Researchers at the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) have successfully tested bilateral shoulder-level prosthetics, allowing a test subject to perform complex tasks using both arms simultaneously. The tests indicate that the system is quick to learn, and it could one day drastically alter the lives of shoulder-level amputees.
For most of us, simple tasks like drinking a cup of coffee or using a vending machine don’t present any problems. But for people like Leslie Baugh, who lost both his arms in an electrical accident some 40 years ago, they can be simply impossible. The research and development of advanced prosthetics, such as those in this study, aims to change this, and has the potential to truly transform people’s lives.
In order for the technology to work, Mr. Baugh was first required to undergo a treatment known as targeted muscle reinnervation, designed to reassign nerves that once controlled the amputated limb. Following the treatment, the team used pattern recognition software to isolate individual contracting muscles, studying the communication between them, as well as the frequency and amplitude of the nerve impulses. That information was then translated into specific movements in the prostheses.
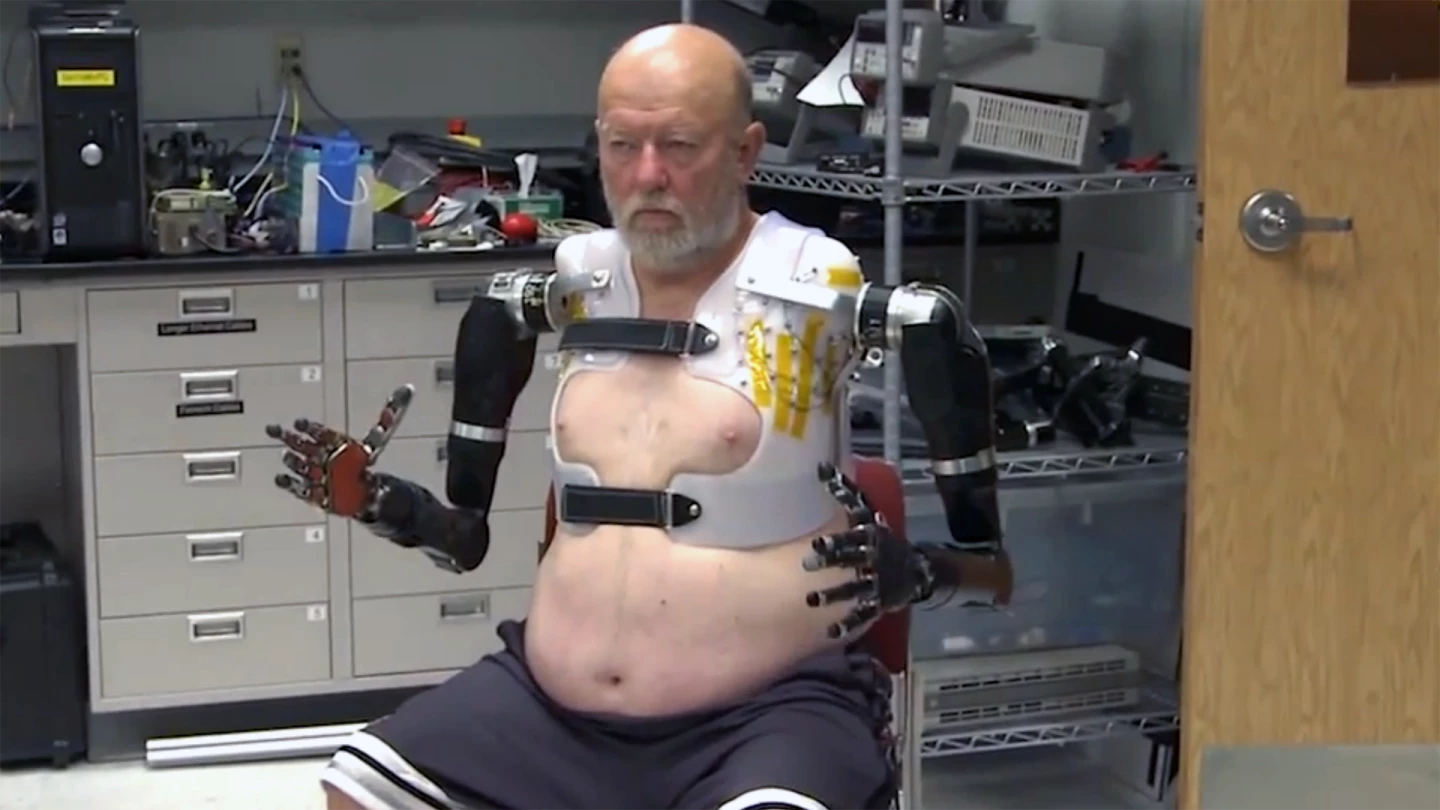
To allow Baugh to control the limbs, a custom socket was created for the top half of his torso, designed for the dual purposes of supporting the artificial limbs and allowing for the neurological connections with the reinnervated nerves. Though a computer-modeled version of the socket was produced first, the need for it to be precisely fitted to Baugh’s torso led to a second version being created, using a more traditional cast technique.
