Columbia University
-
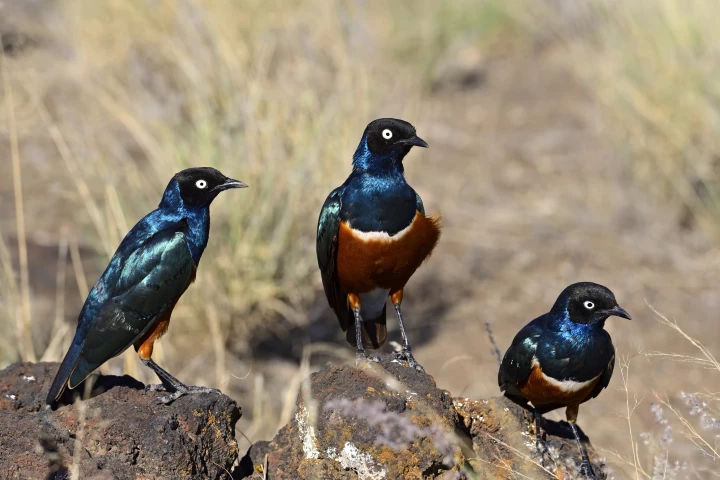
A new study with 20-years of field data has discovered that the African superb starling forms mixed-kin groups with up to 60 members. These findings offer some of the first direct evidence of human-like friendship behavior in animals.
-
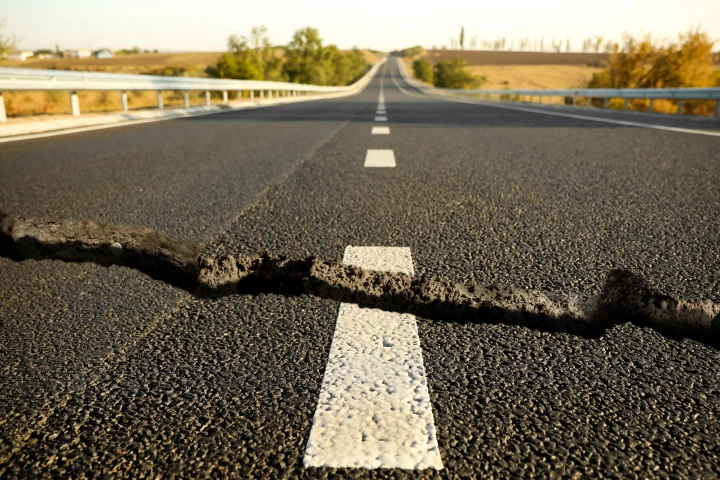
An alarming new report reveals that right across the country, 28 US cities are sinking, showing the kind of geologic subsidence that could impact buildings and infrastructure sooner rather than later. But, scientists say it's not yet too late to fix.
-
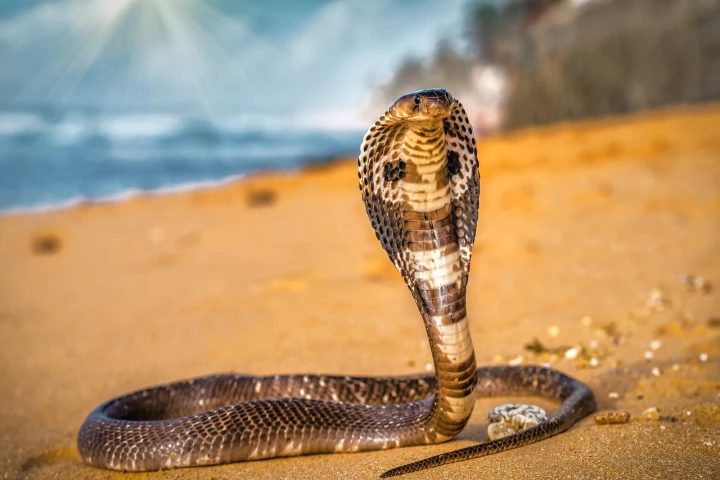
Over the course of 18 years, a truck mechanic from Wisconsin injected himself with snake venom hundreds of times. His actions were considered stunts by some over those years, but his blood has just helped lead the way toward a universal antivenom.
-
Researchers at Columbia University Irving Medical Center have identified the specific neurons in mice brains that tell them they've eaten enough. This fascinating discovery could play a big role in the future of weight loss treatments for humans.
-
A survey of 143 low-, middle-, and high-income countries has revealed which ones are most prepared to support the world’s rapidly aging population in areas like well-being, equity, and security – and which ones aren’t. And it's not good news for the US.
