Chronic pain
-
New research challenges fears about stopping long-term prescription opioid use, uncovering no associated rise in suicide risk and a sharp drop in overdose death. The findings offer reassurance for clinicians and patients managing chronic pain.
-
In a review of more than 200 clinical trials, scientists have identified which exercise offers the most benefits in relieving the symptoms of knee osteoarthritis. It's the most comprehensive look at physical activity in treating the condition yet.
-
People with severe chronic pain were far more likely to have elevated levels of eosinophils, a type of white blood cell, a new study found, hinting at an immune link to pain – but the rise in these cells didn’t make treatments any less effective.
-
A review of existing research has found that tramadol’s pain relief benefits are minimal and may be outweighed by serious side effects, challenging the drug’s reputation as a “safer” opioid option for treating chronic pain.
-
Researchers believe they have developed the first blood test to diagnose chronic fatigue syndrome, or myalgic encephalomyelitis, and it has the potential to be a game-changer for millions around the globe suffering with the debilitation condition.
-
Pain is hard to measure. One person’s “ouch” is another’s agony. Now, scientists say they’ve found a better way to assess pain: putting a price on it. By translating pain into dollars, they’ve created a more accurate, comparable way to measure suffering.
-
In a clinical trial, six sessions of low-dose radiation significantly eased knee osteoarthritis pain and improved function for months afterwards, hinting at a safe, drug-free alternative for millions living with joint degeneration.
-
Healthy eating doesn’t just shrink your waistline; it can ease chronic pain. A new study shows that better diet quality reduced pain severity and improved quality of life, independent of weight loss.
-
A study has found people living with chronic pain tend to be more perfectionistic, less self-compassionate and – depending on the measure – less confident in their ability to cope. These traits may intensify suffering, but also point to new avenues for relief.
-
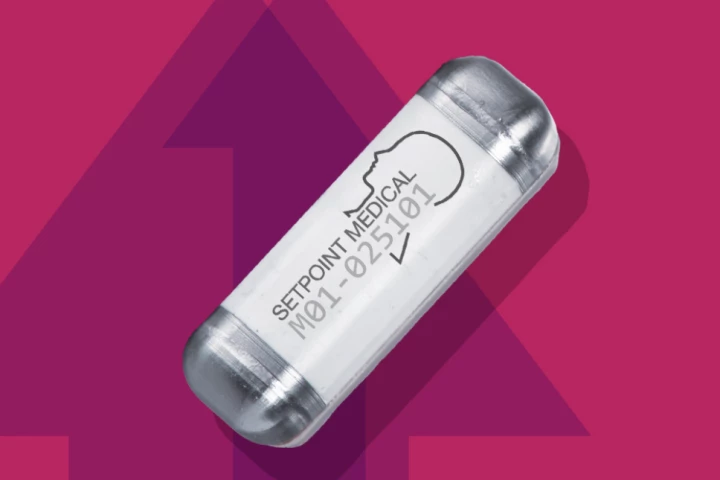
The first-ever neuroimmune modulation implant has been approved for people with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis. It's a potentially life-changing technology that zaps chronic pain with daily one-minute electrical pulses to the vagus nerve.
-
People with fibromyalgia will soon have access to a new drug that treats the chronic pain condition's most elusive trigger: Poor sleep. Tonmya, a non-opioid under-the-tongue tablet, is the first FDA-approved drug for fibromyalgia in more than 15 years.
-
A subtle tweak in the way you walk – putting your toes in or out by a few degrees – could ease knee osteoarthritis pain and slow joint damage, according to new research that found personalized gait retraining can reduce strain on vulnerable cartilage.
Load More