Chemicals
-
Scientists have identified a significant link between levels of choline and the prevalence of anxiety, suggesting that upping intake of this essential nutrient found in many foods could potentially improve symptoms of these debilitating disorders.
-
New research had made a striking link between a mother’s exposure to “forever chemicals” during pregnancy and the shape of her child’s brain at age five. The findings can't say whether these changes are positive or negative.
-
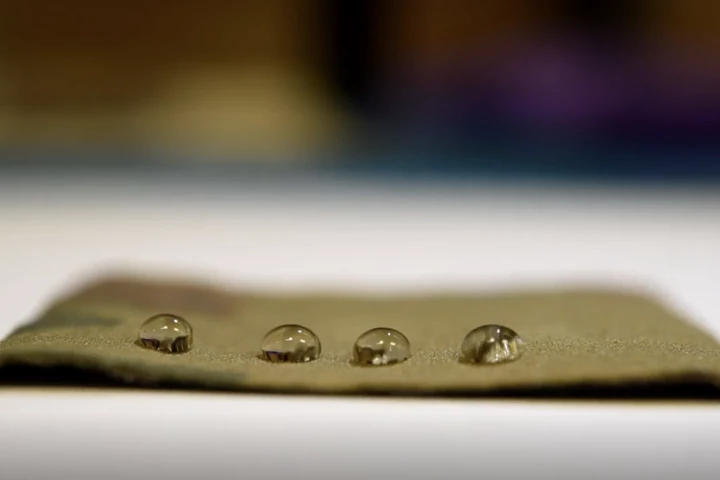
Using a new technique called nanoscale fletching, scientist have created a high-performing nonstick coating that repels water and oil – without the PFAS profile. It's a big step toward the elusive "holy grail" of a safer, greener Teflon.
-
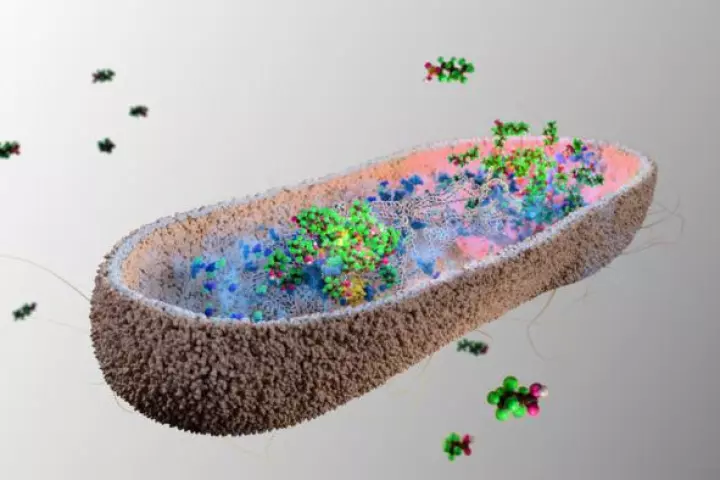
A new study published in Nature Microbiology has reported a naturally occurring family of bacterial species in the human gut that can absorb and break down toxic, long-lasting "forever chemicals" and carry them out as waste through feces.
-
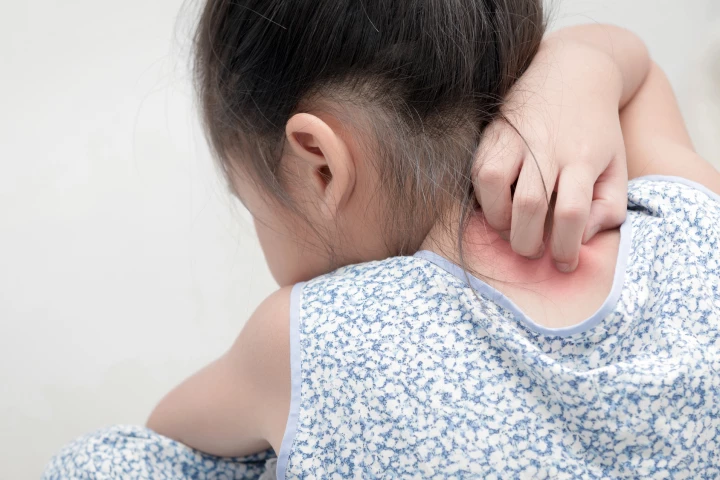
Children exposed to the common antimicrobial triclosan were more likely to develop allergic symptoms, a new study has found. It raises fresh concerns over the health impacts of a chemical widely used in everyday products.