-
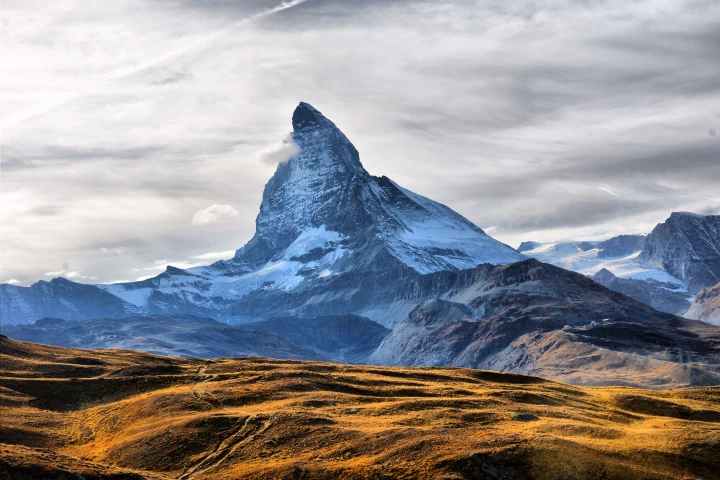
When the Swiss and Italian governments got together to redraw the alpine border that divides the two countries last year, due to rapidly retreating glaciers, it put into stark focus a challenge that is expected to face many nations that have natural structures that mark territories.
-
A severe brain injury can leave patients unresponsive to stimuli, but they may be more aware than we realize. A new study of brain activity has shown that up to a quarter of unresponsive patients may exhibit “hidden consciousness.”
-
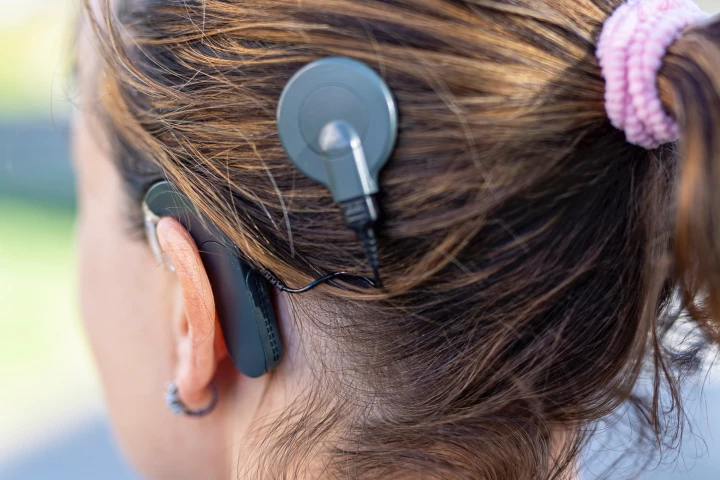
While cochlear implants do allow some deaf people to hear, they also incorporate potentially problematic external components located on the side of the head. That could soon change, however, thanks to an experimental new implantable microphone.
-
The first study to measure the concentration of metals in tampons has found that several brands contain concerning amounts of lead, arsenic and cadmium. More research is needed to determine whether the presence of these toxic metals poses a health risk.
-
Measles is on the rise, attributable to the anti-vaccination movement and exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic. Researchers have identified a new way of tackling one of the most contagious viruses around, offering protection for those at greatest risk.
-
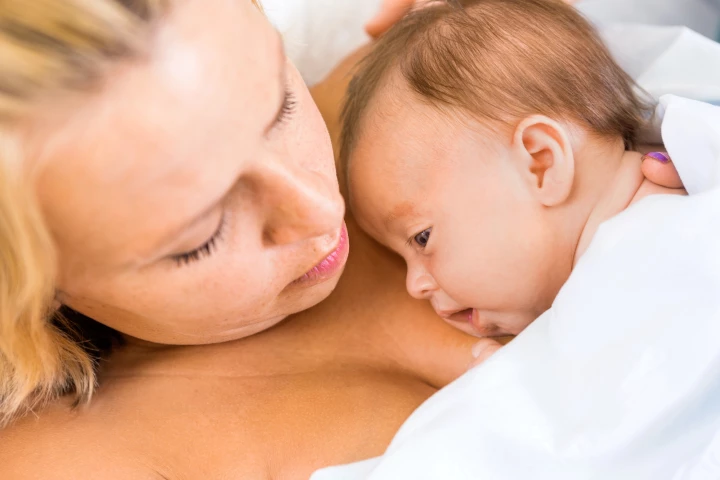
For low-birth-weight (LBW) babies, skin-to-skin contact with their mother can literally be a lifesaver. A new high-tech necklace ensures that they get enough of that snuggling, while also providing essential data on their vital signs.
-
Even brief periods of anger caused by triggering memories can negatively impact our blood vessels' ability to relax. That's the finding of a new study that could have implications on how we look at heart attack and stroke risk.
Load More