While waiting for the finished article to arrive, the team got to work training Baugh to use the prostheses via a Virtual Integration Environment (VIE) – a virtual reality version of the team's Modular Prosthetic Limbs (MPLs). Once the socket and protheses were fitted, he was able to carry out complex tasks such as moving a cup between shelves of varying heights, carrying out as many as eight separate motions to achieve the goals. He was even able to simultaneously control a combination of motions across both arms – a first for the field.
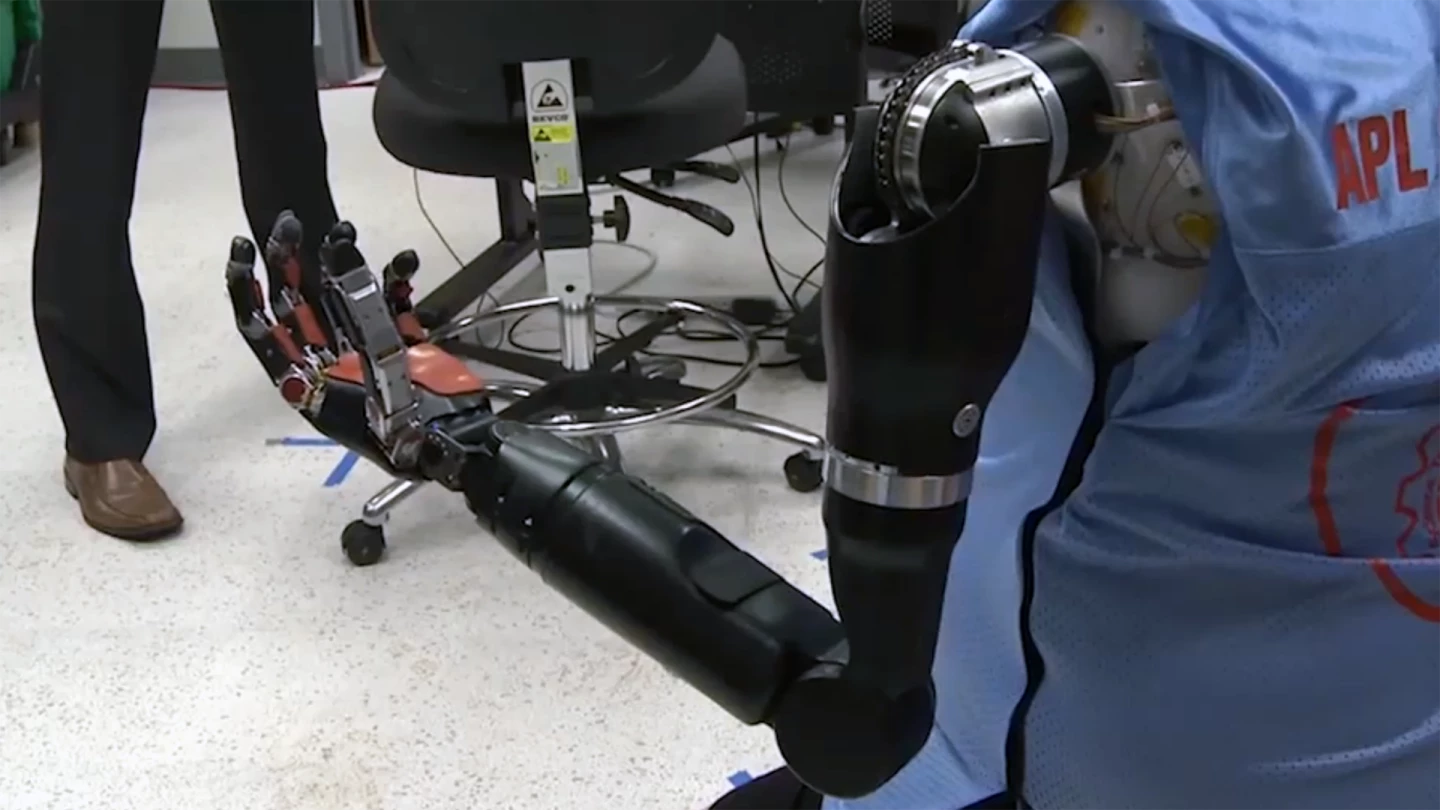

Courtney Moran, a prosthetist working with Mr. Baugh, commented, “We expected him to exceed performance compared to what he might achieve with conventional systems, but the speed with which he learned motions and the number of motions he was able to control in such a short period of time was far beyond expectation.”
It’s been an exciting month for prosthetics research, and the Johns Hopkins University study isn’t the only positive result we’ve seen. Earlier this month, researchers at the University of Pittsburgh published the results of a similarly promising study involving a mind-controlled robotic arm.
Take a look at the video below to see the mind-controlled prostheses in action.
Source: Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory







