Water
-
A new study from scientists at Michigan State University sheds light on a recently discovered microbe and its potential for scavenging pollutants in deep soil. Further work could lead to novel solutions in providing clean drinking water worldwide.
-
There are plenty of ways to suck water out of the air, whether you need a little or a lot. MIT researchers may have just hit upon one of the best ways to do it, with a new device that doesn't need power, or even a filter, to deliver drinking water.
-
What if the water in your coffee pot literally just came out of thin air and you never had to fill it again? That's what the Kara Pod does. True story.
-
If your home has old lead water pipes, there's a chance that harmful concentrations of lead may be present in your water. An experimental new device could soon allow homeowners to check for themselves, instead of waiting for the city to do so.
-
Neighborhoods near golf courses are often considered desirable locations. However, a new study suggests that houses within a few miles of manicured fairways and greens may not be such hot property for your health and wellbeing.
-
Researchers at Australia's RMIT University have devised a simple and clever contraption that could make drinking water available in disaster-stricken areas, by pulling it out of thin air.
-
Tiny drops of water might not seem like powerhouse energy producers, but a new method shows how simple tubes might be able to turn falling rain into an energy source. In tests, the method was able to power up 12 LED lights.
-
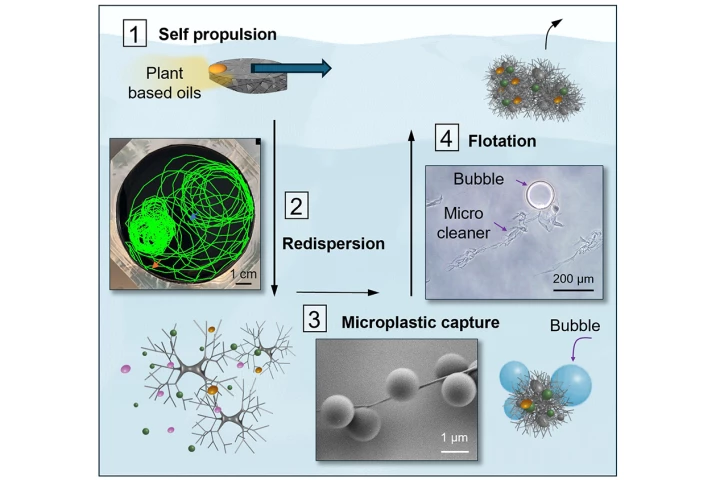
Wouldn't it be great if there were a way of chasing down waterborne microplastic particles and catching them for removal, as opposed to just passively filtering them out of water bodies? Well, new "microcleaners" can reportedly do that very thing.
-
You may think golf course grass is the same everywhere … but you would be wrong. Some greens are known for being dry while others have a rep for being wet, and a new type of golf ball coating could make for better golfing on both.
-
This little piece of riding gear is a full-fledged smart hydration pack that tells you when you're thirsty while out riding and it goes so far as to squirt the water right into your mouth.
-
It’s hard to get glue to work underwater – unless you’re a mussel. Scientists have now created a new adhesive that combines the stickiness of mussel’s natural glue with the slimy, germ-repelling nature of mucus.
-
Water ice is a far more complex substance than we might assume. Scientists have now created an exotic new form of ice in the lab, known as “plastic ice VII.” This strange version could exist naturally on other planets and moons in our solar system.
Load More