University of Massachusetts
-
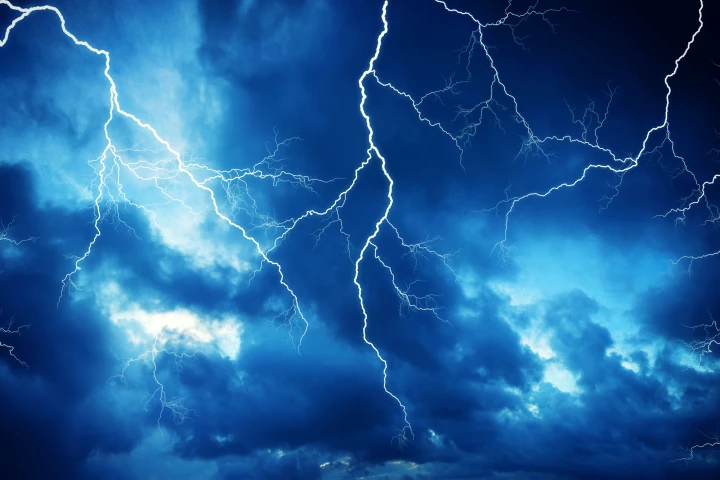
As anyone who's ever seen a bolt of lightning knows, the air around us can be filled with an astonishing amount of energy. A new study shows a way to harvest this power using a perforated nanofilm that can be made from a vast variety of materials.
-
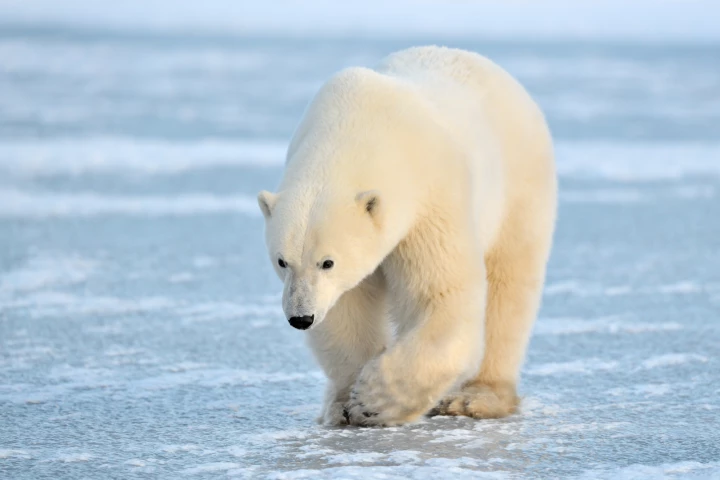
To develop a heat-trapping fabric, researchers looked to polar bears, who thrive in incredibly low temperatures. The secret, they found, has to do with a relationship between the bears' hollow translucent hair and the black skin that lies beneath.
-
Science is quickly catching up to the powerful sniffers on dogs with its own range of artificial noses. Case in point: researchers modified E. coli bacteria to spin electrically conductive nanowires capable of detecting disease-related odor molecules.
-
With new manufacturing techniques comes the opportunity for new metal alloys with a range of possible properties. A team of researchers has now developed a new 3D-printable alloy with a specific nanostructure that makes it ultra strong and ductile.
-
Wearable electronics could soon be powered by dead microbes. New research out of UMass Amherst has demonstrated a biofilm that generates electricity from sweat, harnessing the corpses of dead bacteria – and it's at least as effective as a battery.
-
Inspired by the way plants like Venus flytraps can snap closed and reset themselves, scientists have developed materials that alter their shape in the blink of the eye to propelling themselves forward using their own energy and their environment.
-
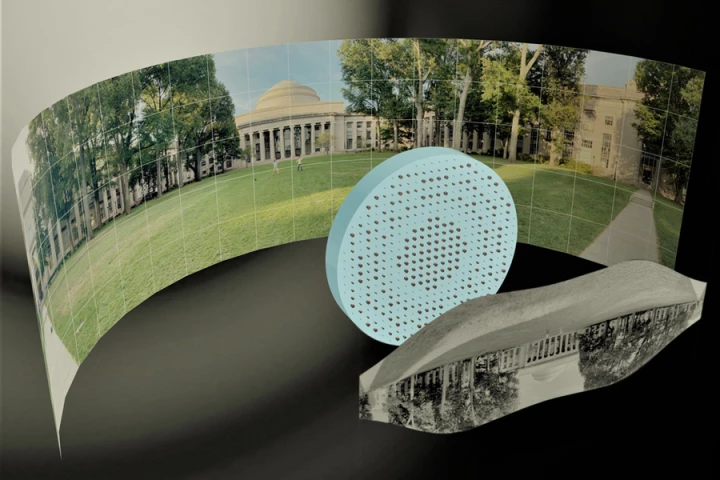
Ultra wide-angle fisheye lenses are typically thick, bulbous contraptions, that can't easily be incorporated into devices such as smartphones. That could be about to change, though, as engineers have now created one that's completely flat.
-
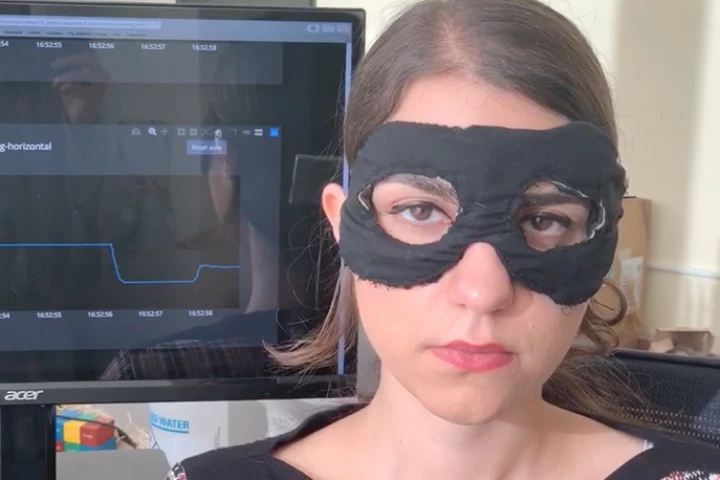
When tracking a sleeping person's eye movements, you typically have to stick hard-wired electrodes onto their face. Soon, however, an unobtrusive flexible mask could do the job – while also measuring their heart rate.
-
The US Army has put the call out for new homegrown uniforms that are not only fire retardant but also insect repellent, and a team has answered with a new material made by treating a commercially available nylon-cotton blend with non-toxic chemicals.
-
New research from the University of Massachusetts Amherst is adding weight to a growing body of evidence suggesting the food additive titanium dioxide, also known as E171, can disrupt the gut microbiome, leading to colonic inflammation.
-
That tiny plastic fragment exists in soil is perhaps not so surprising, but researchers have now conducted one of the first studies on what this means for plant life, finding that it can reduce the total biomass of the finished product.
-
Introduced species are generally seen as a negative for the ecological destruction they cause to native habitats, but could there be a silver lining in some cases? A new study suggest that in fact there could be.
Load More