Baylor College of Medicine
-
In a Phase 3 trial of more than 18,000 volunteers across three countries, a novel mRNA influenza vaccine developed by Pfizer has outperformed standard seasonal flu shots by 34.5%. It's yet another sign that this biotechnology is here to stay.
-
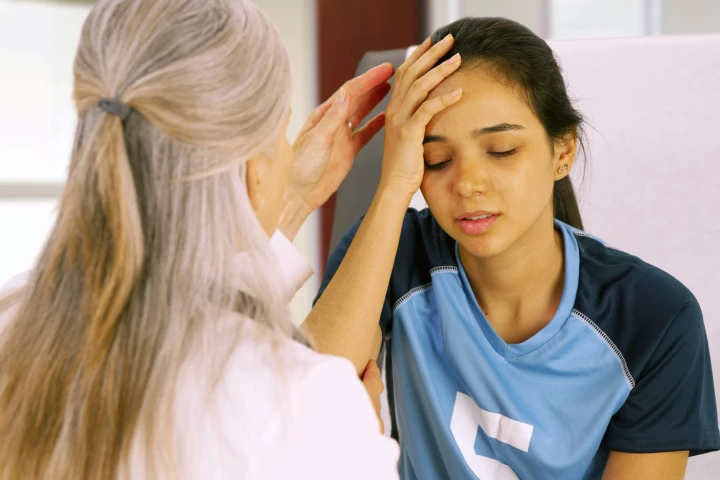
Not all concussions are created equal. A new study has revealed nine early warning signs that a mild head injury might linger longer than expected, and why spotting them within hours could change recovery outcomes.
-
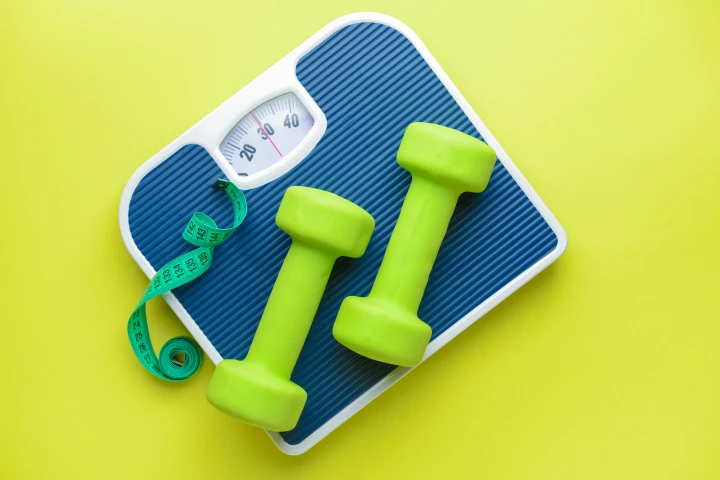
Switching off a single enzyme in immune cells protected mice from obesity, type 2 diabetes, and fatty liver disease in a new study, offering a potential new treatment target for metabolic disorders.
-
Scientists have found out exactly how an exercise-triggered molecule suppresses hunger signals in the brain, leading to weight loss. It could be harnessed as a therapeutic, providing the same benefit without the work it takes to produce it naturally.
-
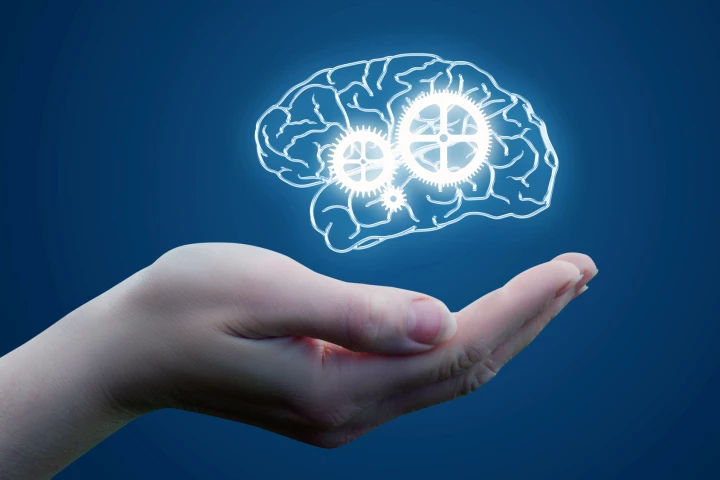
Fascinating new findings uncover how clusters of 'brain stars' retain our learnings – and it changes what we previously understood about how memories are held and retrieved in our minds. The medical implications of this are vast.
-
A new study has somewhat redeemed the tau protein, which up to now has been associated with the development of Alzheimer’s disease. Turns out, the protein has a ‘good guy’ role, helping to protect against harmful free radicals in the brain.
-
A non-hormonal, reversible and safe male pill may be in sight, as scientists successfully silence a protein crucial in fertile sperm production. Knocking out this protein temporarily resulted in unviable sperm, without any lasting impacts on fertility.
-
Even brief periods of anger caused by triggering memories can negatively impact our blood vessels' ability to relax. That's the finding of a new study that could have implications on how we look at heart attack and stroke risk.
-
A natural arms race, usually between predator and prey, is one of the most fascinating phenomena in evolutionary biology. But if humans don't find a way to get ahead in our fight with bacteria, we may be dealing with 10 million deaths a year by 2050.
-
In a world first, scientists from 24 countries have mapped the DNA of 233 different primate species, more than quadrupling the existing genetic data. Then AI jumped on board, offering crucial insights into disease-causing genetic mutations in humans.
-
Instead of injections or pills, why not engineer bacteria to secrete therapeutic molecules from within our gut? A new study is showing how a genetically modified probiotic can produce an anti-inflammatory molecule to treat rheumatoid arthritis in rats.
-
Scientists studying the activity of a drug used to treat rheumatoid arthritis have discovered some surprising metabolic functions, some of which may be useful when it comes to countering diabetes and obesity.
Load More