Addiction
-
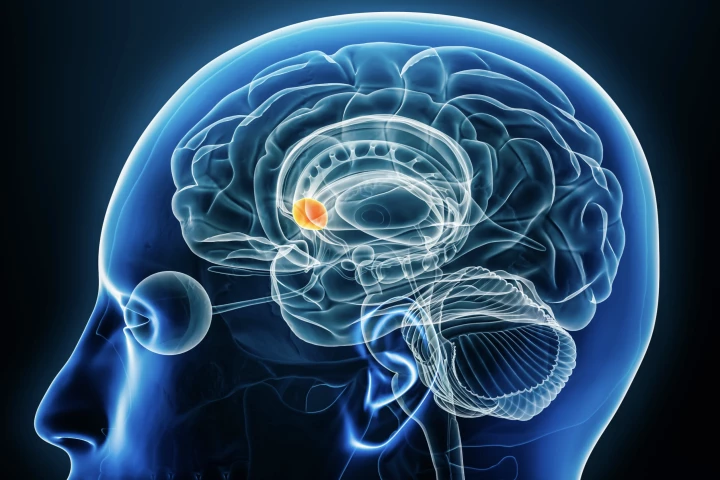
Dopamine doesn’t flood the brain as once believed – it fires in exact, ultra-fast bursts that target specific neurons. The discovery turns a century-old view of dopamine on its head and could transform how we treat everything from ADHD to Parkinson’s.
-
A large-scale human clinical trials is currently underway testing a wild idea. Can fecal transplants reduce a person's cravings for alcohol by altering their microbiome? Early studies are indicating this could be possible.
-
Consuming cannabis can certainly be a way to deal with some health conditions like chronic pain or insomnia. But when a user goes too far and winds up in the hospital, the negative consequences can reach far into the future, says a new study.
-
GLP-1 drugs have reportedly changed people's relationship with more than just food, but it's been largely anecdotal. Now, there's evidence that Ozempic blocks alcohol cravings – which could be a game-changer for people who want to cut back on booze.
-
While scientists seem to love giving cocaine to rats, 27 rodents getting high (for the first time) on the lab's supply uncovers intriguing insights into how some individuals appear wired for addiction, where 'averse cues' fail to deter drug use.
-
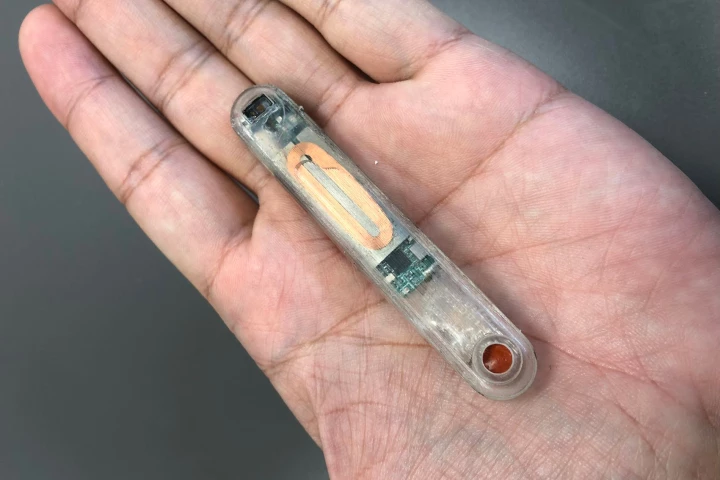
When someone overdoses on opioids, it's critically important that they receive a dose of the opioid-reversing drug naloxone as soon as possible – otherwise, death is a distinct possibility. That's where a new implant comes in, as it automatically dispenses naloxone from within the body.
-
A new study has found that there was no association between using cannabis and non-medical opioid use in people receiving pharmacotherapy for opioid use disorder. The findings neither confirm that using cannabis leads to opioid use nor that it's effective in reducing it.
-
New research found that patients taking the weight-loss and diabetes drug semaglutide had significantly reduced symptoms of alcohol use disorder. Larger studies are currently underway to see whether the drug is an effective treatment for addiction.
-
A new study has found that specific regions of the brain are activated after a drug is taken intravenously but not when the same drug is taken orally. The findings could lead to new treatments for addiction.
-
A new study is offering one of the largest portraits to date of global smartphone use. Surveying thousands of people across nearly 200 countries the study found unexpected use patterns that challenge our current definitions for smartphone addiction.
-
While opioids are among the most powerful painkillers, they're also highly addictive, which makes them hard to get. A new finding may offer hope to pain patients in the form of powerful drugs that lack the most severe side effects of current options.
-
Scientists have discovered how a specific brain circuit functions during fentanyl withdrawal, potentially leading to relapse. Suppression of this could lead to better, targeted medical treatments for opioid use disorders.
Load More