Aarhus University
-
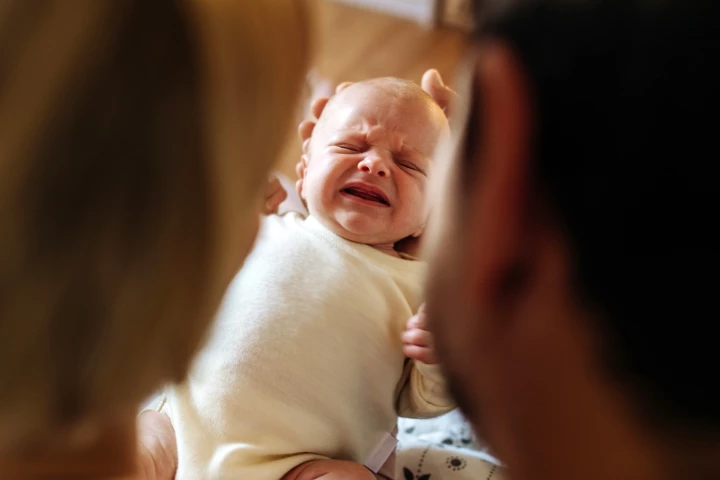
A new study has cast doubt on the idea that women are biologically wired to wake more to a crying baby than men. It suggests that the significant disparity in nighttime care is due to social, rather than biological, factors.
-
Another large study has found a correlation between proton pump inhibitors (PPI) and an increased risk of dementia, particularly for those aged 60-69 years. But frustratingly, scientists still don’t understand exactly what that connection is.
-
Love it or hate it, but the way humans modify their speech when they communicate with their young offspring, commonly known as "baby talk," has now been recorded among bottlenose dolphin mothers. It's the first time it's been heard, too.
-
It is believed that long before Alzheimer's or Parkinson's diseases present obvious symptoms, the disorders may be noticeable in changes to a person's sleep patterns. A new project aims to see if such changes can be detected by an earbud-like device.
-
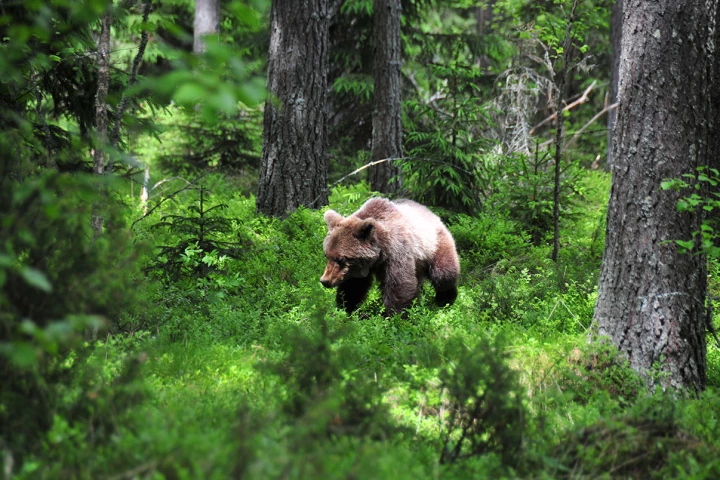
Bears don't move much all winter long, but people are advised to get up frequently during a long flight to prevent blood clots. A new study uncovers why this discrepancy exists, and how it might lead to safer replacements for blood thinners.
-
Researchers have discovered new information about how the body’s antibody-mediated immune system works, calling into question long-held scientific understanding and opening the door for potential advancements in immunological treatment.
-
Sleeping while wired up with an EEG cap would be hard enough here on Earth, but can you imagine trying to do so in the zero-gravity environment of outer space? It could be quite awkward, which is why an earbud has been designed to do the same job.
-
No matter what humans come up with, chances are nature has already done a better job. Now researchers have discovered the latest example – beetles naturally lubricate their knees with a strange substance that works better than Teflon.
-
Just like a tree trunk, the tusk of the narwhal acquires a new growth ring every year. Analyses of those rings have now revealed some interesting facts about the animals' diet, and about changes in their environment.
-
We all know that bats locate prey in the dark using echolocation, but … is that really all there is to it? Scientists decided to get more details on the animals' hunting process, by equipping them with tiny wearable computers.
-
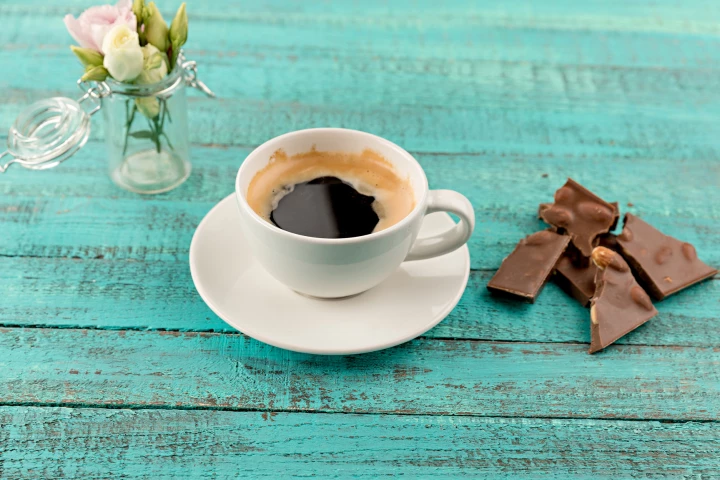
New research has found the bitter characteristics of coffee can make a person more sensitive to sweetness. The study found this effect was independent of caffeine and helps explain why many people enjoy the experience of dark chocolate with coffee.
-
Scientists in Denmark have now offered further insights into how sugar reshapes our brain chemistry, by performing experiments on pigs and taking note of how the reward circuitry lights up after consumption.
Load More