Aging
-
The use of blood-flow restriction cuffs that "hack" your physiology to speed up strength and muscle gains has been growing in popularity. However, researchers have now found that they come with a big downside during use – especially the older you get.
-
In a new study, researchers discovered that the human brain has four pivotal periods when it goes through marked changes, sparking five "epochs" that last for years. The adolescent phase, for example, was found to extend into our early 30s.
-
Our fat tissue could be used to make our bones regrow, with scientists successfully using adipose cells to repair spinal compression fractures. It could change how breaks are treated and improve bone strength in diseases such as osteoporosis.
-
A new study of exceptionally long-lived Rottweilers revealed that keeping their testes for longer may help them age more gracefully, offering fresh clues for how hormones shape frailty and resilience in both dogs and humans.
-
Listening to or playing music later in life could do more than lift your spirits – it might also help keep your mind sharp. A large study has found that older adults who regularly engage with music have significantly lower rates of cognitive decline.
-
In a review of more than 200 clinical trials, scientists have identified which exercise offers the most benefits in relieving the symptoms of knee osteoarthritis. It's the most comprehensive look at physical activity in treating the condition yet.
-
A blend of natural compounds that blocks sugar damage extended lifespan in mice by curbing hunger and improving metabolism in a new study. It hints at a new way to fight obesity, diabetes, and aging without cutting calories.
-
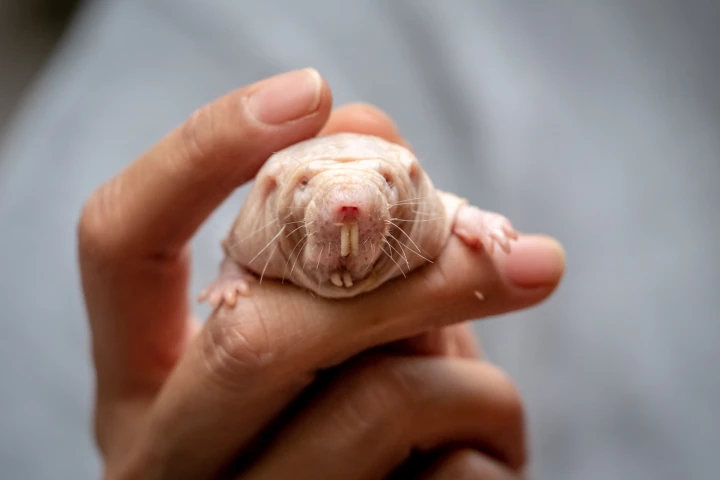
What naked mole-rats lack in the looks department they make up for it in longevity, living healthily for nearly four decades. Now, scientists have found just how they repair their DNA – and it has the potential to be harnessed by humans to do the same.
-
A groundbreaking study has revealed that your mom and dad’s DNA don’t just pass on telomere length, they actively reshape it in the first days of life, influencing how we age and our risk of developing diseases such as cancer.
-
We've known for some time that obesity affects the brain, but now scientists have found that it's where you carry it that matters most. Deep visceral fat around organs has the biggest impact on brain aging, affecting a suite of cognitive functions.
-
Animal studies say rapamycin can slow aging – but does it work in humans? A new review finds the evidence for the off-label, low-dose use of the drug in healthy adults is thin, inconsistent, and far from conclusive.
-
Signs of immune system aging appear years before rheumatoid arthritis takes hold, offering new hope for early diagnosis and treatments that could slow or stop the disease before it starts, according to new research.
Load More