University of New South Wales
-
You may be sitting on – so to speak – a very valuable asset that scientists would love to get their hands on: your poop. As well as blood, plasma and organs, you can now donate fecal samples to stool banks for research and use in transplants.
-
For decades, scientists have suspected that the voices heard by people with schizophrenia might be their own inner speech gone awry. Now, researchers have found brainwave evidence showing exactly how this self-monitoring glitch occurs.
-
New research challenges fears about stopping long-term prescription opioid use, uncovering no associated rise in suicide risk and a sharp drop in overdose death. The findings offer reassurance for clinicians and patients managing chronic pain.
-
A one-week, clinician-supported online therapy program significantly reduced anxiety and improved daily functioning for adults with social anxiety disorder, according to a new study. It’s a promising step toward more flexible, accessible treatments.
-
Time availability can impact the development of dementia perhaps as much as diet and exercise, according to a panel of scientists. The group says its research should cause a paradigm shift in the diagnosis and treatment of the condition.
-
A headline-grabbing study on apple cider vinegar has been pulled from the record, striking a blow to the science and wellness worlds. The research, which claimed that the tonic triggered massive weight loss, was found to be riddled with errors.
-
Doctors may no longer need trial-and-error when prescribing blood pressure drugs. A huge new study has mapped exactly how much each medication, alone or in combos, lowers blood pressure, and offers doctors an online tool to guide treatment.
-
Scientists have identified a protein that acts as a kind of traffic cop for fat inside cells, revealing a mechanism that could help explain how the body regulates energy storage. The discovery provides a new avenue for tackling obesity and diabetes
-
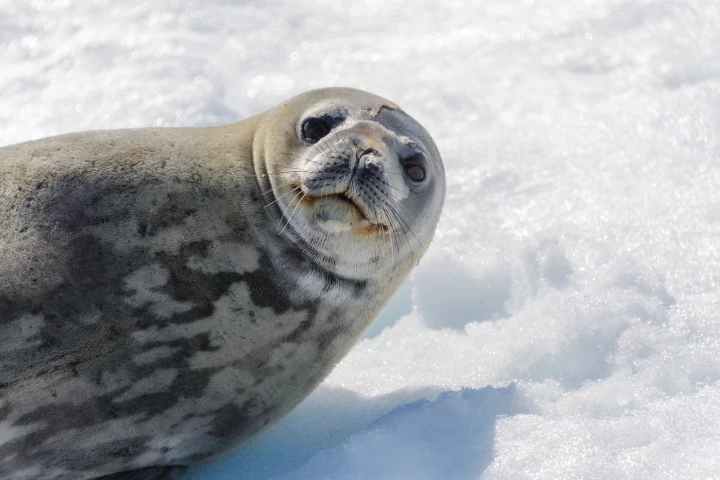
Leopard seals may be one of Antarctica’s most fearsome predators, but these vocalizers sing with the structured charm of a nursery rhyme. In a new study, researchers discovered that the underwater vocal patterns of these mammals resemble human song.
-
Why do some people keep making the same harmful choices, even when they know better? A global study has revealed three distinct decision-making types and why punishment doesn’t work for everyone.
-
To find the right mix of metals for their green ammonia catalyst, scientists turned to AI. The result was a breakthrough that makes their technique of producing ammonia from air and water more efficient and much more accessible.
-
In the ongoing search to find an intervention that does away with opioids, a new game-based system has shown huge promise in tackling chronic neuropathic pain. Using a game and a headset, it "trains" patients to rewire brain signals to relieve pain.
Load More