University of Waterloo
-
A simple haircut may reveal more than just split ends. By testing for the stress hormone cortisol, which is stored in hair, researchers can identify kids with chronic illness who face the greatest risk of anxiety, depression, or behavioral struggles.
-
Across cultures and continents, most people prefer to tackle life’s toughest choices alone, trusting their own gut or inner voice over the counsel of friends or the wisdom of the crowd, according to a new study.
-
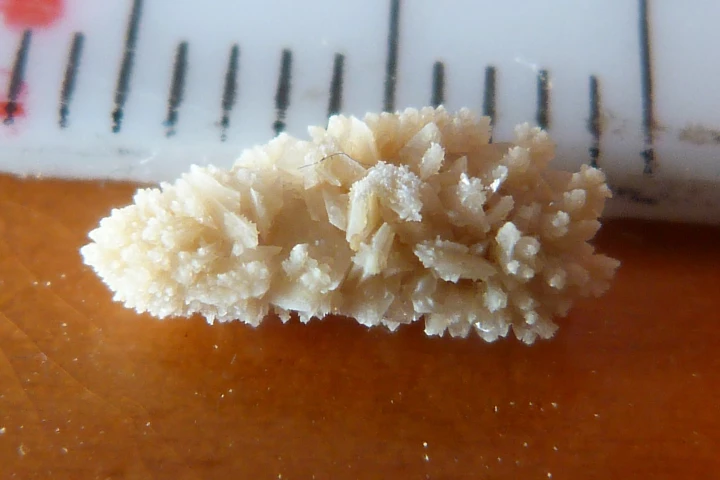
Recurring kidney stones can be an agonizing, debilitating problem, particularly if they can't be treated by orally-administered medication. There may be new hope on the horizon, in the form of a tiny magnetically-steerable stone-dissolving "robot."
-
A new study has found that for older adults receiving in-home care, loneliness doesn’t increase the risk of death. The findings contradict much of the existing research into the link between loneliness and health.
-
Urine doesn't belong on the floor, and it definitely doesn't belong on our clothes. An experimental new urinal design could help keep it from getting to those locations, by virtually eliminating the evils of "splashback."
-
While cutting back on salt intake has long been a mainstay in treating high blood pressure, new research suggests that upping potassium intake might have a greater effect. It might be time to stock up on bananas, apricots, and sweet potatoes.
-
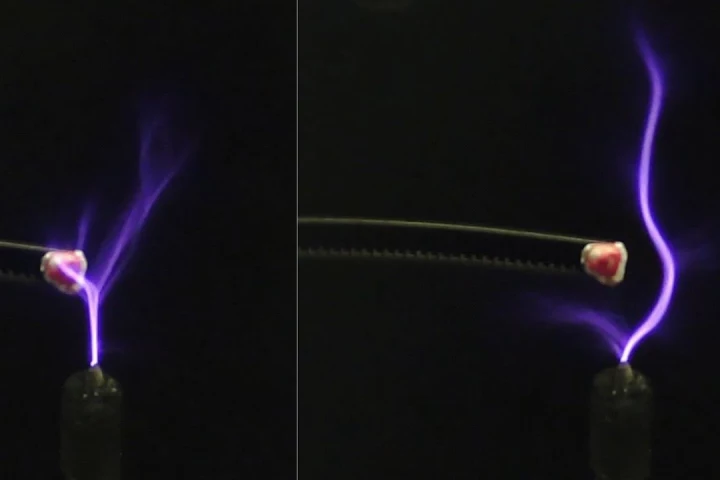
Electricity is chaotic, and we normally need to constrain it to wires and circuits to make use of it. Scientists in Europe and Canada have now managed to guide sparks through thin air and even around obstacles using ultrasound waves.
-
Researchers have developed technology that allows people to do common smartphone tasks – listen to music, take a phone call, and order food – all by making simple, not-too-socially-awkward gestures with their feet while they’re walking.
-
New research has found that men’s and women’s metabolisms favor eating different foods at breakfast time and could be key to developing personalized nutrition strategies that help to address health issues or lose weight.
-
Researchers have developed a plant-based hydrogel to create shape-changing, navigable small-scale robots with potential applications in biomedicine, including conducting medical procedures and delivering therapeutic cargo to cells and tissues.
-
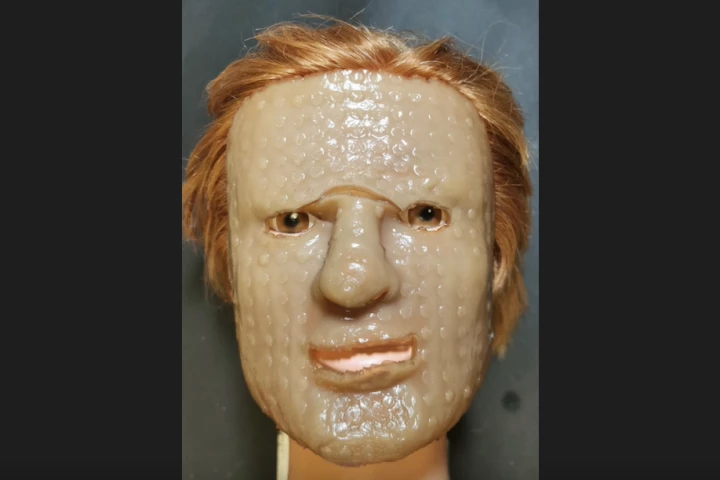
It's a sad fact that burn victims often feel a great deal of pain when the dressings on their wounds are removed. A new hydrogel-based dressing could change that, however, as it easily releases from the skin when cooled.
-
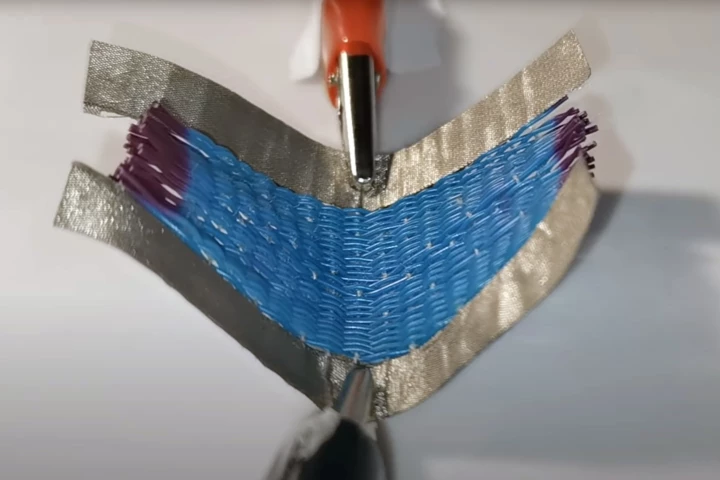
UK researchers have created the first smart fabric that can change shape and color in response to two different stimuli: heat and electricity. The development opens up new possibilities in various fields, including virtual reality and robotics.
Load More