CERN
-
Physicists at CERN have discovered an exotic new particle that’s quite charming. Known as Tcc+, the particle belongs to a rare class called tetraquarks, and its unusual composition makes it the longest-lived exotic hadron found so far.
-
A subatomic particle has been found switching between matter and antimatter, in Large Hadron Collider data. It turns out an unfathomably tiny weight difference between two particles could have saved the universe from annihilation soon after it began.
-
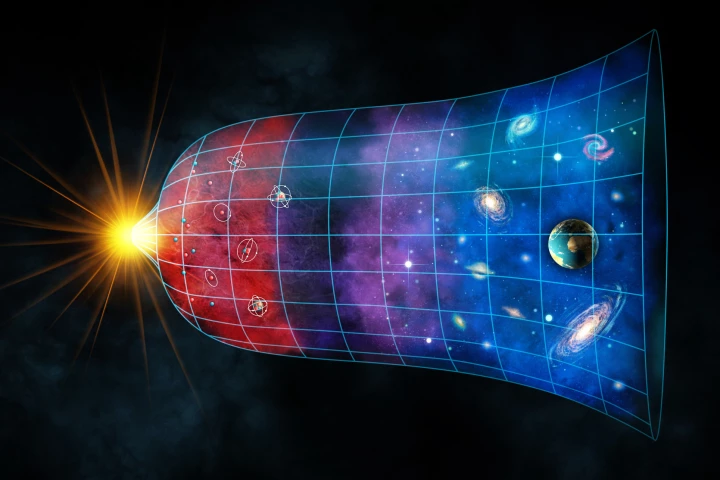
Why is the expansion of the universe accelerating? The leading hypothesis is a repellent force that astrophysicists refer to as “dark energy." But how does it work? What does it mean for our future? And how sure are we that it even exists?
-
Scientists at CERN have used lasers to cool down antimatter for the first time. The milestone could help unlock some of the secrets of this weird substance, including why it didn’t annihilate the universe soon after the Big Bang.
-
In a move that would please the fictional Star Trek engineer Mr. Scott, CERN is working on ways to store and transport antimatter. This isn't to power any starships secretly under construction, but as a way to better study antiprotons.
-
CERN’s Large Hadron Collider probes the fringes of known physics, and now the facility has found particles not behaving as predicted. While it’s early days, the discovery hints at the existence of new particles or forces beyond the Standard Model.
-
A new X-ray scanner adds color and a third dimension, creating high resolution, cutaway 3D models that can diagnose bone fractures and monitor healing. A feasibility study of the machine has now been conducted, with a larger trial set to begin soon.
-
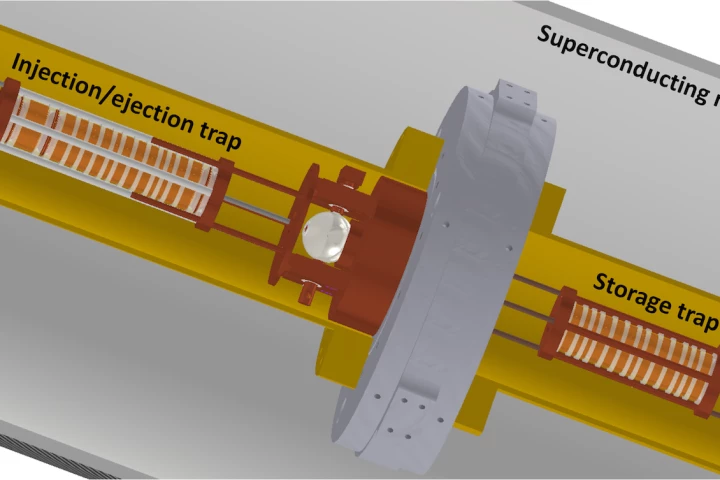
Antimatter is a tricky substance to store and transport, mostly because it annihilates any container you try to put it in. Now CERN researchers have outlined a new antimatter trap designed to safely carry the volatile stuff to new facilities.
-
After a two-year shutdown for repairs and upgrades, CERN’s Large Hadron Collider is beginning to fire back up. The newest particle accelerator, Linac 4, completed its first test run over the past few weeks, and will produce much more powerful beams.
-
It’s been calculated that dark matter is around five times more common than regular matter – and yet, we still haven’t directly detected it. Now CERN has joined the hunt, testing whether the famous Higgs boson could decay into dark matter.
-
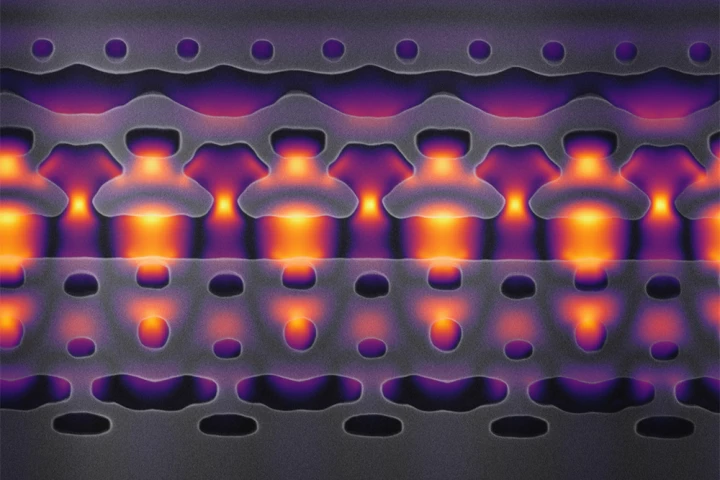
Particle accelerators could be incredibly useful for medicine – if they weren’t so huge. Now, scientists at Stanford have managed to shrink the tech down to fit on a computer chip, which could lead to more precise cancer radiation therapies.
-
The world has seen some major scientific achievements in the last 10 years, as discoveries and developments decades in the making were finally realized. New Atlas rounds up five of the most ground-breaking, history-making milestones of the 2010s.
Load More