Colorado State University
-
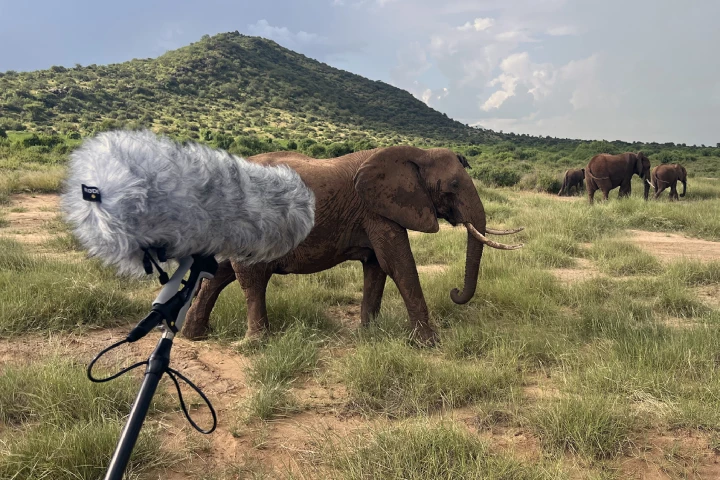
Wild elephants have exhibited a rare ability among animals: communicating with others in their social circle using individual ‘names.’ The new research suggests that their human-like communication may mean elephants are capable of complex thought.
-
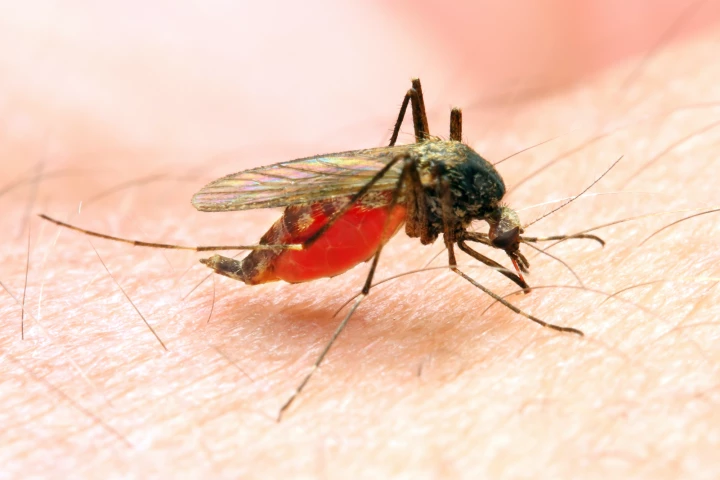
In order to better understand how mosquitoes spread diseases such as malaria, it's important to know how far they range within a given region. A new technique could help scientists do so, and it involves feeding the insects DNA.
-
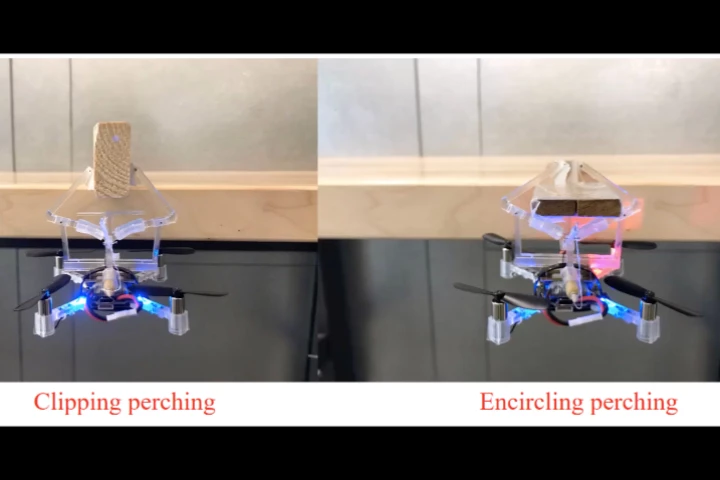
Aerial drones are much more useful if they can grasp and carry objects, plus they use much less power if they can perch on stationary objects instead of hovering. A new attachment allows drones to do both, without using any electricity.
