University of Queensland
-
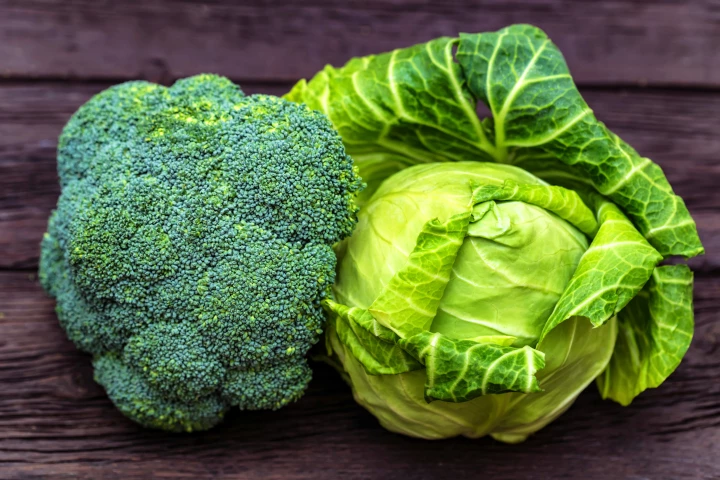
If you have an aversion to the bitterness of foods like cabbage or broccoli, you might be a "super-taster," carrying a specific genetic code that dials up taste sensitivity. It may also put you at higher risk of kidney disease and bipolar disorder.
-
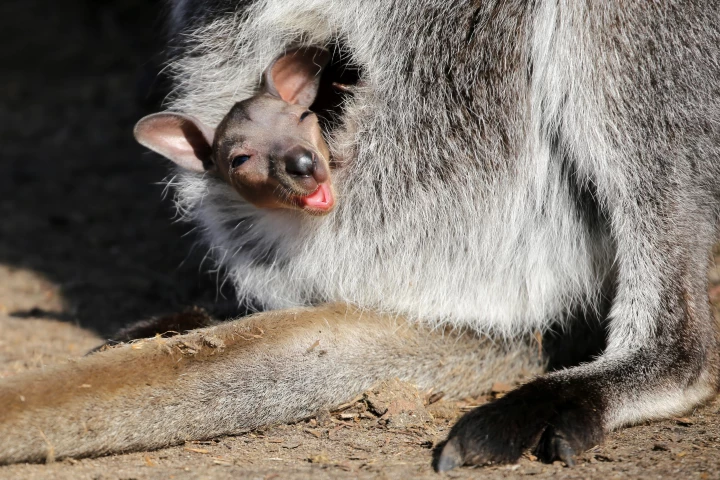
Scientists have created the first kangaroo embryo by in-vitro fertilization, which is a landmark moment for pouch-toting marsupials. Years in the making, it's a massive step in future-proofing hundreds of species facing imminent extinction.
-
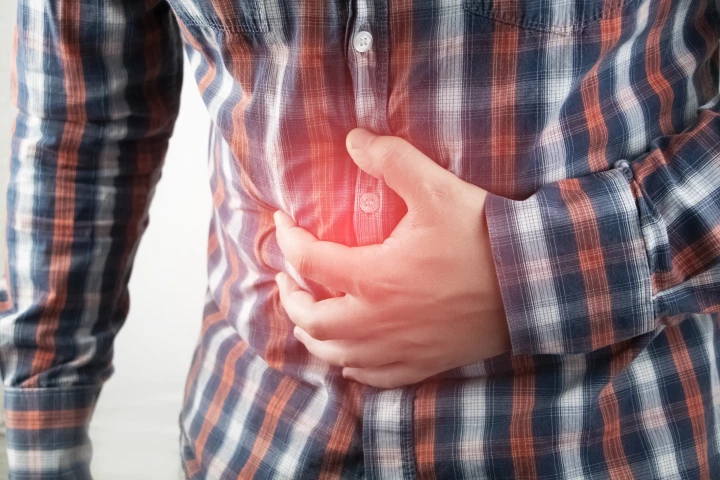
A peptide hormone produced in the brain that triggers physiological changes in reproduction has been 'hacked' to create an effective, safe and non-invasive way to treat chronic gut pain. Scientists are calling it an entirely new class of painkiller.
