Chalmers University of Technology
-
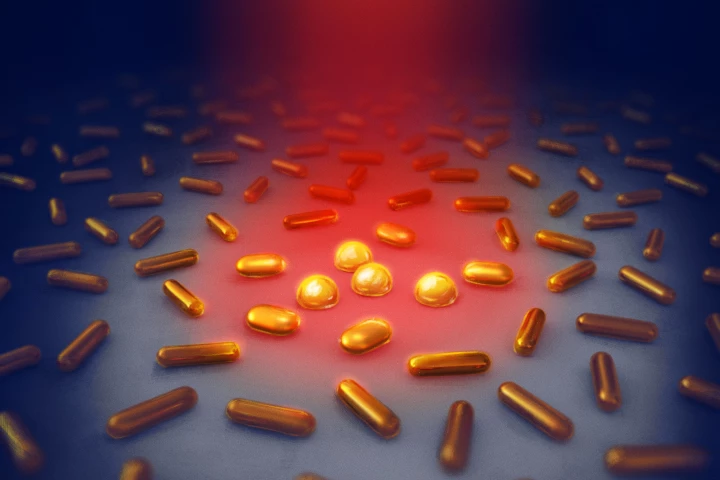
When someone receives an implant such as an artificial hip, there's a real risk of an infection occurring at the implant site. According to a new study, however, a covering of bacteria-frying gold nanorods could keep that from happening.
-
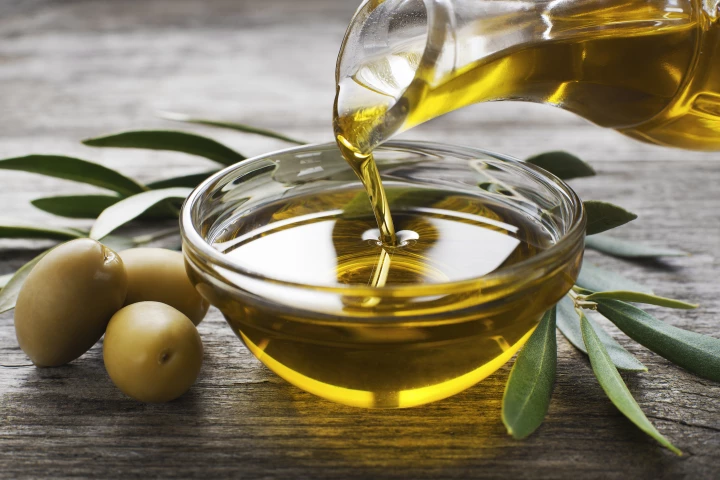
While there has been a general consensus that olive oil and other plant-based fats are better for you than butter, scientists have now put it beyond doubt, combining diet-intervention and previous cohort research to assess serious disease risk.
-
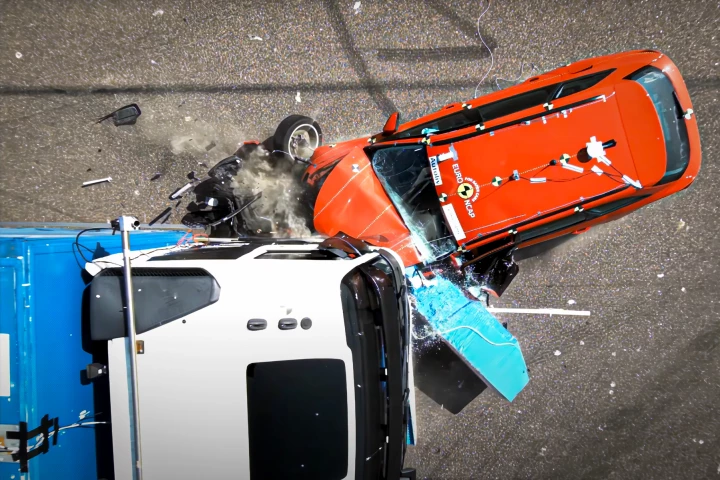
A new Swedish-designed front end for transport trucks could help reduce driver deaths in collisions with passenger cars. The structure is designed to both spread and absorb the force of impact between the two vehicles.
-
In diabetics, wounds tend to progress quickly and heal slowly. Researchers have used electricity to heal diabetic wounds three times faster, which offers great potential for treating those with diseases that lead to reduced wound healing.
-
In countries such as India, a great deal of toxic dye waste from the textile industry is released into waterways, harming people and the environment. A new wood-derived filtration media could remove much of that dye from wastewater streams.
-
It's always good if the use of antibiotics can be avoided, to keep harmful bacteria from developing a resistance to them. A new wound-treatment spray could help, as it kills bacteria using peptides that occur naturally in our bodies.