-
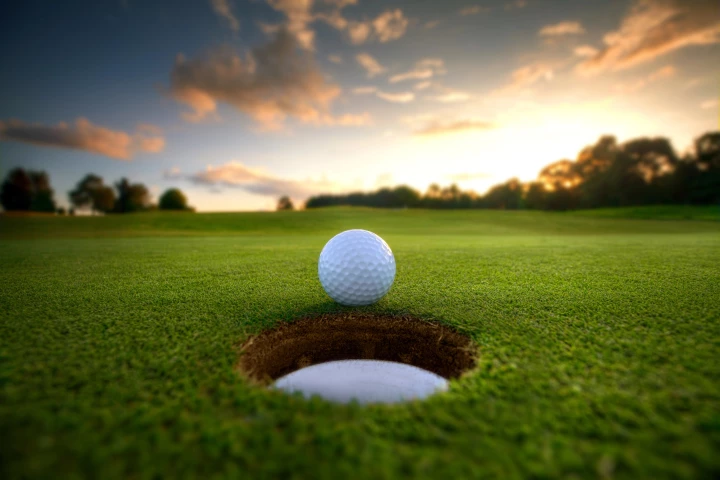
Neighborhoods near golf courses are often considered desirable locations. However, a new study suggests that houses within a few miles of manicured fairways and greens may not be such hot property for your health and wellbeing.
-
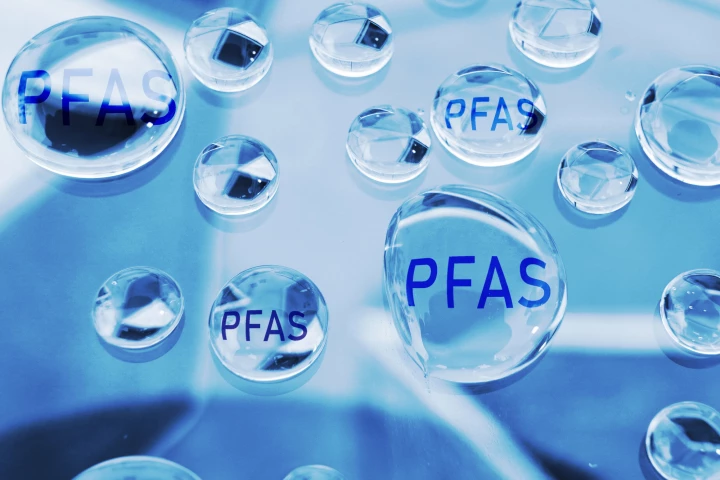
Toxic ‘forever chemicals’ are increasingly showing up in the environment, our food and drinking water, and our bodies. But we might have a new weapon: scientists have identified a bacterium that can eat these chemicals, as well as their byproducts.
