American Chemical Society
-
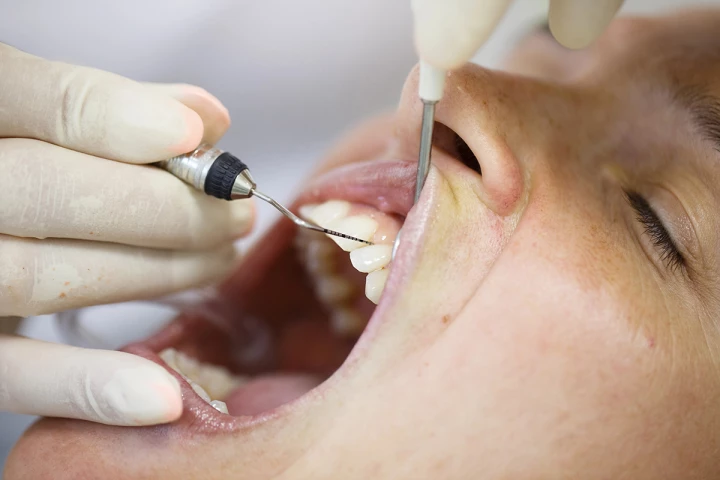
When it comes to dental checkups, no one likes having their gums poked with the periodontal probe. Well, they may soon no longer have to, thanks to a gum-assessing toothbrush-shaped mini ultrasound transducer.
-
As unspent antibiotics pass from our bodies, they contribute to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Scientists are addressing this problem with a new technology which causes such drugs to only become active upon exposure to green light.
-
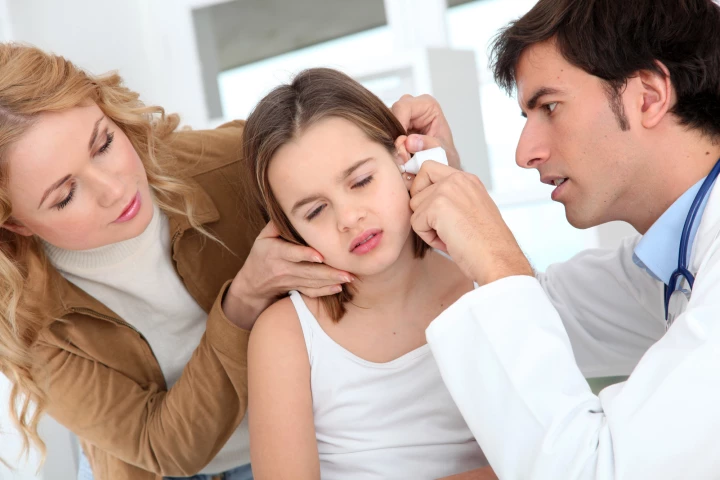
Babies and small children are prone to middle ear infections, which typically have to be treated with orally administered antibiotics. A new fast-acting topical gel could soon replace such drugs, however, potentially reducing unpleasant side effects.
-
If your home has old lead water pipes, there's a chance that harmful concentrations of lead may be present in your water. An experimental new device could soon allow homeowners to check for themselves, instead of waiting for the city to do so.
-
If you're going to try "tattooing" a microscopic animal, it would make sense to select one of the toughest creatures on the planet. That's what scientists have done with the tardigrade, and the tech they used may have some valuable applications.
-
You may think golf course grass is the same everywhere … but you would be wrong. Some greens are known for being dry while others have a rep for being wet, and a new type of golf ball coating could make for better golfing on both.
-
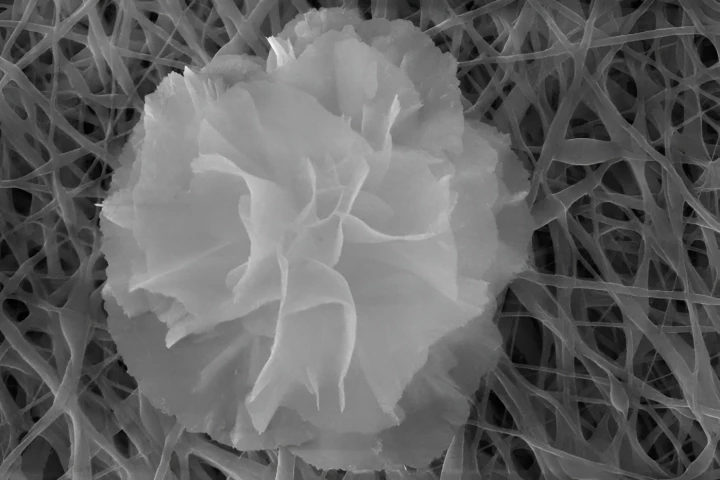
While we've seen antibacterial wound dressings before, Italian scientists have taken the idea to new extremes. They've created a material that kills multiple types of harmful bacteria, and it does so using tiny flowers.
