As compared to their incandescent counterparts, LED bulbs are already known for producing a lot of light using relatively little electricity. According to a new study, however, a thin layer of nanoparticles could allow them to perform even better.
A typical LED diode consists of the actual light-emitting LED chip, which is surrounded by a transparent protective domed casing/lens. And while much of the light produced by the chip passes right through the casing, some of it is reflected back inwards.
Unfortunately that reflected light is wasted, as it doesn't travel out into the diode's surroundings to provide illumination. Additionally, it raises the temperature inside the diode, causing the chip to degrade faster – this means that the LED ultimately won't last as long as it would otherwise.
Seeking a solution to the problem, scientists at Imperial College London and the Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati recently developed a computer model in which a transparent layer of inexpensive metallic nanoparticles was added above the LED chip, between it and the inside of the casing.
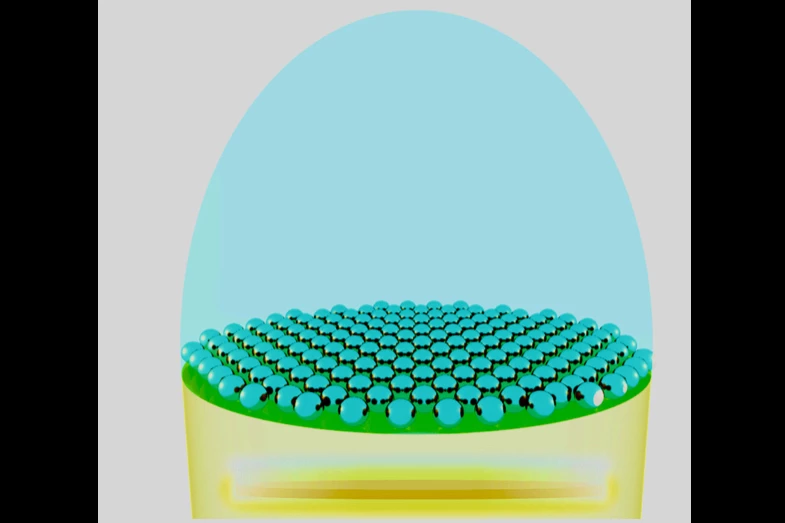
The particles acted somewhat like a grid of micro-lenses, altering the angle at which the light met the casing material. As a result, up to 20 percent more light was able to pass through, as opposed to being reflected back in. This means that a greater amount of light could be emitted using the same amount of electricity, plus the LEDs should stay cooler and thus have a longer lifetime.
Plans now call for the production of prototype diodes utilizing the technology, so that variables such as nanoparticle material, size, shape and spacing can be tested and tweaked.
"While improvements to the casing have been suggested previously, most make the LED bulkier or more difficult to manufacture, diminishing the economic effect of the improvement," says IIT Guwahati's Dr. Debabrata Sikdar, co-author of a paper on the research. "We think that our innovation, based on fundamental theory and the detailed, balanced optimization analysis we performed, could be introduced into existing manufacturing processes with little disruption or added bulk."
The paper was published in the journal Light: Science & Applications.
Source: Imperial College London




