosphere.
-
Scientists have discovered a new crater in the seabed of the North Atlantic Ocean that seems to date to the end of the Cretaceous period. That suggests the extinction event that killed off the dinosaurs could have been triggered by multiple impacts.
-
Astronomers have discovered bizarre “blue blobs” in space. These blobs are clusters of young, blue stars that are isolated from any parent galaxy, suggesting they formed from a galactic “belly flop.”
-
A history-making NASA spacecraft has just received a new lease on life. OSIRIS-REx, which is currently on its way back to Earth with rock samples from asteroid Bennu, will now have its mission extended to visit another asteroid, Apophis.
-
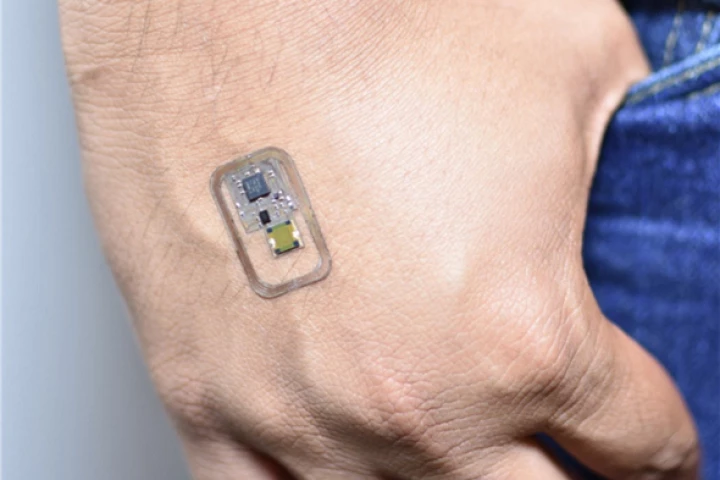
Nicotine is one of the more harmful compounds in electronic cigarette vapor, so non-vapers should avoid breathing it in whenever possible. A new skin-worn sensor could help, by monitoring airborne nicotine levels in the wearer's immediate vicinity.
-
Researchers have developed an ultra-thin device that permanently bonds to bones and beams data out wirelessly. The breakthrough could allow doctors to monitor the health of a patient’s bones over time, or how well they’re healing after an injury.
-
A curious space rock has just gotten curiouser. The asteroid Kamo`oalewa has an odd orbit that makes it almost a mini-moon of Earth – and now it may really earn that title, as new observations show that it could in fact be a fragment of the Moon.
-
A landmark study is reporting the discovery of nearly 500 ancient monuments in Mexico using airborne laser mapping. The newly discovered sites are thought to date back at least 2,500 years, in between the Olmec and Maya civilizations.
-
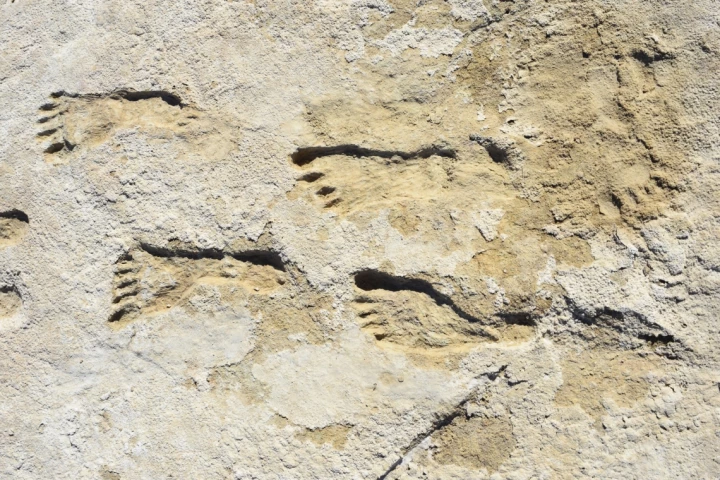
Exactly when humans first set foot in North America remains a mystery, but archeologists have now uncovered the oldest unambiguous evidence. Human footprints have been found at White Sands National Park in New Mexico, dated to about 22,000 years ago.
-
A new study is presenting archeological evidence of the oldest known bone tools used for making clothes. The tools, found in a cave in Morocco, suggest humans were skinning animals for fur to wear as clothes up to 120,000 years ago.
-
New research is offering some of the first empirical evidence of the fatiguing effects of camera use in virtual meetings. The research is part of an increasing body of study into the effects of remote work and the phenomenon known as "Zoom Fatigue."
Load More