Artificial organs
-
A man has lived for more than 100 days with a maglev heart beating inside his chest. In a landmark moment, he was discharged earlier this year, becoming the first person in the world to leave the hospital with the device embedded in his body.
-
Scientists in Japan have created hybrid plant-animal cells, essentially making animal cells that can gain energy from sunlight like plants. The breakthrough could have major benefits for growing organs and tissues for transplant, or lab-grown meat.
-
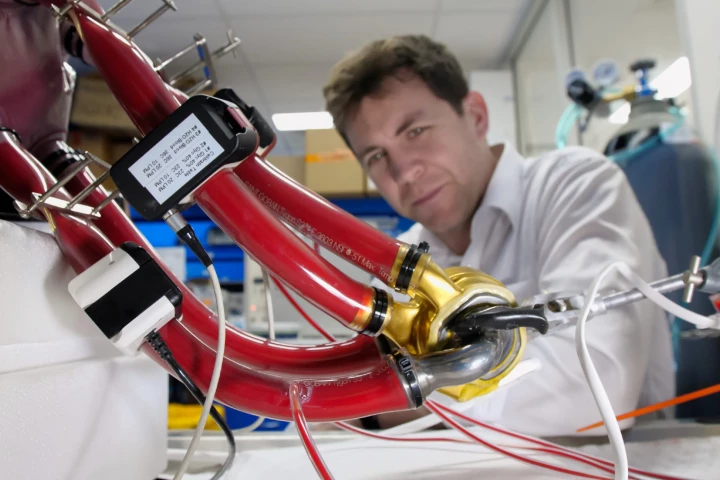
For the first time, the fully mechanical heart made by BiVACOR, which uses the same technology as high-speed rail lines, has been implanted inside a human being. The feat marks a major step in keeping people alive as they wait for heart transplants.
-
Scientists have created models of human embryos by programming stem cells. The models give a glimpse into a key stage of development that can reveal new insights into genetic disorders and preventing failure in early pregnancy.
-
In a historic procedure surgeons have, for the first time, transplanted a genetically modified pig heart into a living human. The patient is still alive, has not rejected the organ and is being monitored at the University of Maryland Medical Center.
-
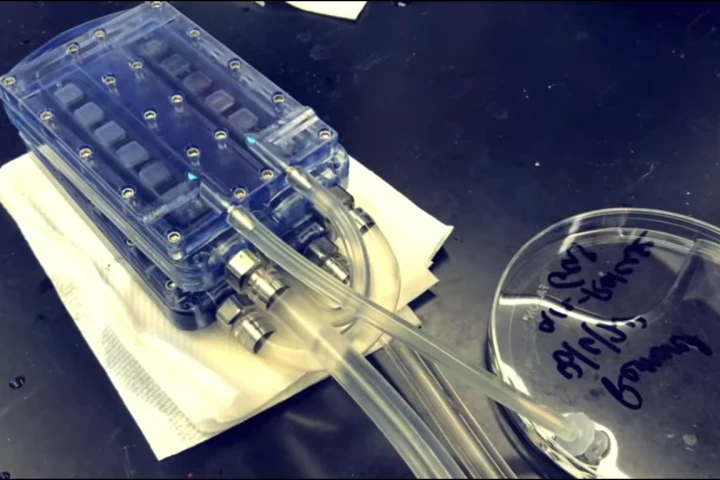
Patients with kidney failure require regular dialysis, an invasive and potentially risky treatment. But now researchers have successfully demonstrated a prototype bioartificial kidney, which can be implanted and works without the need for drugs.
-
Spanish researchers have created a new potential treatment for age-related macular degeneration, which is currently untreatable – a biohybrid artificial retina, made of silk and loaded with new human cells that can integrate and repair the damage.
-
The human eye is incredibly complex, so it's very hard to reverse engineer. Now researchers have unveiled the world’s first 3D artificial eye, which can not only outperform other devices but has the potential to see better than the real thing.
-
Imagine needing a liver transplant and, instead of waiting for a donor, a new one could just be grown from your own skin cells. In a big step towards this, mini human livers grown from stem cells have been successfully transplanted into rats.
-
Researchers at MIT have developed a bionic heart to test heart valves and other cardiac implants under realistic conditions. Built out of an actual living heart, the new device promises improved designs and less expensive development cycles.
-
Scientists have pieced together 10 devices that mimic the functions of different organs to create a functioning Body-on-Chips platform, which can offer new and comprehensive insights into how prospective drugs will behave throughout the human body.
-
Organ development has traditionally been tricky to study, thanks largely to the difficulty in getting sensors in there without damaging the organs. Now, researchers from Harvard have developed a way to create “cyborg organoids” by integrating nanoelectronics into cell cultures.
Load More