American Chemical Society
-
At any given moment, 89,000 terawatts of solar power hits the Earth’s surface. Current technology captures only part of it, limited by the solar spectrum. Researchers at Korea University report using gold nanotechnology to harness the full spectrum.
-
When you're checking the freshness of a piece of fish that you plan on eating, you want results right away. That's where a new microneedle-based sensor comes in, as it delivers a yay or nay in less than two minutes.
-
It's a well-known fact that if you're trying to cool your mouth after eating spicy food, you should drink milk, not water. Bearing that fact in mind, scientists have developed an "artificial tongue" that measures food spiciness using a milk protein.
-
A recently published study shows promising results from combining edible turkey tail fungus with a solution of wood fibers. The end product is a natural sustainable waterproof coating that may be a replacement for single-use plastic food wrap.
-
Among the many problems with the flu is the fact that you can spread the virus before you even know you've got it. An experimental new "sensor" could one day keep you from doing so, by causing you to taste thyme in your mouth.
-
One of the problems with microplastics lies in the fact that the plastic particles can be so small, we don't even know they're present in water in the first place. A new type of engineered bacteria could help, by causing the particles to glow green.
-
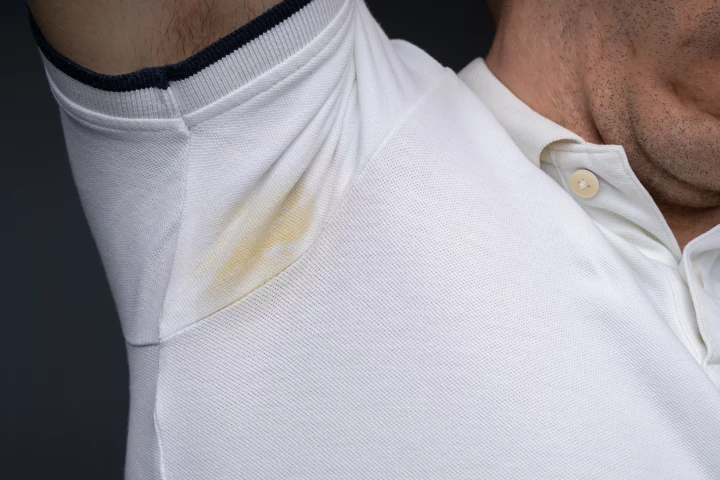
Not to sound like a TV commercial or anything, but … how often have you had to throw out white shirts because of unsightly yellow underarm stains? Well, those stains may not be a problem any longer, thanks to a simple blue light treatment.
-
While it's very important to know if a "date rape" drug has been sneaked into your drink, whipping out a full test kit in a bar may be time-consuming. That's why scientists have developed a temporary tattoo that can detect such drugs in one second.
-
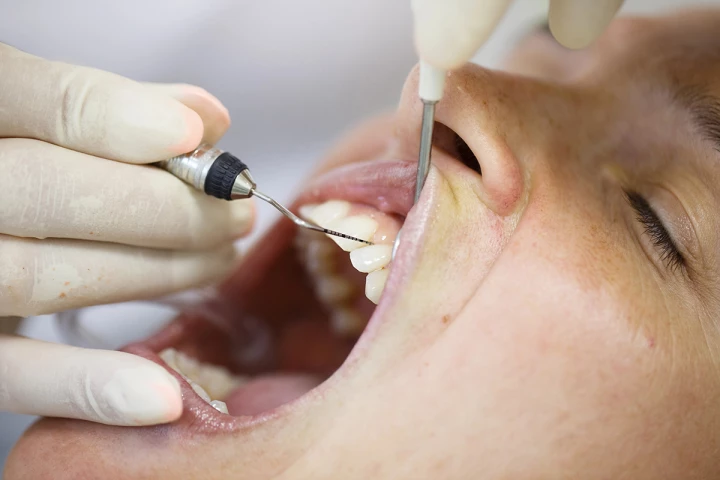
When it comes to dental checkups, no one likes having their gums poked with the periodontal probe. Well, they may soon no longer have to, thanks to a gum-assessing toothbrush-shaped mini ultrasound transducer.
-
As unspent antibiotics pass from our bodies, they contribute to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Scientists are addressing this problem with a new technology which causes such drugs to only become active upon exposure to green light.
-
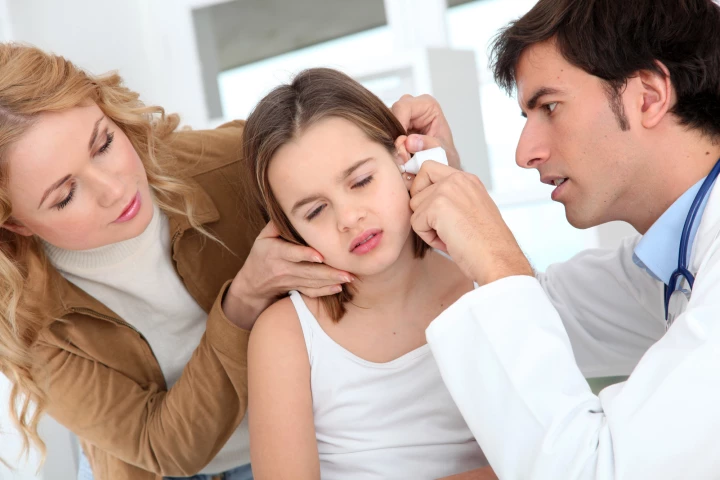
Babies and small children are prone to middle ear infections, which typically have to be treated with orally administered antibiotics. A new fast-acting topical gel could soon replace such drugs, however, potentially reducing unpleasant side effects.
-
If your home has old lead water pipes, there's a chance that harmful concentrations of lead may be present in your water. An experimental new device could soon allow homeowners to check for themselves, instead of waiting for the city to do so.
Load More