University of Cambridge
-
Valvular heart disease (VHD) is a potentially fatal condition, yet it's hard to diagnose with a regular stethoscope. A possibly life-saving new stethoscope is claimed to be much better at the job, plus it can be used by just about anyone.
-
Scientists have created a new type of display with the smallest pixels and highest pixel density ever. Individual pixels were shrunk to 90 nanometers – about the size of a virus – and a record 127,000 of them were crammed into every inch of a display
-
Not many people fancy the idea of spending the night in a sleep clinic with multiple electrodes stuck to their skin. That's why scientists have developed a smart pajama top that assesses sleep disorders while its wearer comfortably slumbers at home.
-
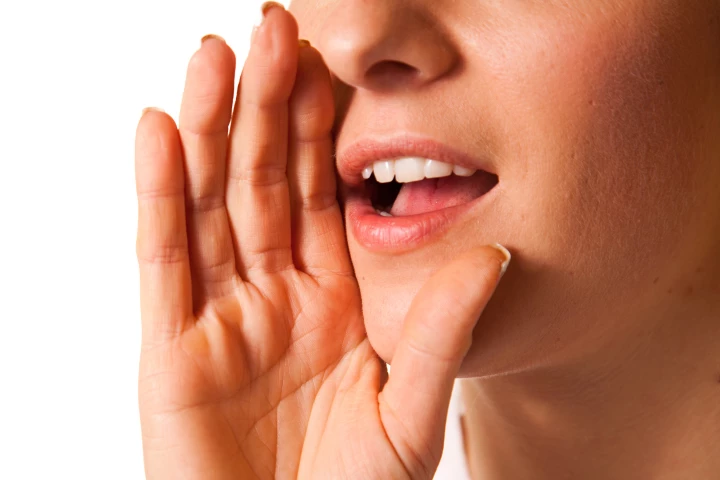
There could soon be a powerful new aid for people who are unable to speak. British scientists have developed a choker that detects its wearer's silently mouthed words, and converts them into audible synthetic speech.
-
Researchers have discovered a fascinating new link between the gut and the brain: swallowing nutritious food causes the release of the feel-good chemical serotonin. The findings open the door to developing new treatments for eating disorders.
-
New research found that even an old mild concussion can have long-lasting effects in otherwise healthy people. The study adds to a growing understanding of traumatic brain injury and is relevant to the evolving legal landscape around brain injuries in sports.
-
A new study has overturned traditional thinking about regulatory T cells, which suppress the body’s inflammatory response, and has significant implications for treating a wide range of conditions, from repairing injured muscles to regrowing hair.
-
Having an extra thumb on one hand may boost your manual dexterity, but wouldn't it be hard to learn to use? Not according to a new study, which found that the majority of a wide variety of people got the hang of the thing in just one minute.
-
A new solution from Cambridge University could recycle both concrete and steel at the same time, by throwing old concrete into steel-recycling furnaces. If done using renewable energy, the process could make for completely carbon-zero cement.
-
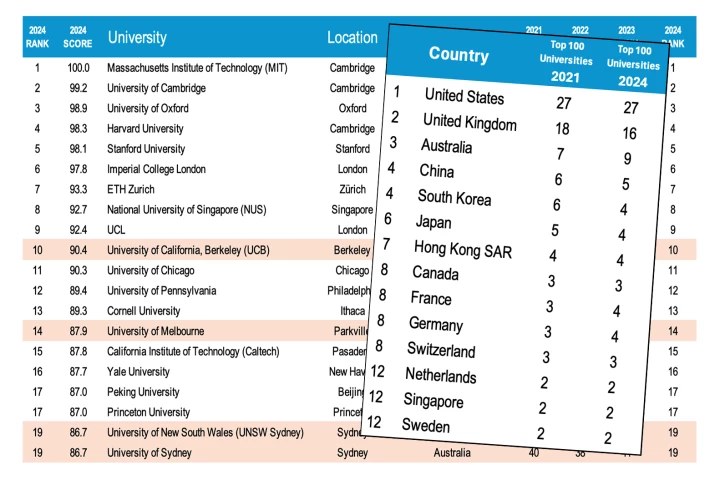
The 2024 QS World University Rankings were released this week, and with three new key metrics added to the scoring process, several universities have rocketed to the international forefront, while traditional icons are being pushed below the fold.
-
Scientists have uncovered the oldest fossilized forest, dating back 390 million years. The ancient forest was made up of the first trees to ever grow on Earth – bizarre “prototype” trees that had to rip their skeletons apart in order to grow.
-
Giving infliximab, an immunotherapy drug, as soon as possible after diagnosis with Crohn’s disease significantly reduced complications, including the need for urgent surgery by a factor of 10, a clinical study has found.
Load More