-
The first Martian colonists will need to figure out how to grow their own food locally, but the soil is less than ideal. A new study has shown that dosing plants with symbiotic bacteria can drastically improve their growth in barren Mars-like soil.
-
Scientists have observed snakes using an entirely unknown way of getting around. Brown tree snakes in Guam have been spotted climbing objects by wrapping themselves into a never-before-seen “lasso” shape.
-
Tiny quadcopter drones, or micro air vehicles (MAVs), have notoriously short battery lives. So, if they can "perch" somewhere instead of hovering in mid-air, more power to them. A new gripper mechanism has been designed with that in mind.
-
We're on the brink of a sixth major extinction event, largely thanks to human activity and climate change. The least we could do is try to prevent some of them, and now a study has quantified how many species we may have saved in the last few decades.
-
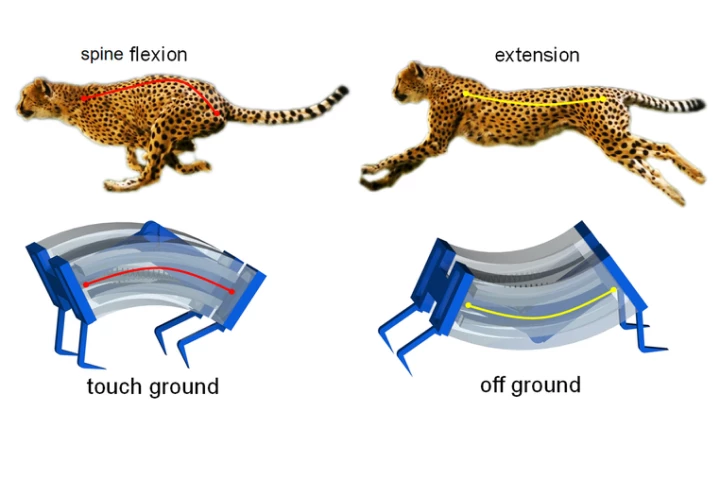
When we think of soft-bodied robots, we tend to picture things that slowly crawl like caterpillars. A new one is able to move much quicker, though, by leaping like a cheetah.
-
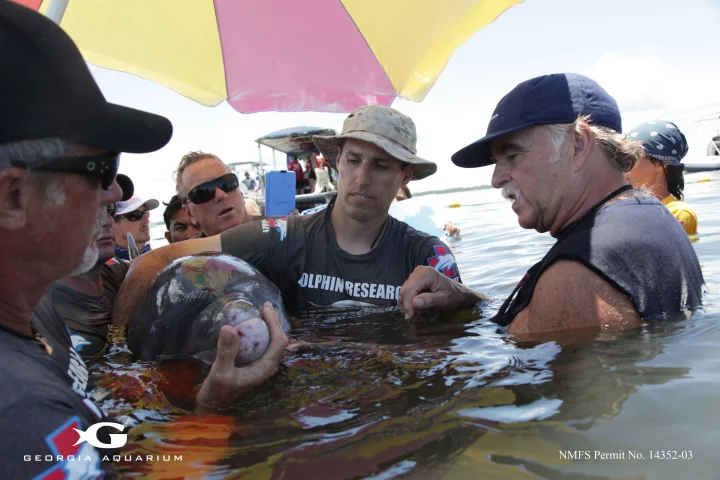
A new long-term study has found high levels of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in wild dolphins, with rates growing over the last decade.
-
Engineers have recently focused on trying to emulate the structure of the brain with artificial synapses. Now, a team of researchers have made a new artificial synapse design that works using a light-based biotechnology technique called optogenetics.
-
In developing nations, unscrupulous companies routinely produce counterfeit or diluted antibiotics. Unfortunately, those same countries often lack the expensive lab equipment needed to detect fakes. There could be hope, however, in the form of a simple new paper device.
-
As useful as it is, plastic isn’t the most environmentally-friendly material. To try to wean us off it, chemists at Colorado State University have now developed a polymer that apparently has all the benefits, but can be easily broken down and recycled over and over.
Load More