Cornell University
-
There are all kinds of critical infrastructure lying underwater – road and rail tunnels, pipelines for oil and gas, dams, and more. Could we simply 3D print such projects beneath the surface of the ocean? Cornell University is about to find out.
-
Extracellular vesicles stopped senescence – cellular deterioration in growth and reproduction – by using the extracellular matrix protein fibronectin. The discovery could lead to a method of slowing the aging process.
-
The rise in popularity of GLP-1 receptor agonist drugs like Ozempic is causing a wider societal shift that is now rocking the food industry. And some are feeling the pain more than others, as people make fundamental changes to their lives and health.
-
Smaller than a grain of salt and possibly the tiniest neurotech implant ever invented, the MOTE sends neuro-telemetry data via infra-red lasers, and could help neuroscientists unlock cures for neurological diseases.
-
If you find 3D printers to be just a little too coldly futuristic, this contraption might be more to your liking. Scientists from Cornell University have created a machine that knits solid 3D objects out of nice old-timey conventional yarn.
-
A dangerous type of bird flu virus (called H5N1) continues to circulate among dairy cows in the US. Infected milk can expose other cows, pets, wild animals, and possibly humans to the virus, a potential threat beyond just the farm.
-
Friendships, community ties and family bonds may apply the brakes to cell aging, providing a simple way to invest in health in older age. In a new study, scientists find that social connections are tied to slower biological aging and less inflammation.
-
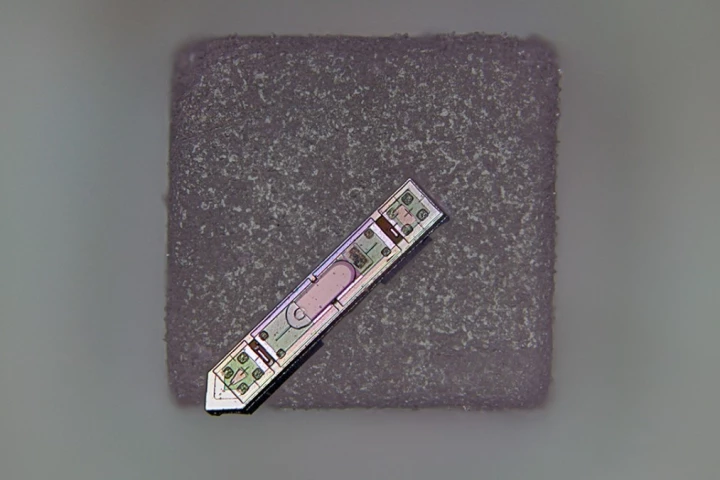
Researchers at Cornell University have developed an electronic chip that they describe as a "microwave brain." The simplified chip is analog rather than digital, yet can process ultrafast data and wireless communication signals simultaneously.
-
Thanks to advances in generative AI, seeing video of an event is no longer proof that it really happened. There could be new hope on the horizon, however, in the form of a system that watermarks videos using fluctuations in the on-location lighting.
-
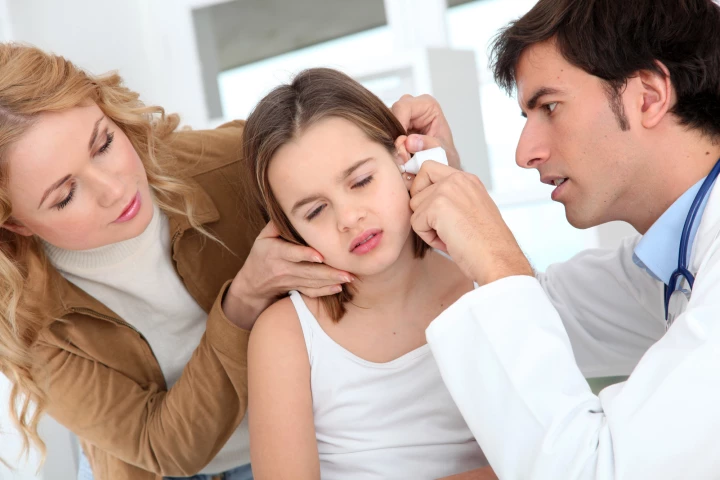
Babies and small children are prone to middle ear infections, which typically have to be treated with orally administered antibiotics. A new fast-acting topical gel could soon replace such drugs, however, potentially reducing unpleasant side effects.
-
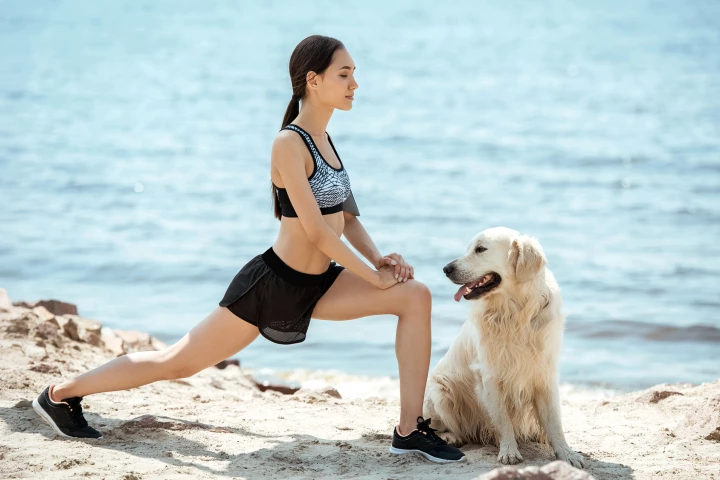
Dogs are proving to be more than just our best friends, with a new study finding that we share proteins that could accelerate our understanding and treatment of a complication of anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury, which affects both species.
-
A stage of sleep – reflected in the size of our pupils – is important to committing recent memories to the brain, which could be manipulated to improve cognitive function and even identify issues with being able to recall newer experiences when awake.
Load More