-
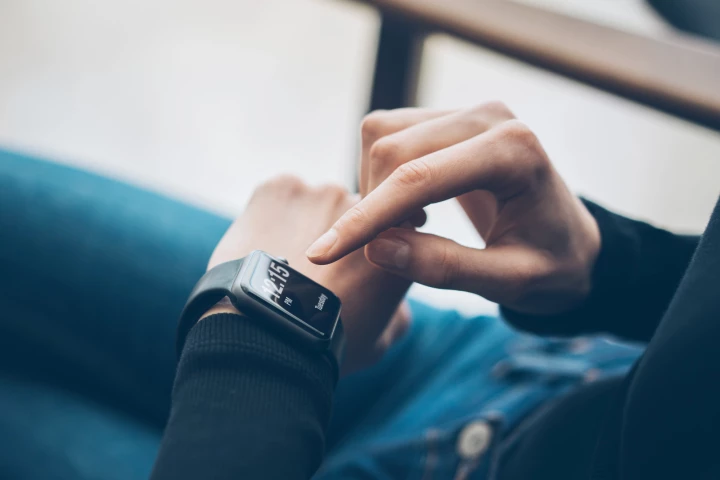
Smartwatches can help improve our health and fitness. But a new report says it's important to consider what kind of bands we put on them, as several popular brands were found to contain high levels of a class of chemicals linked to health issues.
-
Drinking water in developed countries is pretty clean, but hidden nasties can still lurk. One mysterious “phantom chemical” has haunted drinking water for decades, and now researchers have identified it – and found it’s completely new to science.
-
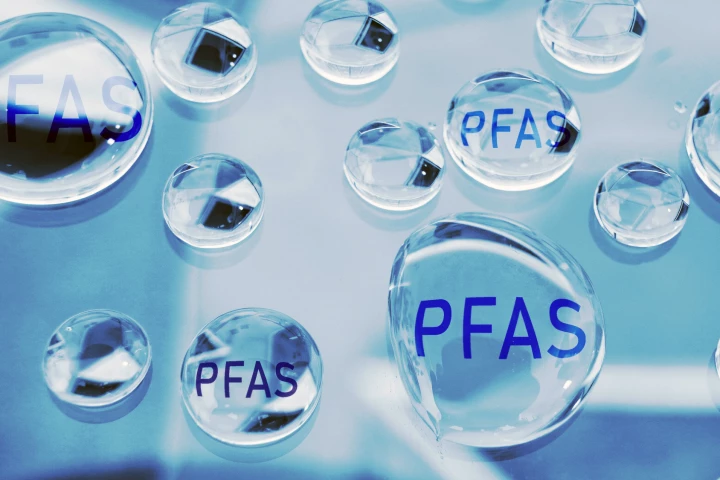
Toxic “forever chemicals” are a major environmental problem, and a growing body of research shows they’re also a major health problem. A new study has found people with higher levels of PFAS in their blood have poorer sleep.
-
Proposed methods of removing toxic ‘forever chemicals’ from water have either only trapped the chemicals or broken them down. A new study has demonstrated a method that does both effectively. And it's quick and cheap.
-
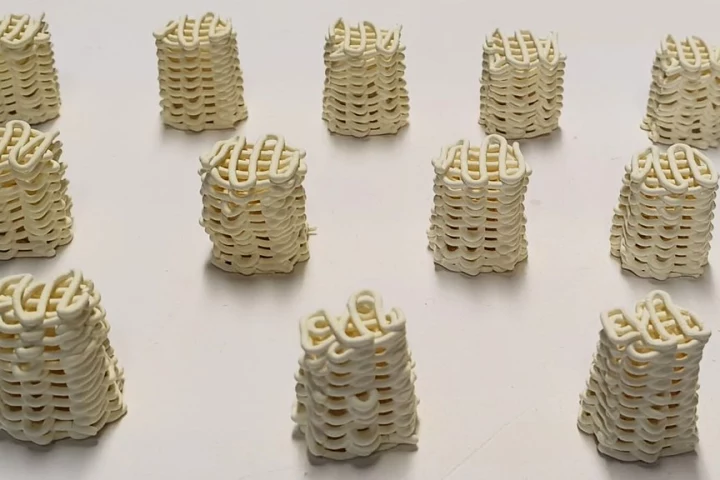
Scientists have developed a new method for removing toxic “forever chemicals” from wastewater. 3D-printed ceramic lattices can remove up to 75% of PFAS from polluted water in three hours – and the structures get better at their job as they’re reused.
Load More