Cells
-
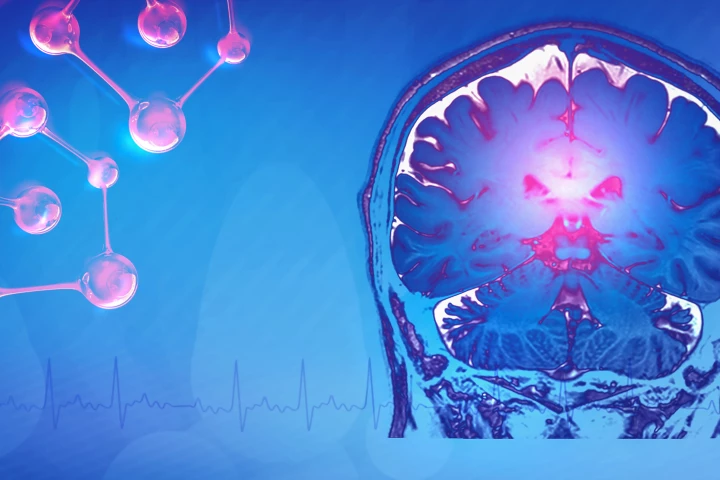
In a first-of-its-kind study, researchers zoomed in on PTSD at the single-cell level to better understand how it affects the brain. The findings revealed how trauma can lead to specific molecular changes in some brain cells.
-
A new organelle has been found by scientists at the University of Virginia. The super-small specialized structure has a role recycling material inside our cells, and its discovery could lead to improved treatments for a wide range of diseases.
-
In a large study, the drug leading the charge in anti-aging science has shown to be just as effective in protecting cells and cognitive function as cutting calories or intermittent fasting. It's the most comprehensive study of rapamycin yet.
-
A protein found in our cells has emerged as a secret weapon against biological aging, acting like a glue to repair damaged DNA and ward off neurological degeneration including that seen in motor neuron, Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases.
-
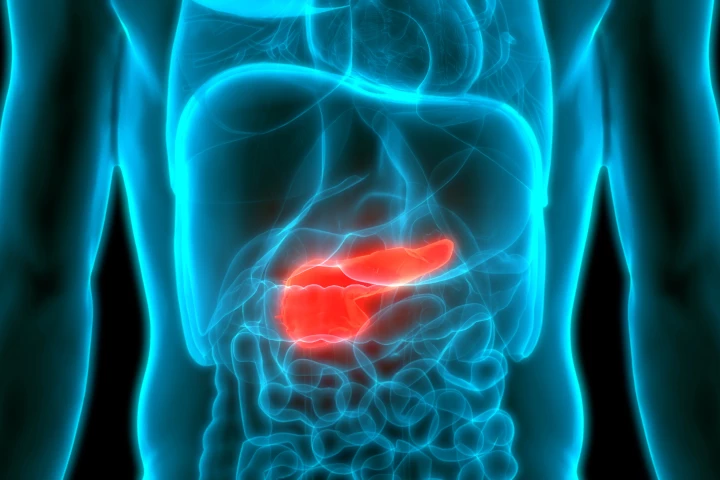
We could be on the verge of a major cancer breakthrough, with a new nanoparticle-based vaccine reportedly obliterating pancreatic cancer cells in preclinical trials. This success now takes it a step closer to a first-of-its-kind human trial.
-
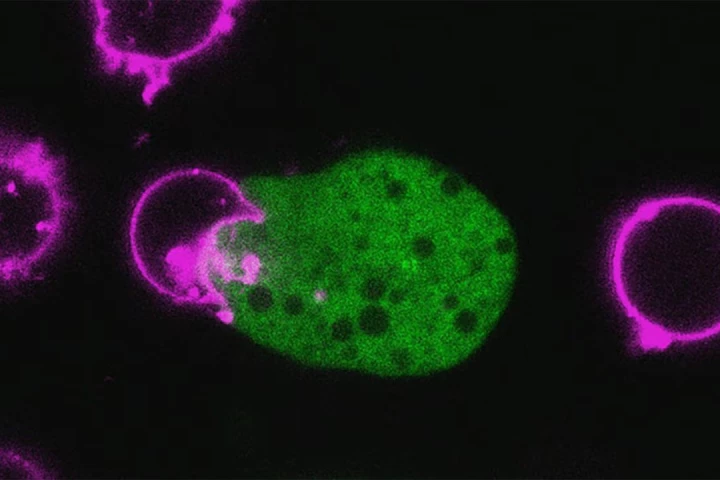
One type of parasite, Entamoeba histolytica, has developed a very intriguing way to evade the defences of our immune system. It rips pieces off human cells and steals the proteins to wear them as a disguise.
-
The existence of orange cats dates back to the 12th century, but the DNA driving this color has been a mystery – until now. Scientists have solved the puzzle, finding a surprise variant that triggers ginger fur, one not seen in any other orange animal.
-
Taking a vitamin D supplement can knock years off your biological aging, according to the results of a large, long-term study. This may not seem like a lot, but it's a significant amount as you become increasingly susceptible to disease as you age.
-
In a new study, researchers have identified a way to stop cells from dying, opening the door to developing treatments that slow the progression of neurodegenerative conditions like Parkinson’s disease.
-
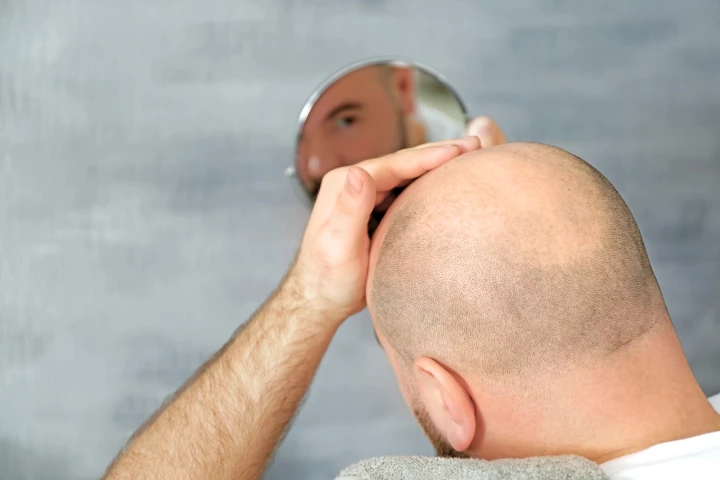
We're one step closer to that elusive goal preventing hair loss and enabling new growth, as scientists identify the crucial role that one all-important protein has in protecting the hard-working cells on the production line.
-
A rice wine native to the Philippines has grabbed the attention of researchers looking into new, natural ways to slow biological aging. But it's not the wine itself – sorry – in the spotlight, but what's leftover after the liquid is ready to bottled.
-
In a major breakthrough for regenerative medicine, MIT scientists have developed a way to convert skin cells directly into brain cells extremely efficiently, without needing to go through the intermediate step of converting them to stem cells first.
Load More