-
The speed record for data transmission using a single light source and optical chip has been shattered. Engineers have transmitted data at a blistering rate of 1.84 petabits per second (Pbit/s), almost twice the global internet traffic per second.
-
Researchers from Chalmers University of Technology are working on a new autonomous search and rescue system made up of a marine vessel that can launch a fleet of fixed-wing drones to scout a predefined area, along with live-feed quadcopters.
-
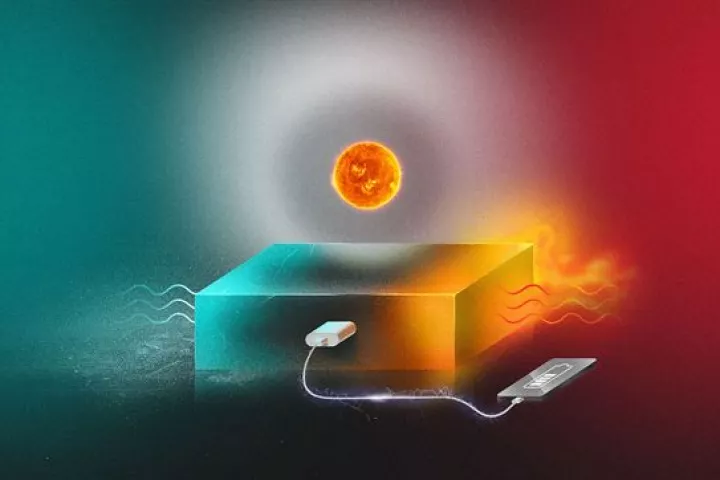
Back in 2017 we caught wind of an interesting energy system designed to store solar power in liquid form for years at a time. By hooking it up to an ultra-thin thermoelectric generator, the team has now demonstrated that it can produce electricity.
-
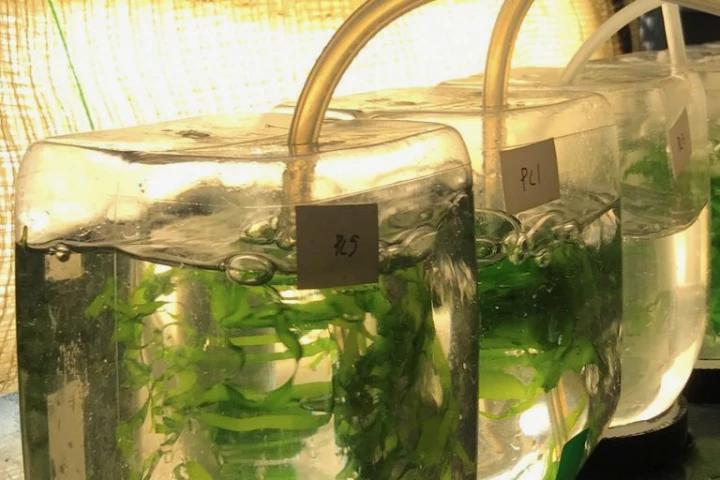
The processing of foods typically generates a lot of wastewater, which has to be cleaned up before being released back into local waterways. According to new research, however, that water could first be put to use as a very effective fertilizer for farmed seaweed.
-
Recent research has uncovered a range of plastic-degrading enzymes, and a new study has revealed this to be part of a broader trend in which such enzymes are increasing in numbers and diversity in direct response to plastic pollution around the world.
-
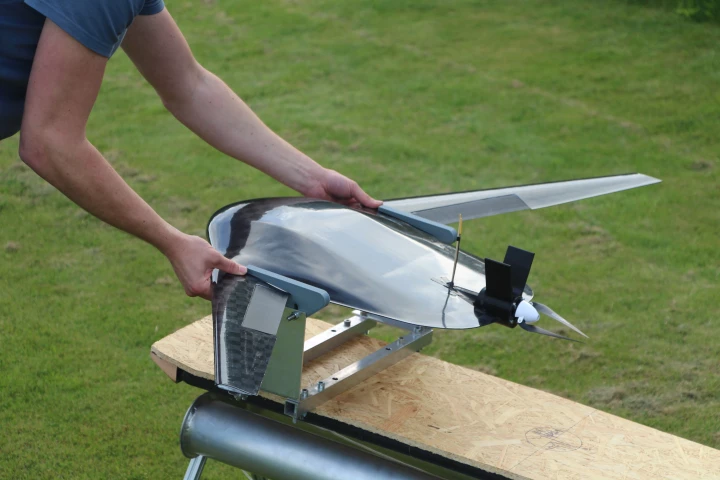
Although solar-powered devices are now fairly common, Swedish scientists have created something a little different. They've built tiny "metavehicles" that are mechanically propelled and guided via waves of light.
Load More