-
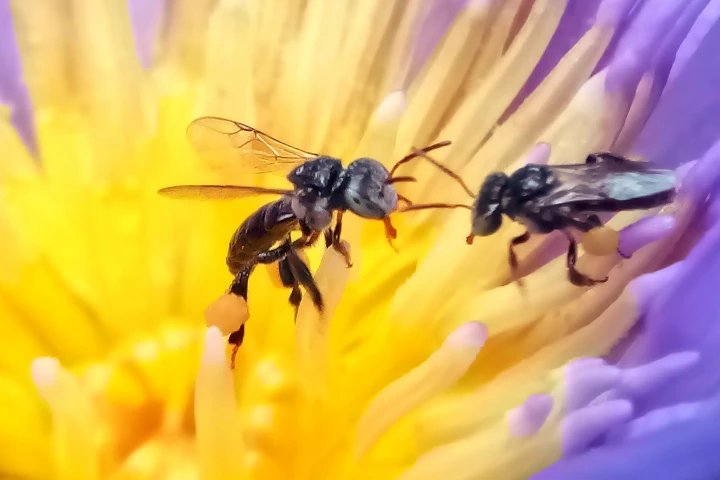
Honey from stingless bees contains large amounts of a unique sugar that’s not a major component of any other food, according to researchers. It has a range of health benefits, from preventing tooth decay and helping with weight loss to managing type 2 diabetes.
-
Insect venom may seem like an unlikely ally in the discovery of new human pain treatments, but the latest findings into the "unique" way a small ant causes us such agony is a big leap forward – and one that's expected to progress rapidly.
-
Geologists have drilled deeper than ever into material from the Earth’s mantle – more than three quarters of a mile. The sample gives a glimpse into the geology and even life in a deep world normally beyond our reach.
-
A fresh cup of coffee in the morning can be vital for facing the day ahead, but what if you had to wait a day to get your caffeine hit? That's on the menu if you like your Joe brewed cold, but researchers have used ultrasound to cold brew in minutes.
-
Examining long-term outcomes for people with atrial fibrillation, the most common heart rhythm disorder, a new study found that 55% survived to 10 years. The researchers say it needs to be treated as a chronic illness with serious long-term consequences.
-
The six-foot-tall raptors in the Jurassic Park movies were terrifying enough, but now scientists have described a giant new raptor species whose legs alone were that tall.
-
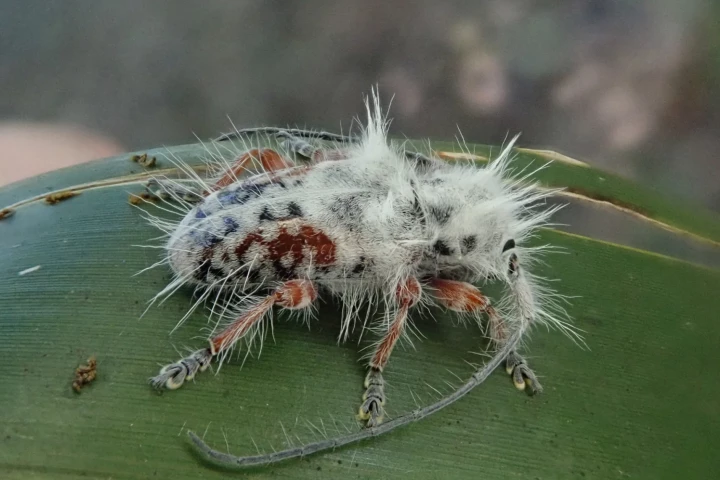
Would you want to eat this beetle? Probably not, as it appears to be covered in fungus. That "fungus" is actually hair, however, which the recently discovered insect may use to put off would-be predators.
-
A new type of storm-resistant fish farm could make aquaculture operations more eco-friendly. The submersible structure is designed to stay in the deep waters of the open ocean, where it should have less environmental impact than shore-adjacent pens.
-
Zinc has been found to be important in reducing lung infections in people with cystic fibrosis, whose immune cells' natural bacteria-fighting ability has been reduced by the genetic mutation that causes the disease.
Load More