Washington State University
-
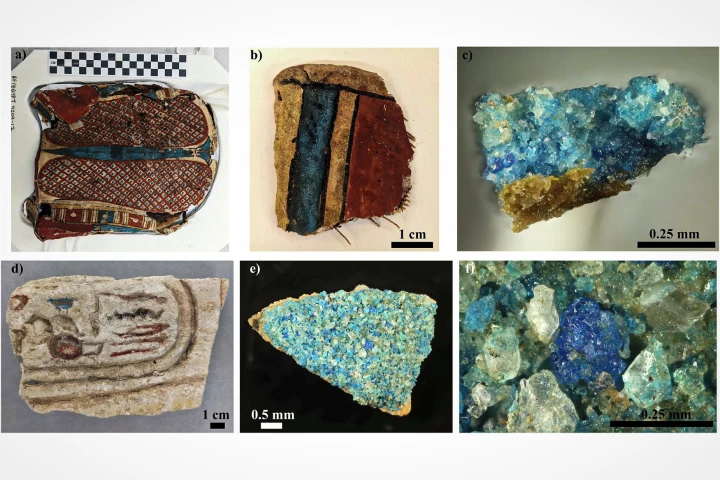
Ancient Egyptians were not only masters of architecture but also wizards of chemistry. Around 5,000 years ago, they crafted the world’s first synthetic pigment, Egyptian blue, and now researchers think they've finally figured out the original recipe.
-
Beekeepers in many regions are having a hard time of it, as their honeybees struggle to find enough pollen. Scientists are now addressing that problem with a new nutritional supplement which is described as being like "a PowerBar for bees."
-
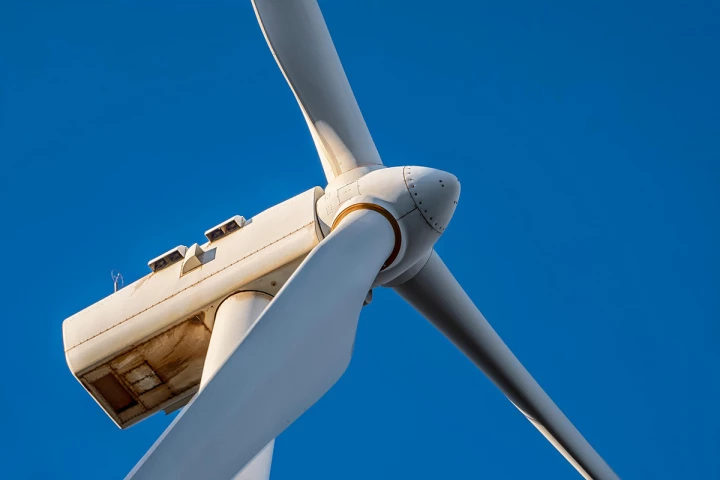
Recycling wind turbine blades is hard because they're built to weather the elements for decades. Researchers have devised a way to use discarded blades to create strong and durable plastics – without resorting to the use of harsh chemicals.
-
A study suggests that a certain salamander may be able to control its grip on trees' bark by pumping blood in and out of the tips of its toes. This strategy could one day be copied in human technology such as prosthetic hands and reusable adhesives.
-
The recognition of same-sex marriage across the European Union has had a negative impact on the US economy, causing the number of highly skilled foreign workers seeking visas to drop by about 21%, according to a new study.
-
While stormwater runoff pollutants in general aren't great for aquatic animals, chemicals from tire particles are particularly harmful to salmon. A study now shows that permeable pavements could keep most of those toxins from ever reaching the fish.
-
In regions where dogs often run loose, don't wear tags and aren't chipped, it can be hard for authorities to keep track of which ones have been vaccinated against rabies. A new app could help, by identifying dogs via facial recognition technology.
-
Water striders are fascinating to watch, as they scoot across the water while supported by surface tension. Scientists have now built a tiny robotic version of the insect, which utilizes a record-breaking actuator to get a move on.
-
Researchers have uncovered a brain mechanism that causes 'the munchies' after cannabis use, paving the way for therapeutics to treat appetite disorders like anorexia and obesity and to improve the appetite of patients undergoing cancer treatment.
-
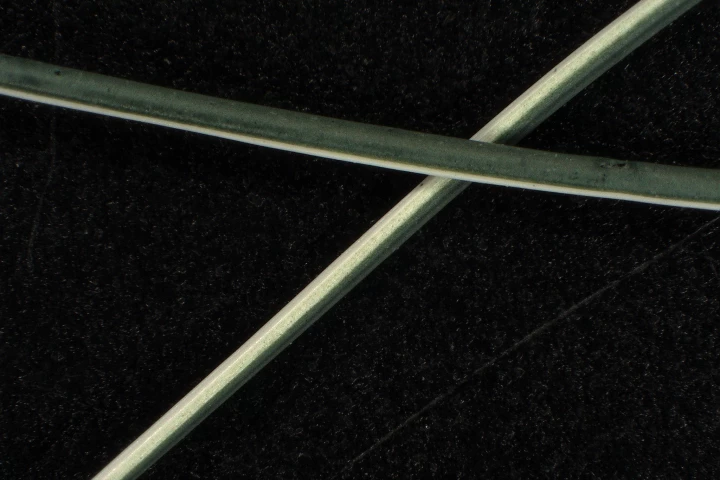
Electrically conductive "smart fabrics" have many potential applications, but their specialized fibers typically aren't as soft and flexible as those made of regular materials. An experimental new fiber, however, is both flexible and conductive.
-
While titanium implants such as artificial hips can greatly improve patients' lives, they're also subject to serious bacterial infections. An experimental new antibacterial titanium alloy, however, could make such problems a thing of the past.
-
There is a growing body of evidence that points to night shift work being extremely bad for our health. But scientists believe some big, hairy "extreme shift workers" may hold the cellular secrets to staying healthy amid circadian rhythm disruptions.
Load More