-
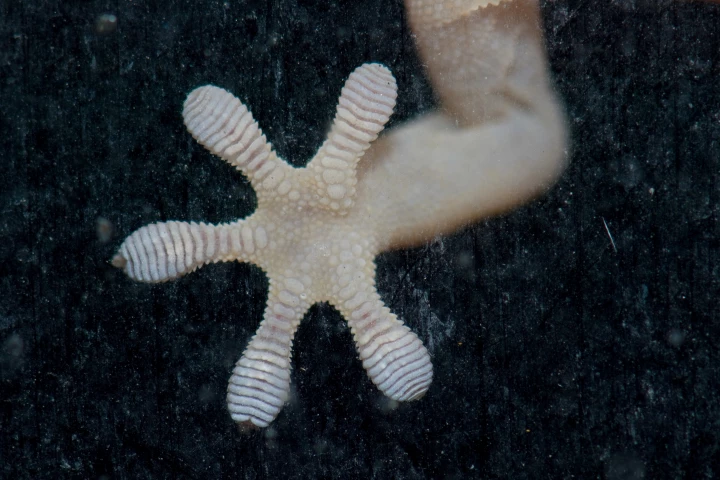
Geckos are able to maintain a grip on wet surfaces not because their toe pads repel water, but because they attract it. A new polymer, which was inspired by this phenomenon, could find use in shoe soles that keep people from slipping on ice.
-
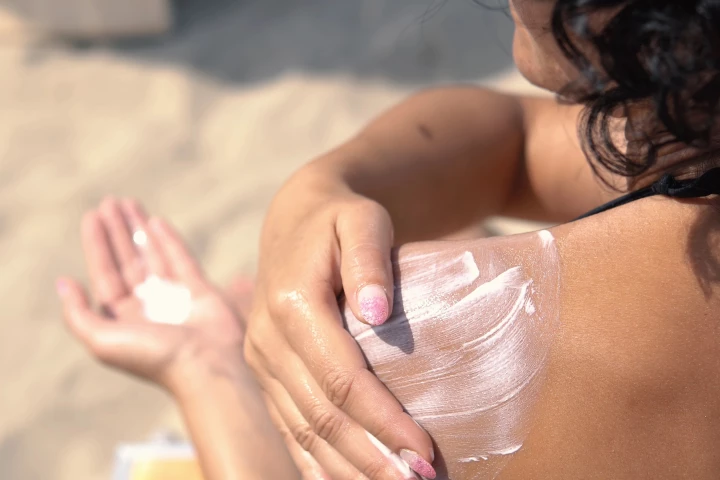
Although sunscreen does help protect our skin from the sun's harmful UV rays, it isn't designed to keep that skin cool. An experimental new sunscreen does that very thing, however, while maintaining an SPF rating of about 50.
-
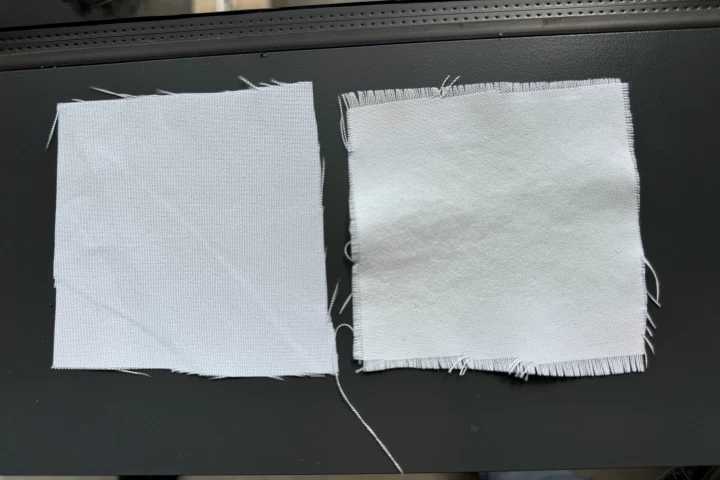
When it comes to keeping cool on hot days, it's not so much a matter of wearing less clothing as it is a matter of wearing the right clothing. A new fabric coating could help in that regard, and it's essentially made of chalk.
-
For babies born with a certain heart defect, implantation of a "shunt" is essential to their survival. A new type of shunt can be expanded using light after it's been implanted, potentially eliminating the need for more heart surgeries down the road.
-
Human-machine interfaces such as phone screens would be a lot cleaner and longer-lasting if we didn't have to touch them. Scientists have now created a proximity-sensing film which makes such a scenario more possible and practical than ever before.
Load More